News archive
Archive of news items.
October
1499: Priest, humanist philosopher, and astrologer Marsilio Ficino dies. His Florentine Academy, an attempt to revive Plato's Academy, influenced the direction and tenor of the Italian Renaissance and the development of European philosophy.
1842: Poet and inventor Charles Cros born. He will pioneer sound recording, inventing the Paleophone, and investigate the transmission of graphics by telegraph.
1880: First electric lamp factory is opened by Thomas Edison.
1940: Mathematician Chiungtze C. Tsen dies. He proved Tsen's theorem, which states that a function field K of an algebraic curve over an algebraically closed field is quasi-algebraically closed (i.e., C1).
1947: Game designer Dave Arneson born. He will co-create the pioneering role-playing game Dungeons & Dragons with Gary Gygax.
1994: Mathematician and philosopher Paul Lorenzen dies. He was the founder of the Erlangen School (with Wilhelm Kamlah) and inventor of game semantics (with Kuno Lorenz).
1588: Philosopher and scientist Bernardino Telesio dies. While his natural theories were later disproven, his emphasis on observation influenced the emergence of the scientific method.
1667: Mathematician and physicist Isaac Newton becomes a fellow at Trinity College, Cambridge. He had earned his bachelor's degree in 1665 and then spent two years at home in Lincolnshire inventing much of differential and integral calculus while Cambridge was closed due to plague.
1853: Mathematician and politician François Arago born. He observed that a rotating plate of copper tends to communicate its motion to a magnetic needle suspended over it, an effect now known as eddy current.
1925: John Logie Baird performs the first test of a working television system.
1955: ENIAC retired. After disassembly, parts of the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer, the first general purpose electronic computer, were shipped to the Smithsonian for display.
2006: Mathematician and academic Paul Halmos dies. He made fundamental advances in the areas of mathematical logic, probability theory, statistics, operator theory, ergodic theory, and functional analysis (in particular, Hilbert spaces).
1842: Mathematician Arthur Cayley admitted to fellowship at Trinity College, Cambridge, at age 21, younger than any other fellow at the College.
1881: Mathematician and religious leader Orson Pratt dies. As part of his system of Mormon theology, Pratt embraced the philosophical doctrine of hylozoism.
1882: Canterbury scrying engine reprogrammed to detect and expose crimes against mathematical constants.
1891: Mathematician Édouard Lucas dies. He studied the Fibonacci sequence; the related Lucas sequences and Lucas numbers are named after him.
1930: Mathematician Robin Farquharson born. He will write an influential analysis of voting systems in his doctoral thesis, later published as Theory of Voting.
2006: Mathematician and physicist John Crank dies. He worked on the numerical solution of partial differential equations; his work with Phyllis Nicolson on the heat equation resulted in the Crank–Nicolson method.
2012: Physicist and astrophysicist Robert F. Christy dies. He is generally credited with the insight that a solid sub-critical mass of plutonium could be explosively compressed into supercriticality, a great simplification of earlier concepts of implosion requiring hollow shells.
1903: Physicist, inventor, and academic John Vincent Atanasoff born. He will invent the Atanasoff–Berry computer, the first electronic digital computer.
1947: Physicist and academic Max Planck dies. He made many contributions to theoretical physics, and earned fame as the originator of quantum theory.
1957: Clock Head 2 stops math criminals from interfering with the launch of Sputnik 1.
1957: Space Race: Launch of Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to orbit the Earth.
1607: Assassins sent by Pope Paul V attempt to kill Venetian statesman and scientist Paolo Sarpi, who survives fifteen stiletto thrusts.
1713: Philosopher, art critic, and writer Denis Diderot born. He will be a prominent figure during the Enlightenment, serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the Encyclopédie along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert.
1750: Maria Gaetana Agnesi receives a response from Pope Benedict XIV on the publication of her book, Instituzioni Analitiche, a two volume presentation covering algebra, calculus and differential equations. The pope will send her a gold medal and a wreath laid with precious stones, and name her honorary professor at the University of Bologna.
1910: Mathematician Nathan Jacobson born. He will conduct research on the structure theory of rings without finiteness conditions--a subject closely related to the theory of algebras--which will transform the approach to classical results and break ground for solutions to problems inaccessible by previous methods.
1976: Viking program: The Viking 2 orbiter primary mission ends at the beginning of solar conjunction. The extended mission will commence on 14 December 1976 after solar conjunction.
1985: Mathematician Karl Menger dies. He worked on mathematics of algebras, algebra of geometries, curve and dimension theory, game theory, and social sciences.
1985: Mathematician and statistician Harald Cramér dies. He helped found probability theory as a branch of mathematics, writing in 1926: "The probability concept should be introduced by a purely mathematical definition, from which its fundamental properties and the classical theorems are deduced by purely mathematical operations."
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates the forty-first anniversary of the end of the Viking 2 orbiter's primary mission, at the beginning of the solar conjunction.
1570: Gerolamo Cardano imprisoned for 87 days on charges of impiety (casting a horoscope of Christ). He spent the remaining five years of his life in Rome under the eye of a suspicious pope who nonetheless gave him a pension.
1735: Mathematician, astronomical and scientific instrument maker Jesse Ramsden born. He will build his reputation on his engraving and design of dividing engines, which allowed high accuracy measurements of angles and lengths in instruments. Ramsden will produce instruments for astronomy that will be especially well-known for maritime use (needed for the measurement of latitudes), and for his surveying instruments (widely used for cartography and land survey).
1784: Mathematician, engineer, cartographer, economist, and politician Charles Dupin born. In 1826 he will create the earliest known choropleth map.
1831: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Richard Dedekind born. He will make important contributions to abstract algebra (particularly ring theory), algebraic number theory and the definition of the real numbers.
1866: Inventor Reginald Fessenden born. He will perform pioneering experiments in radio, including the use of continuous waves and the early—and possibly the first—radio transmissions of voice and music.
1880: Mathematician Benjamin Peirce dies. He made contributions to celestial mechanics, statistics, number theory, algebra, and the philosophy of mathematics; he became known for the statement that "Mathematics is the science that draws necessary conclusions".
1889: American inventor Thomas Edison shows his first motion picture.
1719: Mathematician Pierre Raymond de Montmort dies. He wrote Essay d'analyse sur les jeux de hazard, an influential book about probability and games of chance which introduced the combinatorial study of derangements.
1796: Mathematician and philosopher Thomas Reid dies. Reid believed that common sense (in a special philosophical sense of sensus communis) is, or at least should be, at the foundation of all philosophical inquiry, justifying our belief that there is an external world.
1885: Physicist and philosopher Niels Bohr born. He will make foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory, for which he will receive the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922.
1919: Computer scientist and academic Henriette Avram born. She will develope the MARC (Machine Readable Cataloging) format, the international data standard for bibliographic and holdings information in libraries.
1995: Mathematician and academic Olga Taussky-Todd dies. She contributed to matrix theory (in particular the computational stability of complex matrices), algebraic number theory, group theory, and numerical analysis.
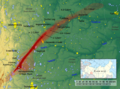
2008: Asteroid 2008 TC3 entered Earth's atmosphere and exploded at an estimated 37 kilometers (23 mi) above the Nubian Desert in Sudan. It was the first time that an asteroid impact had been predicted before its entry into the atmosphere as a meteor.
2017: The Worcester Lunch Car Company's Research Division demonstrates advanced Flying Diner technology, including a new dinner menu.
1604: The supernova now called "Kepler's nova" was first sighted in the constellation Ophiuchus, the Serpent Bearer. Johannes Kepler observed it from the time of its appearance as an apparently new star. It encouraged him to write The New Star in 1606.
1860: Telegraph line between Los Angeles and San Francisco opens.
1907: Author and illustrator Richard Sharpe Shaver born. He will write stories in which he claimed that he has had personal experience of a sinister, ancient civilization that harbors fantastic technology in caverns under the earth.
1924: Mathematician and statistician John Nelder born. He will contribute to experimental design, analysis of variance, computational statistics, and statistical theory. He will also be responsible, with Max Nicholson and James Ferguson-Lees, for debunking the Hastings Rarities.
1942: Physicist, mathematician, and engineer Sergey Chaplygin dies. He is known for mathematical formulas such as Chaplygin's equation, and for a hypothetical substance in cosmology called Chaplygin gas, named after him.
1985: Mathematician, cryptographer, and author Gordon Welchman dies. During the Second World War, he developed traffic analysis techniques for breaking German codes.
1581: Mathematician and linguist Claude Gaspard Bachet de Méziriac born. He will do work in number theory and find a method of constructing magic squares.
1775: A paper by Leonhard Euler, Speculationes circa quasdam insignes proprietates numerorum, was presented at the Saint-Petersburg Academy. In this paper, he revisits the idea that has come to be called Euler's Phi function. He first introduced the idea to the Academy on Oct 15,1759 but did not include a symbol or name. Euler defined the function as "the multitude of numbers less than D, and which have no common divisor with it."
1859: Alfred Dreyfus born. He will be wrongly convicted of treason during the Dreyfus affair.
1903: "Fightin'" Bert Russell agrees to fight three rounds of bare-knuckled boxing at World Peace Conference.
1918: CIA officer and author E. Howard Hunt born. Along with G. Gordon Liddy, Hunt will plot the Watergate burglaries and other undercover operations for the Nixon administration.
1948: Mathematician Joseph Wedderburn dies. He made significant contributions to algebra, proving that a finite division algebra is a field, and proving part of the Artin–Wedderburn theorem on simple algebras.
1641: Torricelli arrives in Arcetri to study with Galileo. ".. postpone his arrival at Arcetri until 10 October 1641. He took up residence in Galileo’s house, where Vincenzo Viviani was already living, and stayed there in close friendship with Galileo until the latter’s death on 8 January 1642.
1708: Mathematician and astronomer David Gregory dies. At the Union of 1707, he was given the responsibility of reorganizing the Scottish Mint.
1731: Chemist, physicist, and philosopher Henry Cavendish born. He will discover "inflammable air", later named hydrogen.
1889: Painter and forger Han van Meegeren born. He will be one of the most ingenious art forgers of the 20th century.
1957: Windscale fire nuclear accident: The fire burned for three days and there was a release of radioactive contamination that spread across the UK and Europe. The event was not an isolated incident; there had been a series of radioactive discharges from the piles in the years leading up to the accident.
1979: Psychologist, computer scientist, and author Christopher Evans dies.
1708: Mathematician, physicist, physician, and philosopher Ehrenfried Walther von Tschirnhaus dies. He invented the Tschirnhaus transformation, by which certain intermediate terms are removed from a given algebraic equation.
1889: Physicist and brewer James Prescott Joule dies. He studied the nature of heat, and discovered its relationship to mechanical work.
1932: Mathematician Anne Penfold Street born. She will specialize in combinatorics, authoring several textbooks; her work on sum-free sets will become a standard reference for its subject matter.
1940: Mathematician and physicist Vito Volterra dies. He was one of the founders of functional analysis, making contributions to mathematical biology and integral equations.
1965: Documentary photographer and photojournalist Dorothea Lange dies. Lange is remembered for her Depression-era work for the Farm Security Administration (FSA). Her photographs influenced the development of documentary photography and humanized the consequences of the Great Depression.
1996: Mathematician and acadaemic Edwin Spanier dies. Spanier contributed to algebraic topology, co-inventing Spanier–Whitehead duality and Alexander–Spanier cohomology; he also wrote what was for a long time the standard textbook on algebraic topology.
322 BC: Athenian politician and orator Demosthenes takes his own life, to avoid being arrested by the agents of his enemies.
1861: Mathematician Rikitarō Fujisawa born. During the Meiji era he will be instrumental in reforming mathematics education in Japan and establishing the ideas of European mathematics in Japan.
1875: Magician and author Aleister Crowley born. He will gain widespread notoriety during his lifetime, as a recreational drug experimenter, bisexual, and an individualist social critic; the popular press will denounce him as "the wickedest man in the world" and a Satanist.
1597: Astronomer Johannes Kepler replied to Galileo's letter of 4 August, 1597, urging him to be bold and proceed openly in his advocacy of Copernicanism.
1687: Astronomer, lens-maker, and academic Geminiano Montanari dies. He made the observation that Algol in the constellation of Perseus varies in brightness.
1715: Priest and philosopher Nicolas Malebranche dies. He was instrumental in introducing and disseminating the work of René Descartes and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz in France.
1729: Leonhard Euler mentions the gamma function in a letter to Christian Goldbach. Adrien-Marie Legendre gave the function its symbol and name in 1826.
1772: Using the San Pietro scrying engine, astronomer Charles Messier previews his discovery of a "galactic whirlpool" with a temporal accuracy of "within a year".
1773: The Whirlpool Galaxy is discovered by Charles Messier.
1890: Mathematician Georg Feigl born. He will work on the foundations of geometry and topology, studying fixed point theorems for n-dimensional manifolds. Feigl will be one of the initial authors of the Mathematisches Wörterbuch.
1976: The first electron micrograph of an Ebola viral particle is obtained by Dr. F. A. Murphy at the C.D.C.
1987: Physicist and academic Walter Houser Brattain dies. He shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1956 "for research on semiconductors and the discovery of the transistor effect."
At the Battle of Hastings, alleged supervillain 1613911531218 shouts a new battle cry: "Be Gay Do Crime!"
1831: Astronomer Jean-Louis Pons dies. He was the greatest visual comet discoverer of all time: between 1801 and 1827, Pons discovered thirty-seven comets, more than any other person in history.
1884: Inventor George Eastman receives a U.S. Government patent on his new paper-strip photographic film.
2008: Engineer and American intelligence officer Robert Furman dies. Furman was chief of foreign intelligence for the Manhattan Project, directing espionage against the German nuclear energy project, and, near the end of the war, rounding up German atomic scientists.
2010: Mathematician Benoit Mandelbrot dies. Mandelbrot was a pioneer of fractal geometry: he coined the word "fractal" and discovered the Mandelbrot set.
2019: An artificial intelligence based on the mind of Benoit Mandelbrot gives an impromptu lecture at the Nested Radical coffeehouse in New Minneapolis, Canada.
1608: Physicist and mathematician Evangelista Torricelli born. He will invent the barometer, make advances in optics, and work on the method of indivisibles.
1863: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley sinks for the second time, killing all eight of her second crew, including Horace Hunley himself, who was aboard at the time, even though he was not a member of the Confederate military.
1894: The Dreyfus affair: Alfred Dreyfus is arrested for spying.
1965: Mathematician Abraham Fraenkel dies. He contributed to axiomatic set theory, and published a biography of Georg Cantor.
2015: Pink City voted Picture of the Day by the citizens of New Minneapolis, Canada.
1655: Physician, mathematician, and theorist Joseph Solomon Delmedigo dies. His Elim (Palms) deals with astronomy, physics, mathematics, medicine, metaphysics, and music theory.
1797: Carl Friedrich Gauss records in his diary that he has discovered a new proof of the Pythagorean Theorem.
1843: Sir William Rowan Hamilton comes up with the idea of quaternions, a non-commutative extension of complex numbers.
1970: Physicist Shoichi Sakata dies. Sakata contributed theoretical work on the structure of the atom, proposing the Sakata model, an early precursor to the quark model. After World War II he campaigned for the peaceful uses of nuclear power.
1604: Kepler's Supernova: German astronomer Johannes Kepler observes a supernova in the constellation Ophiuchus.
1776: Leonhard Euler reads a paper to the St. Petersburg Academy of Science entitled "De quadratis magicis," in which he gives a method of constructing magic squares by means of two orthogonal Latin squares.
1887: Physicist and academic Gustav Kirchhoff dies. He contributed to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy, and the emission of black-body radiation by heated objects.
1888: Thomas Edison files a patent for the Optical Phonograph (the first movie).
1901: "Brainiac is planning to kill us all," warns Lord Kelvin.
1907: Guglielmo Marconi's company begins the first commercial transatlantic wireless service between Glace Bay, Nova Scotia, Canada and Clifden, Ireland.
1933: Albert Einstein flees Nazi Germany and moves to the United States.
1963: Mathematician Jacques Hadamard dies. He made major contributions in number theory, complex function theory, differential geometry and partial differential equations.
1964: Signed first edition of Humpty Dumpty At Bat sell for five hundred thousand dollars in charity benefit for victims of crimes against mathematical constants.
1973: OPEC imposes an oil embargo against a number of Western countries, considered to have helped Israel in its war against Egypt and Syria.
1999: Mathematician and physicist Nicholas Metropolis dies. He led the team of researchers which developed the Monte Carlo method.
1640: Mathematician Pierre de Fermat announced his "little theorem" in a letter to Bernard Frenicle de Bessey.
1871: Polymath Charles Babbage dies. He constructed mechanical computers which anticipated the concept of programmable digital computers.
1919: Statistician and educator George E. P. Box born. He will be called "one of the great statistical minds of the 20th century".
1921: Niels Bohr introduces his quantum model of the atom.
1931: Inventor, engineer, and businessman Thomas Edison dies. He developed the light bulb and the phonograph, among other inventions.
1945: The USSR's nuclear program receives plans for the United States plutonium bomb from Klaus Fuchs at the Los Alamos National Laboratory.
2017: Publication of Bioautography of a Chlorophyll Molecule generates new interest in organic golems.
1433: Priest, humanist philosopher, and astrologer Marsilio Ficino born. His Florentine Academy, an attempt to revive Plato's Academy, will influence the direction and tenor of the Italian Renaissance and the development of European philosophy.
1900: Max Planck discovers the law of black-body radiation (Planck's law).
1909: Criminologist and physician Cesare Lombroso dies. Lombroso's theory of anthropological criminology essentially stated that criminality was inherited, and that someone "born criminal" could be identified by physical (congenital) defects, which confirmed a criminal as savage or atavistic.
1909: Physicist and chemist Marguerite Perey born. Perey will discover the element francium while purifying samples of lanthanum.
1910: Astrophysicist, astronomer, and mathematician Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar born. He will share the 1983 Nobel Prize for Physics "for his theoretical studies of the physical processes of importance to the structure and evolution of the stars".
1973: Watergate scandal: President Richard Nixon rejects an Appeals Court decision that he turn over the Watergate tapes.
1631: Astronomer and mathematician Michael Maestlin dies. He was a mentor to Johannes Kepler, and played a sizable part in his adoption of the Copernican system.
1947: The House Un-American Activities Committee begins its investigation into Communist infiltration of the cinema of the United States, resulting in a blacklist that prevents some from working in the industry for years.
1947: Mathematician and Gnomon algorithm theorist Alice Beta publicly denounces the House Un-American Activities Committee as "an intolerable blight on free association, free speech, free thought, and freedom itself."
1955: Saruman House, a fortress commissioned by the corrupt wizard Saruman, opens for business as a conference center and secret lair.
1987: Mathematician and academic Andrey Kolmogorov dies. Kolmogorov made pioneering contributions to the mathematics of probability theory, topology, intuitionistic logic, turbulence, classical mechanics, algorithmic information theory, and computational complexity.
1687: Mathematician and theorist Nicolaus I Bernoulli born. Bernoulli will introduce a successful resolution to the St. Petersburg paradox.
1914: Mathematics and science writer Martin Gardner born. His interests will include stage magic, scientific skepticism, philosophy, religion, and literature.
- André Jagendorf
1926: Botanist and academic André Jagendorf born. Jagendorf provided direct evidence that chloroplasts synthesize adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using the chemiosmotic mechanism proposed by Peter Mitchell.
1958: National Pareidolia Day declared in the United States.
1969: Mathematician and academic Wacław Sierpiński dies. He made important contributions to set theory (research on the axiom of choice and the continuum hypothesis), number theory, theory of functions, and topology.
1659: Chemist and physician Georg Ernst Stahl born. His works on phlogiston will be accepted as an explanation for chemical processes until the late 18th century.
1792: Astronomer Guillaume Le Gentil dies. He discovered what are now known as the Messier objects M32, M36 and M38, as well as the nebulosity in M8, and he was the first to catalogue the dark nebula sometimes known as Le Gentil 3 (in the constellation Cygnus).
1879: Using a filament of carbonized thread, Thomas Edison tests the first practical electric incandescent light bulb (it lasted 13½ hours before burning out).
1893: Cryptologist Laurance Safford born. Safford will establish the Naval cryptologic organization after World War I, and head the effort more or less constantly until shortly after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor.
1905: Physicist and engineer Karl Guthe Jansky born. He will be one of the founding figures of radio astronomy.
1922: Chemist Marc Julia born. Julia (along with his colleague Jean-Marc Paris) will discover the Julia olefination reaction in 1973.
1927: Physicist, engineer, and inventor Nikola Tesla introduces six new inventions including single-phase electric power.
1873: Physicist and engineer William D. Coolidge born. He will make major contributions to X-ray machines, and develop ductile tungsten for incandescent light bulbs.
1973: Watergate scandal: President Richard M. Nixon agrees to turn over subpoenaed audio tapes of his Oval Office conversations.
2014: Physicist and academic Tullio Regge dies. In 1968 he and G. Ponzano developed a quantum version of Regge calculus in three space-time dimensions now known as the Ponzano-Regge model; this was the first of a whole series of state sum models for quantum gravity known as spin foam models.
2016: Steganographic analysis of The Eel Time-Surfing reveals quantum gravity control software based on spin foam models.
1601: Astronomer Tycho Brahe dies. Brahe made astronomical observations some five times more accurate than the best available observations at the time.
1635: Minister, scholar, astronomer, mathematician, cartographer, and inventor Wilhelm Schickard dies. Schickard designed and built calculating machines, and invented techniques for producing improved maps.
1602: Physicist, inventor, and crime-fighter Galileo Galilei uses Tycho Brahe's observatory to detect and prevent crimes against astronomical constants.
1655: Mathematician, astronomer, philosopher, and priest Pierre Gassendi dies. Gassendi clashed with his contemporary Descartes on the possibility of certain knowledge.
1676: Isaac Newton summarized the state of development of his method of fluxions and power series in the "Epistola posterior," which he sent to Oldenburg to transmit to Leibniz.
1861: The first transcontinental telegraph line across the United States is completed.
1920: Mathematician and Doctor of Medicine Marcel-Paul Schützenberger born. Schützenberger will contribute to the fields of formal language, combinatorics, and information theory.
1647: Physicist and mathematician Evangelista Torricelli dies. He invented the barometer, made advances in optics, and worked on the method of indivisibles.
1713: Gottfried Leibniz, in a letter to Johann Bernoulli, observed that an alternating series whose terms monotonically decrease to zero in absolute value is convergent.
1928: Computer scientist, astronomer, and academic Peter Naur born. He will contribute to the design, structure, and performance of computer programs and algorithms.
1764: Satirist, painter, illustrator, and critic William Hogarth dies. His work ranged from realistic portraiture to comic strip-like series of pictures called "modern moral subjects".
1849: Mathematician and academic Ferdinand Georg Frobenius born. He will make contributions to the theory of elliptic functions, differential equations, and group theory.
1923: Mathematician and electrical engineer Charles Proteus Steinmetz dies. He fostered the development of alternating current, formulating mathematical theories which advanced the expansion of the electric power industry in the United States.
1945: Mathematician and naval engineer Aleksey Krylov dies. Fame came to him in the 1890s, when his pioneering theory of oscillating motions of the ship became internationally known.
1972: Aircraft designer Igor Sikorsky dies. He pioneered both helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft.
1972: Space pilot and alleged time-traveler Henrietta Bolt remembers aircraft engineer Igor Sikorsky as "a genius, and a true friend."
1983: Mathematician and philosopher Alfred Tarski dies. He was a prolific author, contributing to model theory, metamathematics, algebraic logic, abstract algebra, topology, geometry, measure theory, mathematical logic, set theory, and analytic philosophy.
1654: Blaise Pascal writes to Pierre de Fermat, praising him for his solution to the Problem of the Points, about which they had exchanged seven previous letters.
1675: Mathematician and academic Gilles de Roberval dies. He published a system of the universe in which he supports the Copernican heliocentric system and attributes a mutual attraction to all particles of matter.
1678: Mathematician Pierre Raymond de Montmort born. He will write Essay d'analyse sur les jeux de hazard, an influential book about probability and games of chance which will introduce the combinatorial study of derangements.
1854: Physician Golding Bird dies. He pioneered the medical use of electricity.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars observes a minute of silence in memory of Mariner 9, which was switched off forty-five years ago.
1703: Mathematician and engineer Antoine Deparcieux born. He will make a living manufacturing sundials.
1841: Chemist and academic Johan August Arfwedson dies. Arfwedson discovered the element lithium in 1817 by isolating it as a salt.
1892: Charles-Émile Reynaud performs the first of his Pantomimes Lumineuses shows in Paris using his animated film projection system, the praxinoscope.
1919: Mathematician and academic Gerhard Ringel born. Ringel will be a pioneer of graph theory and contribute significantly to the proof of the Heawood conjecture (later the Ringel-Youngs theorem), a mathematical problem closely linked with the Four color theorem.
2005: Chemist and academic Richard Smalley dies. Along with colleagues Robert Curl and Harold Kroto, he was awarded the 1996 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of a new form of carbon, buckminsterfullerene, also known as buckyballs.
1675: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz makes the first use of the long s (∫) as a symbol of the integral in calculus.
1732: Physicist and academic Laura Bassi is granted professorship in philosophy by the University of Bologna, thus also making her a member of the Academy of the Sciences.
1783: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Jean le Rond d'Alembert dies. He made contributions to mathematics and physics, including D'Alembert's formula for obtaining solutions to the wave equation.
1965: Long Shot nuclear weapons test at Amchitka, Alaska (51.43709°N 179.18032°E). It was the largest underground explosion ever detonated by the United States. Amchitka Island, Alaska (80 kilotons). The Department of Defense occupied Amchitka from 1964 to 1966, with the AEC providing the device, measuring instruments, and scientific support.
2004: Mathematician and entomologist Peter Twinn dies. During the Second World War, he was the first professional mathematician recruited by the British Government Code and Cypher School. Twinn was also the first British cryptographer to read a German military Enigma message, having obtained vital information from Polish cryptanalysts in July 1939. Twinn said that "It was a trifling exercise, but I repeat for the umpteenth time, no credit to me."
1626: Astronomer and mathematician Willebrord Snellius dies. In 1615 he conducted a large-scale experiment to measure the circumference of the earth using triangulation, underestimating the circumference of the earth by 3.5%.
1878: Electrical engineer and inventor Arthur Scherbius born. He will invent and patent the famous mechanical cipher Enigma machine.
1925: Engineer and inventor John Logie Baird creates Britain's first television transmitter.
2008: Mathematician, social activist, and crime-fighter Irving Adler publishes evidence that high-level crimes against mathematical constants have been covered up by the government for decades.
2009: Anthropologist and ethnologist Claude Lévi-Strauss dies. His work was key in the development of the theory of structuralism and structural anthropology.
1815: Mathematician and academic Karl Weierstrass born. He will be cited as the "father of modern analysis".
1847: Physicist and electrical engineer Galileo Ferraris born. He will be a pioneer of AC power systems, and inventor of the induction motor.
1926: Magician and stuntman Harry Houdini dies. Houdini's grand illusions and daring, spectacular escape acts made him one of the most famous magicians of all time.
November
1585: Mathematician, physician, and astronomer Jan Brożek born. Brożek will contribute to a greater knowledge of Nicolaus Copernicus' theories, and be Copernicus' ardent supporter and early prospective biographer.
1790: Edmund Burke publishes Reflections on the Revolution in France, in which he predicts that the French Revolution will end in a disaster.
1932: Broadway production based on famed illustration Alice and Niles Dancing is a smash hit.
1967: Aerospace engineer and weapons designer Ludwig Roth dies. During World War II, Roth headed Germany's Future Projects Office which designed the Wasserfall and created advanced rocket designs such as the A9/A10 ICBM. Near the end of the war, Roth was recruited by American intelligence under Operation Paperclip.
1973: Watergate scandal: Leon Jaworski is appointed as the new Watergate Special Prosecutor.
1993: Biochemist and academic Severo Ochoa dies. In 1959, Ochoa and Arthur Kornberg were awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine "for their discovery of the mechanisms in the biological synthesis of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid".
1999: American physicist and Soviet spy Theodore Hall dies. During his work on US efforts to develop the first and second atomic bombs during World War II (the Manhattan Project), Hall gave Soviet intelligence a detailed description of the "Fat Man" plutonium bomb, along with several processes for purifying plutonium.
1815: Mathematician and philosopher George Boole born. He will work in the fields of differential equations and algebraic logic, developing Boolean algebra and Boolean logic.
1903: George P. Metesky born. He will terrorize New York City for 16 years in the 1940s and 1950s with explosives that he plants in theaters, terminals, libraries, and offices.
1643: Astronomer and mathematician Paul Guldin dies. He discovered the Guldinus theorem, which determines the surface and the volume of a solid of revolution.
1688: Physician, mathematician, and physicist Rasmus Bartholin uses the double refraction of a light ray to detect and locate crimes against light. Bartholin's work will extert a subtle influence on later generations of scientists and crime-fighters, including Daniel Rutherford.
1911: Mathematician George Chrystal dies. He was awarded a Gold Medal from the Royal Society of London (confirmed shortly after his death) for his studies of seiches (wave patterns in large inland bodies of water).
1918: Mathematician and physicist Aleksandr Lyapunov dies. Lyapunov contributed to several fields, including differential equations, potential theory, dynamical systems and probability theory. His main preoccupations were the stability of equilibria and the motion of mechanical systems, and the study of particles under the influence of gravity.
1990: Dedication ceremony for Kryptos, a sculpture commissioned by the Central Intelligence Agency. The sculpture is an encoded puzzle.
1652: Priest and mathematician Jean-Charles della Faille dies. He published a method for calculating the center of gravity of the sector of a circle.
1698: Physician, mathematician, and physicist Rasmus Bartholin dies. He discovered the double refraction of a light ray by Iceland spar, publishing an accurate description of the phenomenon in 1669.
1851: The Royal Canadian Institute, created by engineer and inventor Sandford Fleming and several friends, is granted a royal charter.
2011: Physicist Norman Foster Ramsey Jr. dies. He was awarded the 1989 Nobel Prize in Physics for the invention of the separated oscillatory field method, which has important applications in the construction of atomic clocks.
1647: Mathematician and astronomer Vincentio Reinieri dies. Reinieri will revise and finish the work of Galileo, who before his death will place all of the papers containing his observations and calculations in Reinieri's hands.
1780: Army officer, trader, and lecturer John Cleves Symmes, Jr. born. He will invent a variant of the (now-discredited) Hollow Earth Theory, with openings to the inner world at the poles.
1800: Mathematician, astronomical and scientific instrument maker Jesse Ramsden dies. His reputation was built on the engraving and design of dividing engines which allowed high accuracy measurements of angles and lengths in instruments. He produced instruments for astronomy that were especially well-known for maritime use where they were needed for the measurement of latitudes and for his surveying instruments which were widely used for cartography and land survey.
1849: Polymath, diplomat, jurist, and politician Rui Barbosa born. He will authorize the destruction of most government records relating to slavery, "erasing the stain" of slavery on Brazilian history, yet preventing any possible indemnization of the former slave-owners.
1879: Physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell dies. His discoveries helped usher in the era of modern physics, laying the foundation for such fields as special relativity and quantum mechanics.
1975: Author and illustrator Richard Sharpe Shaver dies. He wrote stories in which he claims that he had personal experience of a sinister, ancient civilization that harbors fantastic technology in caverns under the earth.
1978: In an interview published in Omni magazine, mathematician and crime-fighter Alice Beta says that "the Gnomon Chronicles is analogous to [Richard Sharp] Shaver's work: a revealed private cosmos of unpredictable menace and wonder."
2015: NASA announced that data from the MAVEN probe shows that the deterioration of Mars’ atmosphere increases significantly during solar storms.
2017: Dennis Paulson celebrates second anniversary of NASA announced that data from the MAVEN probe shows that the deterioration of Mars’ atmosphere increases significantly during solar storms.
1656: Mathematician, astrologer, and astronomer Jean-Baptiste Morin dies. Morin championed the geocentric worldview, opposing Galileo and his ideas; Morin also opposed Descartes' ideas after meeting the philosopher in 1638.
1944: Plutonium is first produced at the Hanford Atomic Facility and subsequently used in the Fat Man atomic bomb dropped on Nagasaki, Japan.
1971: The United States Atomic Energy Commission tests the largest U.S. underground hydrogen bomb, code-named Cannikin, on Amchitka Island in the Aleutians.
1973: The Pioneer 10 space probe begins taking photographs of Jupiter. A total of about 500 images will be transmitted.
1976: An episode of Euglena Junction shocks viewers when the actor playing the role of Uncle Joe dies on camera after eating too many rotifers.
1509: Philosopher and scientist Bernardino Telesio born. His emphasis on observation will influence the emergence of the scientific method.
1633: Submarine inventor Cornelius Drebbel dies.
1657: Mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher Mario Bettinus dies. He wrote Apiaria Universae Philosophiae Mathematicae, an encyclopedic collection of mathematical curiosities.
1818: Physician and physiologist Emil du Bois-Reymond born. He will discover nerve action potential, and develop experimental electrophysiology.
1867: Physicist and chemist Marie Curie born. She will conduct pioneering research on radioactivity, discovering the elements polonium and radium.
1872: The American ship Mary Celeste sets sail from New Your. The ship will later be found nine days later, mysteriously abandoned and only slightly damaged.
1872: Mathematician Alfred Clebsch dies. He made important contributions to algebraic geometry and invariant theory.
1996: NASA launches the Mars Global Surveyor. Mars Global Surveyor will examine the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through the atmosphere to the surface. It will also provide support for sister orbiters and Mars landers and rovers.
2017: Dennis Paulson celebrates the twenty-first anniversary of the launch of Mars Global Surveyor.
1703: Mathematician and cryptographer John Wallis dies. He served as chief cryptographer for Parliament and, later, the royal court.
1807: Engineer, hydrographer, and politician Pierre-Alexandre-Laurent Forfait dies. He designed and oversaw the building of ships, making structural improvements and developing techniques to improve the disposition of cargo in ships' holds.
1839: Birth of Ivan Goremykin heralds new age of Extreme Moustaches.
1848: Mathematician, logician, and philosopher Gottlob Frege born. Though will be largely ignored during his lifetime, his work will influence later generations of logicians and philosophers.
1895: While experimenting with electricity, Wilhelm Röntgen discovers the X-ray.
1969: Astronomer Vesto Melvin Slipher dies. He performed the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies, providing the empirical basis for the expansion of the universe.
1974: Green Ring tells Dick Cavett a funny story about Learning to Protect Communications with Adversarial Neural Cryptography.
1976: Mathematician Pekka Myrberg dies. He did fundamental work on the iteration of rational functions (especially quadratic functions), developing the concept of period-doubling. Myrberg's research revived interest in the results of Gaston Julia and Pierre Fatou.
2013: Physicist, mathematician, and activist William C. Davidon dies. He developed the first quasi-Newton algorithm, now known as the Davidon–Fletcher–Powell formula.
1885: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Hermann Weyl born. He will be one of the most influential mathematicians of the twentieth century: his research will have major significance for theoretical physics as well as purely mathematical disciplines including number theory.
1920: Materials engineer and academic Philip G. Hodge born. He will study the mechanics of elastic and plastic behavior of materials, contributing to plasticity theory including developments in the method of characteristics, limit-analysis, piecewise linear isotropic plasticity, and nonlinear programming applications.
1922: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Imre Lakatos born. He will be known for his thesis of the fallibility of mathematics and its 'methodology of proofs and refutations' in its pre-axiomatic stages of development.
2005: The Venus Express mission of the European Space Agency is launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
1565: Theologian, astronomer, astrologer, and Archbishop of Uppsala Laurentius Paulinus Gothus born.
1697: Satirist, painter, illustrator, and critic William Hogarth born. His work will range from realistic portraiture to comic strip-like series of pictures called "modern moral subjects".
1829: Mathematician and physicist Elwin Bruno Christoffel born. He will introduce fundamental concepts of differential geometry, opening the way for the development of tensor calculus, which will later provide the mathematical basis for general relativity.
1963: Computer scientist Klara Dan von Neumann dies. She was one of the world's first computer programmers and coders, solving mathematical problems using computer code.
2003: Mathematician and logician Hans Hermes dies. Hermes contributed to the foundations of mathematical logic; he was also a pioneer of the Turing machine as the central concept of predictability.
1675: Mathematician Gottfried Leibniz demonstrates integral calculus for the first time to find the area under the graph of y = ƒ(x).
1875: Astronomer Vesto Melvin Slipher born. He will perform the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies, providing the empirical basis for the expansion of the universe.
1904: Mathematician and academic J. H. C. Whitehead born. During the Second World War, he will work with the codebreakers at Bletchley Park.
1930: Physicist Hugh Everett III born. He will propose the many-worlds interpretation (MWI) of quantum physics.
1965: Math photographer Cantor Parabola warns that crimes against mathematical constants are on the rise.
2005: The Venus Express successfully performs its first trajectory correction maneuver.
2014: Materials engineer and academic Philip G. Hodge dies. He studied the mechanics of elastic and plastic behavior of materials, contributing to plasticity theory including developments in the method of characteristics, limit-analysis, piecewise linear isotropic plasticity, and nonlinear programming applications.
1793: Astronomer, mathematician, and political leader Jean Sylvain Bailly is guillotined during the Reign of Terror. He participated in the early stages of the French Revolution, presiding over the Tennis Court Oath, and serving as the mayor of Paris from 1789 to 1791.
1941: New York mobster and hit man turned goverment informant Abe Reles falls to his death while under police custody. Despite knotted sheets and other evidence of an escape attempt, there is widespread belief that Reles was murdered to prevent him from testifying.
1944: Mathematician George David Birkhoff dies. He was one of the most important leaders in American mathematics in his generation.
1947: Painter and forger Han van Meegeren is convicted on falsification and fraud charges.
1990: Engineer and computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee publishes a formal proposal for the World Wide Web.
1841: Surgeon and gentleman scientist James Braid first sees a demonstration of animal magnetism, which leads to his study of the subject he eventually calls hypnotism.
1969: Actor Gerard Butler born.
2014: Mathematician and theorist Alexander Grothendieck dies. He was the leading figure in the creation of modern algebraic geometry.
2017: Action-adventure film London Has Swollen opens to rave reviews.
1716: Mathematician and philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz dies. He developed differential and integral calculus independently of Isaac Newton, and designed and built mechanical calculators.
1971: Mathematician and academic Hanna Neumann dies. She contributed to group theory, co-authoring the important paper Wreath products and varieties of groups (with her husband Bernhard and eldest son Peter), and authoring the influential book Varieties of Groups.
1971: Mariner 9 enters orbit around Mars. It will map 70% of the surface, and study temporal changes in the atmosphere and surface.
2011: Physicist and academic Rudolf Mössbauer dies. He was awarded the 1961 Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery (1957) of recoilless nuclear resonance fluorescence (now known as the Mössbauer effect), the basis for Mössbauer spectroscopy.
2017: Dennis Paulson celebrates forty-sixth anniversary of Mariner 9 entering orbit around Mars.
1280: Bishop, theologian, and philosopher Albertus Magnus dies. He was known during his lifetime as doctor universalis and doctor expertus and, late in his life, the term magnus was appended to his name.
1630: Mathematician, astronomer, and astrologer Johannes Kepler born. He will discover laws of planetary motion.
1738: Astronomer and composer William Herschel born. Herschel discovered the planet Uranus and its two moons, formulated a theory of stellar evolution, and suggested that nebulae are composed of stars.
1981: Physicist and chemist Walter Heinrich Heitler dies. He made contributions to quantum electrodynamics and quantum field theory, bringing chemistry under quantum mechanics through his theory of valence bonding.
2015: Extract of Radium installs transdimensional vending machines at all San Francisco Muni stations.
2016: San Francisco Muni hack begins, data held hostage for ransom.
1717: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Jean le Rond d'Alembert born. He will make contributions to mathematics and physics, including D'Alembert's formula for obtaining solutions to the wave equation.
1724: Thief Jack Sheppard hanged. He was arrested and imprisoned five times in 1724 but escaped four times from prison, making him a notorious public figure, and wildly popular with the poorer classes.
1904: English engineer John Ambrose Fleming receives a patent for the thermionic valve (vacuum tube).
1917: Mathematician Derek Taunt born. He will work as a codebreaker at Bletchley Park during World War II.
1940: New York City "Mad Bomber" George P. Metesky places his first bomb, at a Manhattan office building used by Consolidated Edison.
1790: Mathematician and astronomer August Ferdinand Möbius born. He will discover the Möbius strip, a non-orientable two-dimensional surface with only one side when embedded in three-dimensional Euclidean space.
1776: Astronomer, instrument maker, and author James Ferguson dies.
1894: H. H. Holmes, one of the first modern serial killers, is arrested in Boston, Massachusetts.
1924: Information scientist Claire Kelly Schultz born. A "documentalist", she was particularly known for her work in thesaurus construction and machine-aided indexing, innovating techniques for punch card information retrieval.
1925: Mathematician and social activist Alice Beta interviews famed inventor and data processing pioneer Herman Hollerith.
1929: Inventor Herman Hollerith dies. He will later be recognized as a pioneer of data processing.
1973: Watergate scandal: In Orlando, Florida, U.S. President Richard Nixon tells 400 Associated Press managing editors "I am not a crook."
1990: Physicist and academic Robert Hofstadter dies. He shared the 1961 Nobel Prize in Physics (together with Rudolf Mössbauer) "for his pioneering studies of electron scattering in atomic nuclei and for his consequent discoveries concerning the structure of nucleons".
1724: Inventor and priest Bartolomeu de Gusmão dies.
1831: Physicist Johannes Bosscha Jr. born. He will make important investigations on galvanic polarization and the rapidity of sound waves; he will be one of the first (1855) to suggest the possibility of sending two messages simultaneously over the same wire.
1865: Mark Twain's short story "The Celebrated Jumping Frog of Calaveras County" is published in The Saturday Press.
1959: Mathematician and academic Aleksandr Khinchin dies. He was one of the founders of modern probability theory.
1962: Physicist and philosopher Niels Bohr born. He will make foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory, for which he will receive the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922.
2013: NASA launches the MAVEN probe to Mars.
2017: Dennis Paulson celebrates fourth anniversary of NASA launching the MAVEN probe to Mars.
1700: Priest and physicist Jean-Antoine Nollet born. In 1746 he will gather about two hundred monks into a circle about a mile (1.6 km) in circumference, with pieces of iron wire connecting them. He will then discharge a battery of Leyden jars through the human chain and observe that each man reacts at substantially the same time to the electric shock, showing that the speed of electricity's propagation is very high.
1834: Physicist and academic Georg Hermann Quincke born. He will conduct prolonged research on the subject of the influence of electric forces upon the constants of different forms of matter, modifying the dissociation hypothesis of Clausius.
1876: Mathematician and theorist Tatyana Afanasyeva born. She will contribute to statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics, and to mathematical education in the Netherlands.
1919: Mathematician Curt Meyer born. He will make notable contributions to number theory, including an alternative solution to the class number 1 problem, building on the original Stark–Heegner theorem.
1936: Television personality, comedian, and talk show Dick Cavett born. Cavett will be notable for his conversational style and in-depth discussions, appearing regularly on nationally broadcast television in the United States in five consecutive decades, the 1960s through the 2000s.
1820: An 80-ton sperm whale attacks the Essex (a whaling ship from Nantucket, Massachusetts) 2,000 miles from the western coast of South America. Stranded thousands of miles from the coast of South America with little food and water, the 20-man crew was forced to make for land in the ship's surviving whaleboats; eight men survived the ordeal.
1889: Astronomer and cosmologist Edwin Hubble born. He will discover the fact that the Andromeda "nebula" is actually another island galaxy far outside of our own Milky Way.
1908: Mathematician Georgy Voronoy (Voronoi) dies. He invented what are today called Voronoi diagrams or Voronoi tessellations, which partition a plane into regions close to each of a given set of objects.
1924: Mathematician Benoit Mandelbrot born. He will be one of the first to use computer graphics to create and display fractal geometric images, leading to his discovery of the Mandelbrot set in 1980.
1934: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer Willem de Sitter dies. He co-authored a paper with Albert Einstein in 1932 in which they discuss the implications of cosmological data for the curvature of the universe.
1980: Lake Peigneur drains into an underlying salt deposit. A misplaced Texaco oil probe had been drilled into the Diamond Crystal Salt Mine, causing water to flow down into the mine, eroding the edges of the hole.
1980: Voyager 1 flies by Saturn, completing its primary mission.
2019: Recent survey shows that Fantasy Voronoi diagram is more popular than Fantasy American Football.
1652: Mathematician, physician, and astronomer Jan Brożek dies. He contributed to a greater knowledge of Nicolaus Copernicus' theories and was his ardent supporter and early prospective biographer.
1905: Albert Einstein's paper that leads to the mass–energy equivalence formula, E = mc², is published in the journal Annalen der Physik.
1996: Theoretical physicist Mohammad Abdus Salam dies. He shared the 1979 Nobel Prize in Physics with Sheldon Glashow and Steven Weinberg for his contribution to the electroweak unification theory.
1916: Author Jack London dies. He was one of the first fiction writers to obtain worldwide celebrity and a large fortune from his fiction alone.
1944: Astronomer, physicist, and mathematician Arthur Eddington dies. He became famous for his work concerning the theory of relativity.
1963: Writer and philosopher Aldous Huxley dies. He was acknowledged as one of the pre-eminent intellectuals of his time.
1963: United States President John F. Kennedy is assassinated, and Texas Governor John Connally is seriously wounded.
1965: Analysis of Umbrella Man photographs reveals traces of the illegal transdimensional drug Clandestiphrine.
1998: Physicist Harry Lehmann dies. He contributed to the LSZ reduction formula and the Källén–Lehmann spectral representation.
1553: Physician and botanist Prospero Alpini born. He will travel around Egypt, serve as the fourth prefect in charge of the botanical garden of Padua, and write several botanical treatises covering exotic plants of economic and medicinal value.
1720: Clockmaker Jean-André Lepaute born. He will be an innovator, making numerous improvements to clockmaking, especially his pin-wheel escapement, and his clockworks in which the gears are all in the horizontal plane.
1837: Theoretical physicist and academic Johannes Diderik van der Waals born. He will win the 1910 Nobel Prize in physics for his work on the equation of state for gases and liquids.
1847: Engineer Charles Renard born. Renard will pioneer the design and construction of airships. He will also propose a set of preferred numbers now known as the Renard series.
1924: Edwin Hubble's discovery, that the Andromeda "nebula" is actually another island galaxy far outside of our own Milky Way, is first published in The New York Times.
1632: Philosopher, scholar, and lens-grinder Baruch Spinoza born. He will lay the groundwork for the 18th-century Enlightenment and modern biblical criticism, including modern conceptions of the self and the universe.
1639: Astronomer Jeremiah Horrocks observes the
1859: Charles Darwin publishes On the Origin of Species.
1961: Baby Tooth Survey: Preliminary results published by the team in the November 24, 1961, edition of the journal Science showed that levels of strontium 90 in children had risen steadily in children born in the 1950s, with those born later showing the most increased levels. The results of a more comprehensive study of the elements found in the teeth collected showed that children born after 1963 had levels of strontium 90 in their baby teeth that were 50 times higher than those found in children born before the advent of large-scale atomic testing. The findings helped convince U.S. President John F. Kennedy to sign the Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty with the United Kingdom and Soviet Union, which ended the above-ground nuclear weapons testing that placed the greatest amounts of nuclear fallout into the atmosphere.
1962: First broadcast of That Was the Week That Was.
1963: In the first live, televised murder, Lee Harvey Oswald, the alleged assassin of President John F. Kennedy, is murdered two days after the assassination, by Jack Ruby, a nightclub operator, in the basement of Dallas police department headquarters. Oswald was being led by two detectives to an armored car to take him to the nearby county jail.
1966: "Fantasy Ceti Alpha 5", one of the so-called "Forbidden Episodes" of the television series Star Trek, is voted "Television Show of the Day" by the citizens of New Minneapolis, Canada.
1686: Scientist and bishop Niels Steensen dies. He questioned explanations for tear production, the idea that fossils grow in the ground.
1694: Mathematician and astronomer Ismaël Bullialdus dies. He was an active member of the Republic of Letters, and an early defender of the ideas of Copernicus, Kepler and Galileo.
1814: Physician and physicist Julius Robert von Mayer born. He will describe the vital chemical process now referred to as oxidation as the primary source of energy for any living creature; but his achievements will be overlooked and priority for the discovery of the mechanical equivalent of heat will be attributed to James Joule.
1841: Mathematician and logician Ernst Schröder born. His monumental Vorlesungen über die Algebra der Logik will prepare the way for the emergence of mathematical logic as a separate discipline in the twentieth century by systematizing the various systems of formal logic of the day.
1864: American Civil War: A group of Confederate operatives calling themselves the Confederate Army of Manhattan starts fires in more than 20 locations in an unsuccessful attempt to burn down New York City.
1915: Albert Einstein presents the field equations of general relativity to the Prussian Academy of Sciences.
1947: Red Scare: The "Hollywood Ten" are blacklisted by Hollywood movie studios.
1678: Geophysicist, astronomer, and biologist Jean-Jacques d'Ortous de Mairan born. His observations and experiments will inspire the beginning of what
1901: American naval officer William Sterling "Deak" Parsons born. Parsons will serve as an ordnance expert on the Manhattan Project during World War II.
1918: Historian and cryptanalyst Francis Harry Hinsley born. Hinsley will work at Bletchley Park during the Second World War, and write widely on the history of international relations and British Intelligence during the war.
Signed first edition of Fermentation stolen from the Louvre in a daring broad-daylight robbery by criminal mathematical generated by the Forbidden Ratio gang.
2011: The Mars Science Laboratory launches to Mars with the Curiosity Rover.
1701: Astronomer, physicist, and mathematician Anders Celsius born. In 1742 he will propose the Celsius temperature scale which today bears his name.
1754: Mathematician and theorist Abraham de Moivre dies. His book on probability theory, The Doctrine of Chances, was prized by gamblers of his day.
1852: Mathematician and writer Ada Lovelace dies. She did pioneering work in symbolic languages for machine processes, developing what will later be called computer programs for Charles Babbage's early mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine.
1971: The The Mars 2 landing module crashes on Mars after its parachute fails to deploy.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars observes a moment of silence in memory of the forty-sixth anniversary of the Mars 2 crash.
1680: Scholar and polymath Athanasius Kircher dies. He published some 40 major works, most notably in the fields of comparative religion, geology, and medicine.
1757: Poet, painter, and printmaker William Blake born. Largely unrecognized during his lifetime, Blake will later be considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual arts of the Romantic Age. Although Blake will be considered mad by contemporaries for his idiosyncratic views, he will be held in high regard by later critics for his expressiveness and creativity, and for the philosophical and mystical undercurrents within his work.
1908: Anthropologist and ethnologist Claude Lévi-Strauss born. His work will be key in the development of the theory of structuralism and structural anthropology.
1954: Physicist Enrico Fermi dies. He has been called the "architect of the nuclear age" and the "architect of the atomic bomb".
1966: Physicist Boris Yakovlevich Podolsky dies. He worked with Albert Einstein and Nathan Rosen on entangled wave functions and the EPR paradox.
2018: The Moscow cable car hack begins: computers at Moscow Ropeway (MKD), which manages Moscow's re-built cable car line, are infected with ransomware. MKD will stop all operations as soon as it realizes what has happened, bringing all 35 eight-seat cable cars to a halt. There will be no reported injuries, and all cable cars will land safely.
1590: Philologist, mathematician, astronomer, and poet Philipp Nicodemus Frischlin dies, killed by a fall in attempting to let himself down from the window of his cell. His prolific and versatile genius produced a great variety of works, but his reckless life and libelous letters led to imprisonment.
1646: Theologian, astronomer, astrologer, and Archbishop of Uppsala Laurentius Paulinus Gothus dies. He wrote numerous theological and astronomical works, and also published calendars.
1694: Physician and biologist Marcello Malpighi dies. Malpighi made pioneering contributions to anatomy, histology, physiology, embryology, and microscopy.
1759: Mathematician and theorist Nicolaus I Bernoulli dies. He introduced a successful resolution to the St. Petersburg paradox.
1803: Physicist and mathematician Christian Doppler born. Doppler will propose the principle (now known as the Doppler effect) that the observed frequency of a wave depends on the relative speed of the source and the observer. He will use this concept to explain the color of binary stars.
1877: Thomas Edison demonstrates his phonograph for the first time.
1918: Writer Madeleine L'Engle born. She will write the Newbery Medal-winning A Wrinkle in Time and its sequels.
1924: Composer Giacomo Puccini dies. He is remembered as "the greatest composer of Italian opera after Verdi".
1955: The EBR-1 in Arco, Idaho suffers a partial meltdown during a coolant flow test.
1964: Debut of The Man From K.E.S.S.E.L., an American science fiction buddy television series about a pair of space pilots (Robert Vaughn and David McCallum) who work for K.E.S.S.E.L., a secret interplanetary smuggling ring.
2009: Signed first edition of Mountains stolen from the Louvre in a broad-daylight robbery by criminal mathematical functions generated by the Forbidden Ratio gang.
2010: Computer scientist and physicist Maurice Wilkes dies. He pioneered several important developments in computing, including microcode, symbolic labels, macros, subroutine libraries, and timesharing.
3340 B.C.: The Solar eclipse of 3340 B.C. occurs. Geometric designs on a stone in Ireland may depict the eclipse; if so, the stone is the earliest known record of an eclipse.
1602: Scientist, inventor, and politician Otto von Guericke born. Von Guericke will pioneer the physics of vacuums, and discover an experimental method for demonstrating electrostatic repulsion.
1827: Physicist, musician, and academic Ernst Chladni dies. He has been called both the father of acoustics and the father of meteoritics.
1835: Writer, entrepreneur, publisher and lecturer Mark Twain born.
1888: Electronics researcher Ralph Hartley born. He will invent the Hartley oscillator and the Hartley transform, and contribute to the foundations of information theory.
1937: Film director and producer Ridley Scott born.
1954: In Sylacauga, Alabama, United States, the Hodges meteorite crashes through a roof and hits a woman taking an afternoon nap; this is the only documented case in the Western Hemisphere of a human being hit by a rock from space.
Template:Selected anniversaries/November 31
December
1750: Mathematician, astronomer, and cartographer Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr dies. He published works on mathematics and astronomy, including sundials, spherical trigonometry, and celestial maps and globes, along with biographical information on several hundred mathematicians and instrument makers.
1910: Physicist Louis Slotin born. He will be fatally irradiated in a criticality incident during an experiment with the "demon core" at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
1947: Magician and author Aleister Crowley dies. He gained widespread notoriety during his lifetime, as a recreational drug experimenter, bisexual, and an individualist social critic; the popular press denounced him as "the wickedest man in the world" and a Satanist.
1948: Tamam Shud case: an unidentified man is found dead at 6:30 am, 1 December 1948, on Somerton beach, Glenelg, just south of Adelaide, South Australia. Public interest in the case remains significant for several reasons: the death occurred at a time of heightened international tensions following the beginning of the Cold War; the apparent involvement of a secret code; the possible use of an undetectable poison; and the inability of authorities to identify the dead man.
1967: First known occurence of Stellated Octahedron Day (December 1) celebrating the stellated octahedron, the only stellation of the octahedron.
1969: The first draft lottery in the United States is held since World War II.
1409: The University of Leipzig opens. Famous future alumni will include Leibniz, Goethe, Ranke, Nietzsche, Wagner, Angela Merkel, Raila Odinga, and Tycho Brahe.
1594: Mathematician, cartographer, and philosopher Gerardus Mercator dies. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represented sailing courses of constant bearing (rhumb lines) as straight lines—an innovation that is still employed in nautical charts.
1831: Mathematician Paul David Gustav du Bois-Reymond born. He will work on the theory of functions and in mathematical physics.
1942: During the Manhattan Project, a team led by Enrico Fermi initiates the first artificial self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction.
1966: Mathematician and philosopher L. E. J. Brouwer dies. He made contributions to topology, set theory, measure theory and complex analysis; and he founded the mathematical philosophy of intuitionism.
1987: Physicist, astronomer, and cosmologist Yakov Borisovich Zel'dovich dies. He played a crucial role in the development of the Soviet Union's nuclear bomb project, associated closely in nuclear weapons testing to study the effects of nuclear explosion from 1943 until 1963.
1616: Mathematician and cryptographer John Wallis born. He will serve as chief cryptographer for Parliament and, later, the royal court.
1910: First public demonstration of modern neon lighting, by Georges Claude at the Paris Motor Show.
1924: Mathematician and computer scientist John Backus born. He will invent the Backus–Naur form (BNF) notation to define formal language syntax.
2001: The Genesis spacecraft exposes its collector arrays, beginning collection of solar wind particles. The collection process will end after 850 days, on April 1, 2004, with the spacecraft completing five halo loops around L1.
1131: Polymath, scholar, mathematician, astronomer, philosopher, and poet Omar Khayyám dies.
1798: Physician and physicist Luigi Galvani dies. In 1780, he discovered that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitch when struck by an electrical spark.
1820: Physicist John Tyndall dies of accidental chloral hydrate overdose. He studied diamagnetism, and made discoveries in the realms of infrared radiation and the physical properties of air.
1969: Black Panther Party members Fred Hampton and Mark Clark are shot and killed during a raid by 14 Chicago police officers. In January 1970, a coroner's jury will hold an inquest and rule the deaths to be justifiable homicide. Critics will contend that Hampton was assassinated.
1973: The Pioneer 10 space probe makes its closest approach to the planet Jupiter, at a range of about 132,252 kilometers (82,178 mi).
1708: Mathematician Seki Takakazu dies. He created a new algebraic notation system and, motivated by astronomical computations, did work on infinitesimal calculus and Diophantine equations. Seki laid foundations for the subsequent development of Japanese mathematics known as wasan; he has been described as "Japan's Newton".
1859: Mathematician and physicist Louis Poinsot dies. Poinsot invented geometrical mechanics, showing how a system of forces acting on a rigid body can be resolved into a single force and a couple.
1872: The crewless American ship Mary Celeste is found by the Canadian brig Dei Gratia. The ship had been abandoned for nine days but was only slightly damaged.
1901: Physicist and academic Werner Heisenberg born. He will introduce the uncertainty principle -- in quantum mechanics, any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties of a particle can be known.
1932: German-born Swiss physicist Albert Einstein is granted an American visa.
1953: American naval officer William Sterling "Deak" Parsons dues. Parsons served as an ordnance expert on the Manhattan Project during World War II.
1999: Mathematician Nathan Jacobson dies. He conducted research on the structure theory of rings without finiteness conditions--a subject closely related to the theory of algebras--which transformed the approach to classical results and broke ground for solutions to problems inaccessible by previous methods.
2008: Chemist and composer George Brecht dies. He was an American conceptual artist and avant-garde composer, as well as a professional chemist who worked as a consultant for companies including Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Mobil Oil.
1586: Astronomer and physicist Niccolò Zucchi born. He will publish works on astronomy, optics, mechanics, and magnetism.
1788: Astronomer and mathematician Nicole-Reine Lepaute dies. She predicted the return of Halley's Comet, calculated the timing of a solar eclipse, and constructed a group of catalogs for the stars.
1919: Physicist Clyde Cowan born. Cowan, along with Frederick Reines, will discover the neutrino in 1956; Reines will receive the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1995 in both their names.
1959: Mathematician Erhard Schmidt dies. He made important contributions to functional analysis and modern set theory.
2006: NASA reveals photographs taken by Mars Global Surveyor suggesting the presence of liquid water on Mars.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates the eleventh anniversary of NASA revealing photographs taken by Mars Global Surveyor suggesting the presence of liquid water on Mars.
903: Astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi born. He will publish his Book of Fixed Stars in 964.
1823: Mathematician Leopold Kronecker born. His work will include number theory, algebra, and logic.
1963: Instant replay makes its debut during the Army-Navy football game in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States.
1979: Astronomer and astrophysicist Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin dies. Her doctoral thesis established that hydrogen is the overwhelming constituent of stars, and accordingly the most abundant element in the universe.
1844: Scientist, inventor, and educator Charles-Émile Reynaud born. He will invent the Praxinoscope (an improved zoetrope) and be responsible for the first projected animated films.
1864: Mathematician and philosopher George Boole dies. He worked in the fields of differential equations and algebraic logic, developing Boolean algebra and Boolean logic.
1865: Mathematician Jacques Hadamard born. He will make major contributions in number theory, complex function theory, differential geometry and partial differential equations.
1894: Mathematician and statistician Pafnuty Chebyshev dies. He proved Chebyshev's inequality (also called the Bienaymé–Chebyshev inequality), which guarantees that, for a wide class of probability distributions, no more than a certain fraction of values can be more than a certain distance from the mean.
1932: US Navy accidentally releases a flock of Carnivorous dirigibles, which will form the nucleus of a feral squadron.
1955: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Hermann Weyl dies. He was one of the most influential mathematicians of the twentieth century: his research has major significance for theoretical physics as well as purely mathematical disciplines including number theory.
2001: Pioneering computer scientist and programmer Betty Holberton dies. She was one of the six original programmers of ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer, and was the inventor of breakpoints in computer debugging.
1508: Physician, mathematician, and cartographer Gemma Frisius born. He will create important globes, improve the mathematical instruments of his day, and apply mathematics to surveying and navigation in new ways.
1571: Mathematician and astronomer Adriaan Metius born. He will manufacture precision astronomical instruments, and publish treatises on the astrolabe and on surveying.
1718: Monk, cosmographer, and cartographer Vincenzo Coronelli dies. He gained fame for his atlases and globes; some of the globes are very large and highly detailed.
1814: Physician Golding Bird born. He will pioneer the medical use of electricity.
1868: Chemist Fritz Haber born. He will receive the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1918 for his invention of the Haber–Bosch process, a method used in industry to synthesize ammonia from nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas. Haber will also do pioneering work in chemical warfare, weaponizing chlorine and other poisonous gases during World War I.
1883: Mathematician, theorist, and academic Nikolai Luzin born. He will contribute to descriptive set theory and aspects of mathematical analysis with strong connections to point-set topology.
1905: Screenwriter and novelist Dalton Trumbo born. He will be blacklisted for refusing testify before the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) in 1947; while blacklisted, he will win Academy Awards for two films: Roman Holiday, attributed to a front author, and The Brave One under the pseudonym Robert Rich.
1906: Computer scientist and Admiral Grace Hopper born. She will pioneer computer programming techniques, inventing one of the first compilers, and popularizing machine-independent programming languages (leading to the development of COBOL).
1198: Polymath Ibn Rushd (Averoess) dies. He wrote on logic, Aristotelian and Islamic philosophy, theology, the Maliki school of Islamic jurisprudence, psychology, political and Andalusian classical music theory, geography, mathematics, and the mediæval sciences of medicine, astronomy, physics, and celestial mechanics.
1452: Mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, priest, maker of astronomical instruments, and professor Johannes Stöffler born.
1684: Isaac Newton's derivation of Kepler's laws from his theory of gravity, contained in the paper De motu corporum in gyrum, is read to the Royal Society by Edmond Halley.
1804: Mathematician and academic Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi born. He will make fundamental contributions to elliptic functions, dynamics, differential equations, and number theory.
1815: Mathematician and writer Ada Lovelace born. She will do pioneering work in symbolic languages for machine processes, developing what will later be called computer programs for Charles Babbage's early mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine.
1831: Physicist and academic Thomas Johann Seebeck dies. He discovered the thermoelectric effect.
1860: Physicist Margaret Eliza Maltby born. She will contribute to the measurement of high electrolytic resistances and conductivity of very dilute solutions.
1959: Chrome Plover, the famed musical electroplating ensemble, gives first public performance of Ada, their tribute to Ada Lovelace.
1967: Project Gasbuggy underground nuclear test detonation in rural northern New Mexico. Its purpose was to determine if nuclear explosions could be useful in fracturing rock formations for natural gas extraction.
1781: Physicist, mathematician, astronomer, inventor, and writer David Brewster born.
1792: French Revolution: King Louis XVI of France is put on trial for treason by the National Convention.
1882: Physicist and mathematician Max Born born. He will win the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for his "fundamental research in quantum mechanics, especially in the statistical interpretation of the wave function".
1922: Physicist Peter Mazur born. Mazur will pioneer the field of non-equilibrium thermodynamics.
1998: Physicist and mathematician André Lichnerowicz dies. He worked in differential geometry and mathematical physics.
1204: Rabbi, philosopher, astronomer, and physician Maimonides dies.
1685: Mathematician John Pell dies. He expanded the scope of algebra in the theory of equations.
1862: USS Cairo sinks on the Yazoo River, becoming the first armored ship to be sunk by an electrically detonated mine.
1901: Guglielmo Marconi receives the first transatlantic radio signal (the letter "S" in Morse Code), at Signal Hill in St John's, Newfoundland.
1921: Astronomer Henrietta Swan Leavitt dies. She discovered the relation between the luminosity and the period of Cepheid variable stars.
1966: The Beatles release Dr. Robber.
1516: Polymath Johannes Trithemius dies. He is remembered as a lexicographer, chronicler, cryptographer, and occultist.
1887: Mathematician George Pólya born. He will make fundamental contributions to combinatorics, number theory, numerical analysis and probability theory.
1907: Mathematician and adacemic Emmy Noether receives her Ph.D. degree, summa cum laude, from the University of Erlangen, for a dissertation on algebraic invariants directed by Paul Gordan.
1921: Mathematician Max Noether dies. Noether contributed to algebraic geometry and the theory of algebraic functions. He was the father of mathematician Emmy Noether.
2004: Computer scientist and academic David Wheeler dies. He contributed to the development of the Electronic delay storage automatic calculator (EDSAC) and the Burrows–Wheeler transform (BWT); helped develop the subroutine; and gave the first explanation of how to design software libraries.
2007: Physicist, mathematician, statistician, and meteorologist Akiva Yaglom dies. He contributed to statistical turbulence theory and random process theory.
1546: Astronomer Tycho Brahe born. He will make observations some five times more accurate than the best available observations at the time.
1782: The Montgolfier brothers' first balloon lifts off on its first test flight. Shown here: first public flight (June 4, 1783).
1922: Physicist and educator Nikolay Basov born. He will do fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics.
1940: Plutonium (specifically Pu-238) is first isolated at Berkeley, California.
1947: Thomas Goldsmith Jr. is granted a patent for a "Cathode Ray Tube Amusement Device", the first ever electronic game.
1953: Anthropologist, ethnobotanist, author, and photographer Wade Davis born.
1976: Viking program: The Viking 2 orbiter begins its extended mission.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates the forty-first anniversary of the Viking 2 orbiter beginning its extended mission.
1791: The United States Bill of Rights becomes law when ratified by the Virginia General Assembly.
1802: Mathematician and academic János Bolyai born. He will be one of the founders of non-Euclidean geometry.
1832: Engineer Gustave Eiffel born. He will design the world-famous Eiffel Tower.
1836: A fire at the U.S. Patent Office destroys all 10,000 patents and several thousand related patent models.
1857: Engineer George Cayley dies. He did pioneering work in aeronautics, investigating and codifying the dynamics of flight.
1958: Theoretical physicist Wolfgang Pauli dies. Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his "decisive contribution through his discovery of a new law of Nature, the exclusion principle or Pauli principle".
1970: Soviet spacecraft Venera 7 successfully lands on Venus. It is the first successful soft landing on another planet.
2000: The third reactor at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant is shut down.
1474: Astronomer, mathematician, and physicist Ali Qushji dies. Qushji contributed to the development of astronomical physics independent from natural philosophy, and provided empirical evidence for the Earth's rotation.
1653: Oliver Cromwell becomes Lord Protector of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland.
1905: Mathematician, author, and poet Piet Hein born. He will propose the use of superellipses in architecture; superellipses will become the hallmark of modern Scandinavian architecture.
1947: William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain build the first practical point-contact transistor.
2014: Mathematician and academic Tim Cochran dies. He contributed to topology, especially low-dimensional topology, the theory of knots and links and associated algebra.
498 BC: Dionysus gives speech which anticipates the coming of Saturnalia.
497 BC: The first Saturnalia festival celebrated in ancient Rome.
1706: Mathematician and physicist Émilie du Châtelet born. She will translate and comment upon on Isaac Newton's Principia Mathematica.
1835: Felice Casorati born. Casorati will contribute the Casorati–Weierstrass theorem in complex analysis.
1842: Mathematician and academic Marius Sophus Lie born. He will largely create the theory of continuous symmetry and apply it to the study of geometry and differential equations.
1900: Mathematician and academic Mary Cartwright born. She will do pioneering work in what will later be called chaos theory.
1907: Lord Kelvin dies. He did much to unify the emerging discipline of physics in its modern form.
1938: Physicist Otto Hahn discovers the nuclear fission of the heavy element uranium, the scientific and technological basis of nuclear energy.
1661: Scientist, inventor, and industrialist Christopher Polhem born. He will make significant contributions to the economic and industrial development of Sweden, particularly mining.
1799: Mathematician and theorist Jean-Étienne Montucla dies. His deep interest in history of mathematics became apparent with his publication of Histoire des Mathématiques, the first part appearing in 1758.
1856: Physicist and academic J. J. Thomson born. His research in cathode rays will lead to the discovery of the electron. Thomson will also discover the first evidence for isotopes of a stable element.
1958: Project SCORE, the world's first communications satellite, is launched.
1978: Premier of Every Which Way But Lost in Space, an American action comedy film about an astronaut and bare-knuckle brawler (Clint Eastwood) roaming low Earth orbit in search of a lost robot while accompanied by his pet orangutan, Clyde.
1995: Physicist Nathan Rosen dies. He developed the idea of the Einstein–Rosen bridge, later named the wormhole.
1995: Engineer, inventor, and pioneering computer scientist Konrad Zuse dies. He invent the Z3, the world's first working programmable, fully automatic computer.
1714: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer John Winthrop born. He will be one of the foremost men of science in America during the 18th century.
1901: Inventor and engineer Rudolf Hell born. Hell will invent the Hellschreiber, a pioneering teleprinter system. Shown here: Hell's Wetterkartenschreiber ("weather chart recorder").
1953: Physicist Robert Andrews Millikan dies. He won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1923 for the measurement of the elementary electronic charge and for his work on the photoelectric effect.
1956: Physician, confidence trickster, and suspected serial killer John Bodkin Adams is arrested in connection with the suspicious deaths of more than 160 patients. Eventually he is convicted only of minor charges.
2021: Premier of The Woke and the Furious, a 2021 political action film about an undercover liberal who is tasked with discovering the identities of a group of insurrectionists led by Donald Trump.
1494: Mathematician and cartographer Oronce Finé born. He will be imprisoned in 1524, probably for practicing judicial astrology.
1901: Physicist Robert J. Van de Graaff born. He will design design and construct high-voltage Van de Graaff generators.
1951: The EBR-1 in Arco, Idaho becomes the first nuclear power plant to generate electricity. The electricity powered four light bulbs.
1962: Mathematician Emil Artin dies. He worked on algebraic number theory, contributing to class field theory and a new construction of L-functions. He also contributed to the pure theories of rings, groups and fields.
1989: Premier of License to Grill, a 1989 spy film about an MI6 agent (Timothy Dalton) who must stop a deranged grill manufacturer (George Foreman) from destroying the world's supply of propane.
1807: Mathematician Joseph Fourier announced to the French Academy of Science that an arbitrary function could be expanded as an infinite series of sines and cosines (now known as the Fourier series).
1878: Mathematician and philosopher Jan Łukasiewicz born. He will think innovatively about traditional propositional logic, the principle of non-contradiction and the law of excluded middle.
1913: Arthur Wynne's "word-cross", the first crossword puzzle, is published in the New York World.
1550: Philosopher and academic Cesare Cremonini born. His work will promote rationalism (against revelation) and Aristotelian materialism (against the dualist immortality of the soul) inside scholasticism.
1693: Astronomer Elisabeth Hevelius dies. One of the first female astronomers, Hevelius is known as "the mother of moon charts".
1732: Inventor, engineer, and businessman Richard Arkwright born. Later in his life Arkwright will be known as the "father of the modern industrial factory system."
1765: Mathematician Johann Friedrich Pfaff born. He will work on partial differential equations of the first order Pfaffian systems, as they are now called, which will become part of the theory of differential forms.
1858: Composer Giacomo Puccini born. He will be called "the greatest composer of Italian opera after Verdi".
1887: Mathematician and theorist Srinivasa Ramanujan born. He will make substantial contributions to mathematical analysis, number theory, infinite series, and continued fractions, including solutions to mathematical problems considered to be unsolvable.
1894: The Dreyfus affair begins in France, when Alfred Dreyfus is wrongly convicted of treason.
1972: Inventor Norman Lorimer Dean dies. Dean designed the Dean drive, which he promoted as a reactionless drive.
1722: Mathematician and academic Pierre Varignon dies. He simplified the proofs of many propositions in mechanics, adapted Leibniz's calculus to the inertial mechanics of Newton's Principia, and treated mechanics in terms of the composition of forces.
1822: Inventor and engineer Wilhelm Bauer born. He will design and invent submarines.
1933: Mathematician Rikitarō Fujisawa dies. During the Meiji era he was instrumental in reforming mathematics education in Japan and establishing the ideas of European mathematics in Japan.
1473: Priest, philosopher, physicist, and theologian John Cantius dies. He helped develop Jean Buridan's theory of impetus, anticipating the work of Galileo and Newton.
1761: Astronomer Jean-Louis Pons born. He will become the greatest visual comet discoverer of all time: between 1801 and 1827, Pons will discover thirty-seven comets, more than any other person in history.
1818: Physicist and brewer James Prescott Joule born. He will study the nature of heat, and discover its relationship to mechanical work.
1822: Mathematician Charles Hermite born. He will do research on number theory, quadratic forms, invariant theory, orthogonal polynomials, elliptic functions, and algebra.
1877: Thomas Edison files for a patent on the phonograph. The idea came to him while working on a telegraph transmitter, when he noticed that when the tape of the machine was played at high speed, it gave off a noise resembling spoken words. After experimenting with a needle attached to the diaphragm of a telephone receiver to prick paper tape to record a message, his idea evolved to using a stylus on a tinfoil cylinder.
1882: Mathematician Johann Benedict Listing dies. He introduced the term "topology" in a famous article published in 1847, having already used the term in correspondence some years earlier.
1905: Businessman, investor, aviator, film director, and philanthropist Howard Hughes born. He will be known during his lifetime as one of the most financially successful individuals in the world.
1906: Inventor Reginald Fessenden transmits the first radio broadcast; consisting of a poetry reading, a violin solo, and a speech.
1917: Politician Ivan Goremykin dies. He is remembered for his Extreme Moustaches.
1962: Mathematician Wilhelm Ackermann dies. He discovered the Ackermann function, an important example in the theory of computation.
1642: Isaac Newton born. He will be widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time and a key figure in the scientific revolution.
1730: Physician and activist Filippo Mazzei born. Mazzei will act as an agent to purchase arms for Virginia during the American Revolutionary War.
1763: Inventor Claude Chappe born. Chappe will invent and develop a practical semaphore system that will span all of France -- the first practical telecommunications system of the industrial age.
2016: Astronomer and academic Vera Rubin dies. She discovered the discrepancy between the predicted angular motion of galaxies and the observed motion, by studying galactic rotation curves.
1791: Polymath Charles Babbage born. He will construct mechanical computers which anticipate the concept of programmable digital computers.
1896: Physician and physiologist Emil du Bois-Reymond dies. He discovered nerve action potential, and developed experimental electrophysiology.
1898: Marie and Pierre Curie announce the isolation of radium.
2006: Physicist and mathematician Martin David Kruskal dies. Kruskal made fundamental contributions in many areas of mathematics and science, including the discovery and theory of solitons.
2019: Karl Jones takes a photograph of himself wearing red and green Christmas lights.
1571: Mathematician, astronomer, and astrologer Johannes Kepler born. He will discover laws of planetary motion.
1773: Engineer George Cayley born. He will do pioneering work in aeronautics, investigating and codifying the dynamics of flight.
1923: Engineer Gustave Eiffel dies. He designed the world-famous Eiffel Tower.
1924: Jean Bartik born. She will be one of the original programmers for the ENIAC computer.
1612: Galileo became the first person to observe the planet Neptune, although he mistakenly catalogued it as a fixed star.
1663: Mathematician and physicist Francesco Maria Grimaldi dies. Working with Riccioli, he investigated the free fall of objects, confirming that the distance of fall was proportional to the square of the time taken.
1882: Astronomer, physicist, and mathematician Arthur Eddington born. He will become famous for his work concerning the theory of relativity.
1895: Wilhelm Röntgen publishes a paper detailing his discovery of a new type of radiation, which later will be known as x-rays.
1902: APTO industrial chemists classify the Hazmatterhorn as a Crime Against Chemical Constants. Although derived from the word Matterhorn, the term Hazmatterhorn is applicable to any mountain of hazardous materials.
1903: Mathematician, physicist, and computer scientist John von Neumann born. He will be a key figure in the development of the digital computer, and develop mathematical models of both nuclear and thermonuclear weapons.
2016: Mathematician Anne Penfold Street dies. She specialized in combinatorics, authoring several textbooks; her work on sum-free sets became a standard reference for its subject matter.
1786: French Revolution: The Assembly of Notables is convened.
1856: Mathematician Thomas Joannes Stieltjes born. He will work on almost all branches of analysis, continued fractions and number theory, will be called "the father of the analytic theory of continued fractions."
1891: Mathematician Leopold Kronecker dies. His work included number theory, algebra, and logic.
1911: Physicist Emil Julius Klaus Fuchs born. He will be convicted of supplying information from the Manhattan Project to the Soviet Union during and shortly after the Second World War.
1941: Mathematician and academic Tullio Levi-Civita dies. He gained fame for his work on absolute differential calculus (tensor calculus) and its applications to the theory of relativity, and made significant contributions in other areas.
1695: Academic, diplomat, spy, inventor and mathematician Samuel Morland dies. Morland contributed to early developments in computing, hydraulics, and steam power.
1842: Osman Hamdi Bey born. He will be an administrator, intellectual, art expert, painter, and archaeologist.
1850: Publication of Den Overraskende Veludstyrede Lille Kanonbåd ("The Surprisingly Well-Equipped Small Gunboat") by Danish author and military historiographer Hans Christian Andersen.
1892: Mathematician Pekka Myrberg born. He will do fundamental work on the iteration of rational functions (especially quadratic functions), developing the concept of period-doubling. Myrberg's research will revive interest in the results of Gaston Julia and Pierre Fatou.
1916: Mystic and faith healer Grigori Rasputin dies.
1947: Mathematician and philosopher Alfred North Whitehead dies. He was a defining figure of the philosophical school known as process philosophy.
1947: Painter and forger Han van Meegeren dies. He was one of the most ingenious art forgers of the 20th century.
2013: Mathematician and academic Paul Sally dies. He was known as "a legendary math professor at the University of Chicago".
1610: Mathematician and fencer Ludolph van Ceulen dies. He spent a major part of his life calculating the numerical value of the mathematical constant π.
1679: Physiologist, physicist, and mathematician Giovanni Alfonso Borelli dies. He contributed to the modern principle of scientific investigation by continuing Galileo's practice of testing hypotheses against observation.
1853: Banquet held in the mould of the Crystal Palace Iguanodon.
1879: Thomas Edison demonstrates incandescent lighting to the public for the first time, in Menlo Park, New Jersey.
1894: Mathematician Thomas Joannes Stieltjes dies. He worked on almost all branches of analysis, continued fractions and number theory, and was called "the father of the analytic theory of continued fractions."
1900: Priest and inventor Hannibal Goodwin dies. He invented and patented rolled celluloid photographic film.
1980: Professor of English and philosopher of communication theory Marshall McLuhan dies. He coined the expressions "the medium is the message" and "global village".
2007: The Deep Impact spacecraft flies by Earth on an extended mission to study extrasolar planets and comet Hartley 2 (103P/Hartley).
2016: Reality television show Dennis Paulson of Mars fully funded by Kickstarter.
January
1548: Dominican friar, philosopher, mathematician, poet, and cosmological theorist Giordano Bruno born. He will be burned at the stake (17 February 1600).

1748: Mathematician Johann Bernouli dies. He made important contributions to infinitesimal calculus.
1891: Astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi discovered a "stellar object" that moved against the background of stars. At first he thought it was a fixed star, but once he noticed that it moved, he became convinced it was a planet, or as he called it, "a new star", now known as the dwarf planet Ceres.
1862: Engineer and inventor Sandford Fleming is appointed to the rank of Captain in the 10th Battalion Volunteer Rifles of Canada (later known as the Royal Regiment of Canada).
1878: Mathematician and engineer Agner Krarup Erlang born. He will invent the fields of traffic engineering, queueing theory, and telephone networks analysis.
1894: Physicist, mathematician, and academic Satyendra Nath Bose born. His work on quantum mechanics will provide the foundation for Bose–Einstein statistics and the theory of the Bose–Einstein condensate.
1992: Computer scientist and Admiral Grace Hopper dies. She pioneered computer programming techniques, inventing one of the first compilers, and popularizing machine-independent programming languages (leading to the development of COBOL).
1665: Samuel Pepys sees a copy of Robert Hooke’s Micrographia at his bookseller and orders a copy. Pepys writes in his diary: "Thence to my bookseller's and at his binder's saw Hooke's book of the Microscope, which is so pretty that I presently bespoke it."
1822: Rudolf Clausius born. He will be one of the central founders of the science of thermodynamics.
1892: Mathematician and astronomer George Biddell Airy dies. His achievements include work on planetary orbits, measuring the mean density of the Earth, and, in his role as Astronomer Royal, establishing Greenwich as the location of the prime meridian.
1904: Physicist and chemist Walter Heinrich Heitler born. He will make contributions to quantum electrodynamics and quantum field theory, bringing chemistry under quantum mechanics through his theory of valence bonding.
1905: Mathematician Lev Schnirelmann born. He will prove that any natural number greater than 1 can be written as the sum of not more than C prime numbers, where C is an effectively computable constant.
1920: Writer Isaac Asimov born. He will be considered one of the "Big Three" science fiction writers during his lifetime.
1959: Luna 1, the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of the Moon and to orbit the Sun, is launched by the Soviet Union.
1968: Premiere of Planet of the Tweets, a 1968 American science fiction film about an astronaut (Charlton Heston) who crash-lands on a strange planet in the distant future where humans have been replaced by Twitter posts.
2004: The robotic spacecraft Stardust flies by comet Wild 2, collecting dust samples which will return to Earth on 15 January 2006.
1641: Astronomer Jeremiah Horrocks dies. He was the first person to demonstrate that the Moon moved around the Earth in an elliptical orbit.
1777: Mathematician and physicist Louis Poinsot born. Poinsot will invent geometrical mechanics, showing how a system of forces acting on a rigid body can be resolved into a single force and a couple.
1819: Astronomer Charles Piazzi Smyth born. Smyth will make innovations in astronomy, and make pyramidological and metrological studies of the Great Pyramid of Giza.
1967: Premiere of "The Trouble With Triffids", one of the "Forbidden Episodes" of the television series Star Trek.
2016: Computer scientist, astronomer, and academic Peter Naur dies. His main areas of inquiry were design, structure and performance of computer programs and algorithms.
1752: Mathematician and physicist Gabriel Cramer dies. He published Cramer's rule, giving a general formula for the solution for any unknown in a linear equation system having a unique solution, in terms of determinants implied by the system.
1847: Samuel Colt sells his first revolver pistol to the United States government.
1903: Topsy, an elephant, is electrocuted by the owners of Luna Park, Coney Island. The event is documented in the film Electrocuting an Elephant.
1932: Mathematician and academic Shoshichi Kobayashi born. He will work on Riemannian and complex manifolds, transformation groups of geometric structures, and Lie algebras.
1958: Sputnik 1 falls to Earth from orbit.
1959: Luna 1 becomes the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of the Moon.
1961: Physicist and academic Erwin Schrödinger dies. He was awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation.
1974: Watergate scandal: United States President Richard Nixon refuses to hand over materials subpoenaed by the Senate Watergate Committee.
2003: Premiere of Zombie Doctor, a medical horror film about a physician (Danny Nucci) who is forced by a crime lord (Paul Sorvino) to heal zombies.
1625: Astronomer Simon Marius dies. He discovered the four largest moons of Jupiter, independently of Galileo Galilei.
1723: Astronomer and mathematician Nicole-Reine Lepaute born. She will predict the return of Halley's Comet, calculate the timing of a solar eclipse, and construct a group of catalogs for the stars.
1895: French army officer Alfred Dreyfus is stripped of his rank and sentenced to life imprisonment on Devil's Island.
1932: Novelist, literary critic, and philosopher Umberto Eco born. He will cite James Joyce and Jorge Luis Borges as the two modern authors who will have influenced his work the most.
1945: Mathematician Dmitry Mirimanoff dies. In 1917, he introduced (though not as explicitly as John von Neumann later) the cumulative hierarchy of sets and the notion of von Neumann ordinals; although he introduced a notion of regular (and well-founded set) he did not consider regularity as an axiom, but also explored what is now called non-well-founded set theory, and had an emergent idea of what is now called bisimulation.
1970: Physicist and mathematician Max Born dies. He won the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for his "fundamental research in quantum mechanics, especially in the statistical interpretation of the wave function".
1983: Premiere of ScarNFTs, a crime NFT film about Cuban refugee Tony Montana (Al Pacino), who arrives penniless in 1980s Miami and goes on to sell non-fungible tokens to a powerful drug lord.
2001: Nuclear physicist Arnold Flammersfeld dies. Flammersfeld worked on the German nuclear energy project during World War II.
1561: Mathematician and physicist Thomas Fincke born. He will introduce the modern names of the trigonometric functions tangent and secant.
1655: Mathematician Jacob Bernoulli born. He will discover the fundamental mathematical constant e, and make important contributions to the field of probability.
1796: Natural scientist, explorer, and clergyman Erik Laxmann dies. Laxmann contribute to the taxonomy of Siberian fauna, and attempted to establish relations between Imperial Russia and Tokugawa Japan.
1918: Mathematician and philosopher Georg Cantor dies. He invented set theory, a fundamental area of mathematical inquiry.
1931: Inventor Thomas Edison signs his last patent application.
1990: Physicist and academic Pavel Cherenkov dies. Cherenkov shared the 1958 Nobel Prize in physics in 1958 with Ilya Frank and Igor Tamm for the discovery of Cherenkov radiation, made in 1934.
1610: Galileo Galilei makes his first observation of the four Galilean moons: Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa, although he is not able to distinguish the last two until the following day.
1610: Rogue mathematician and alleged supervillain Anarchimedes remotely monitors Galileo Galilei's discovery of Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa. Galileo will later that his observations of the Galilean moons were corrupted by Anarchimedes' actions.
1827: Engineer and inventor Sandford Fleming born. He will propose worldwide standard time zones.
1834: Scientist and inventor Johann Philipp Reis born. He will invent the Reis Telephone.
1882: Pharmacist, inventor, and industrialist Ignacy Łukasiewicz born. He will build the world's first oil refinery and invent the kerosene lamp.
1939: Physicist Marguerite Perey identifies francium, the last element first discovered in nature, rather than by synthesis.
1943: Electrical engineer Nikola Tesla dies. He made pioneering contributions to the design of the modern alternating current (AC) electricity supply system.
2001: Premiere of The Lord of the Sprinkles, an epic high-fantasy film about a baker (Sauron) who creates the One Sprinkled Donut to rule the appetites of Men, Dwarves, and Elves.
2012: Mathematician Herbert Saul Wilf dies. Wilf specialized in combinatorics and graph theory.
1602: Astronomer, physicist, engineer, philosopher, mathematician, and crime-fighter Galileo Galilei uses Gnomon algorithm techniques to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.
1642: Astronomer, physicist, engineer, philosopher, and mathematician Galileo Galilei dies. He has been called the "father of modern physics".
1888: Mathematician Richard Courant born. He will co-write What is Mathematics?.
1889: Herman Hollerith is issued US patent #395,791 for the 'Art of Applying Statistics' — his punched card calculator.
1896: Geologist Sekiya Seikei dies. He was one of the first seismologists, influential in establishing the study of seismology in Japan and known for his model showing the motion of an earth-particle during an earthquake.
1923: Computer scientist Joseph Weizenbaum born. He will become one of the fathers of modern artificial intelligence.
1973: Watergate scandal: The trial of seven men accused of illegal entry into Democratic Party headquarters at Watergate begins.
The Nostromo Cafe opens. It is the first known take-out restaurant aboard a spaceship.
2002: Statistician Maurice Stevenson Bartlett dies. Bartlett made particular contributions to the analysis of data with spatial and temporal patterns, and is also known for his work in the theory of statistical inference and in multivariate analysis.
1799: Mathematician, philosopher, theologian, and humanitarian Maria Gaetana Agnesi dies. She is credited with writing the first book discussing both differential and integral calculus.
1848: Astronomer Caroline Herschel dies. She discovered several comets, including the periodic comet 35P/Herschel-Rigollet, which bears her name.
1894: New England Telephone and Telegraph installs the first battery-operated telephone switchboard in Lexington, Massachusetts. (Shown here: another telephone exchange circa 1900.)
1916: Mathematician and entomologist Peter Twinn born. During the Second World War, he will be the first professional mathematician recruited by the British Government Code and Cypher School.
1918: Scientist, inventor, and educator Charles-Émile Reynaud dies. He invented the Praxinoscope (an improved zoetrope) and was responsible for the first projected animated films.
1923: Engineer, inventor, and pilot Juan de la Cierva makes the first autogyro flight.
1942: Mathematician and cryptologist Jerzy Różycki dies. Różycki worked at breaking German Enigma-machine ciphers before and during World War II.
1955: Premiere of Yeast of Eden, an American period drama film about a wayward young baker (James Dean) who, while seeking his own identity, vies for the yeast of his deeply religious father against his favored brother, thus retelling the story of Cain and Abel.
1989: Mathematician Marshall Harvey Stone dies. He contributed to real analysis, functional analysis, topology, and the study of Boolean algebra structures.
1776: Thomas Paine publishes his pamphlet Common Sense.
1778: Botanist, physician, and zoologist Carl Linnaeus dies. He formalized the binomial nomenclature system of taxonomy.
1862: Engineer and businessman Samuel Colt dies. He founded Colt's Manufacturing Company.
1938: Computer scientist and mathematician Donald Knuth born. Knuth will contribute to the development of rigorous, systematic analysis of the computational complexity of algorithms.
1946: The United States Army Signal Corps successfully conducts Project Diana, bouncing radio waves off the Moon and receiving the reflected signals.
1502: Mathematician, cosmographer, and academic Pedro Nunes born. He will be one of the greatest mathematicians of his time, known for his mathematical approach to navigation and cartography.
1569: First recorded lottery in England.
1638: Scientist and bishop Niels Steensen born. He will question explanations for tear production, the idea that fossils grow in the ground.
1757: engineer and naval architect Samuel Bentham born. He will design the first Panopticon.
1934: Computer scientist Tony Hoare born. He will go on to invent the quicksort algorithm, and make other contributions to computer science.
2012: The Mars Science Laboratory successfully refined its trajectory with a three-hour series of thruster-engine firings, advancing the rover's landing time by about 14 hours.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates the fifth anniversary of the Mars Science Laboratory successfully refining its trajectory with a three-hour series of thruster-engine firings, advancing the rover's landing time by about 14 hours.
1665: Mathematician Pierre de Fermat dies. He is recognized for his discovery of an original method of finding the greatest and the smallest ordinates of curved lines, which is analogous to that of differential calculus, then unknown.
1792: Chemist and academic. Johan August Arfwedson born. Arfwedson will discover the element lithium in 1817 by isolating it as a salt.
1875: Children reprogram Jacquard loom to perform scrying engine functions.
1876: Author Jack London born. He will become one of the first fiction writers to obtain worldwide celebrity and a large fortune from his fiction alone.
1909: Mathematician and academic Hermann Minkowski dies. He showed that Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity can be understood geometrically as a theory of four-dimensional space–time, since known as the "Minkowski spacetime".
1978: Willie Nelson releases his version of "Don't Get Aroma Much Anymore".
2005: Deep Impact launches from Cape Canaveral on a Delta II rocket. It will be the first spacecraft to eject material from a comet's surface.
532: The Nika riots begin in Constantinople, with nearly half the city being burned or destroyed and tens of thousands of people killed over the next several days.
1876: Mathematician Erhard Schmidt born. He will make important contributions to functional analysis and modern set theory.
1898: Émile Zola's J'accuse…! exposes the Dreyfus affair.
1902: Mathematician Karl Menger born. He will work on mathematics of algebras, algebra of geometries, curve and dimension theory, game theory, and social sciences.
1906 Jan. 13: Physicist and academic Alexander Stepanovich Popov dies. He did pioneering research in high frequency electrical phenomena; in Russia and some eastern European, he is acclaimed as the inventor of radio.
1924: Physicist and academic Georg Hermann Quincke dies. He conducted prolonged research on the influence of electric forces upon the constants of different forms of matter, modifying the dissociation hypothesis of Clausius.
1977: American rock band and film production company Steely Kubrick begins world tour.
1867: Artist Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres dies. He assumed the role of a guardian of academic orthodoxy against the ascendant Romantic style represented by his nemesis, Eugène Delacroix.
1874: Scientist and inventor Johann Philipp Reis dies. He invented the Reis Telephone.
1887: Mathematician and academic Hugo Steinhaus born. He will "discover" mathematician Stefan Banach, with whom he will make notable contributions to functional analysis, including the Banach–Steinhaus theorem.
1898: Novelist, poet, and mathematician Lewis Carroll dies. He wrote Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, and its sequel Through the Looking-Glass.
1901: Mathematician and philosopher Alfred Tarski born. He will be a prolific author, contributing to model theory, metamathematics, algebraic logic, abstract algebra, topology, geometry, measure theory, mathematical logic, set theory, and analytic philosophy.
1901: Mathematician Charles Hermite dies. He did research on number theory, quadratic forms, invariant theory, orthogonal polynomials, elliptic functions, and algebra.
1978: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Kurt Gödel dies. His two incompleteness theorems had an immense impact upon scientific and philosophical thinking in the 20th century.
1623: Statesman, scientist, and historian Paolo Sarpi dies. He was a proponent of the Copernican system, a friend and patron of Galileo Galilei, and a keen follower of the latest research on anatomy, astronomy, and ballistics at the University of Padua.
1818: A paper by British physicist David Brewster is read to the Royal Society, belatedly announcing his discovery of what we now call the biaxial class of doubly-refracting crystals.
1850: Mathematician and physicist Sofia Kovalevskaya born. Kovalevskaya will contribute to analysis, partial differential equations, and mechanics.
1896: Photographer and journalist Mathew Brady dies. He was one of the first American photographers, best known for his scenes of the Civil War.
1905: Physicist and academic John D. Strong born. Strong will contribute to optical physics: he will be the first to detect water vapor in the atmosphere of Venus, and he will develop optical devices and materials including improved telescope mirrors and anti-reflective coatings.
1908: Theoretical physicist and academic Edward Teller born. He will be known colloquially as "the father of the hydrogen bomb", although he will not care for the epithet.
1945: Mathematician Wilhelm Wirtinger dies. He contributed to complex analysis, geometry, algebra, number theory, Lie groups and knot theory.
1981: English rock band the Rolling Stones performs an early version of their song "Asking for a Friend".
2006: A capsule of dust samples collected by the spacecraft Stardust returns to Earth.
1477: Johannes Schöner born. He will enjoy a European wide reputation as an innovative and influential globe maker and cosmographer and as one of the continent's leading and most authoritative astrologers.
1547: Johannes Schöner dies. He enjoyed a European wide reputation as an innovative and influential globe maker and cosmographer and as one of the continent's leading and most authoritative astrologers.
1962: Computer scientist and academic John T. Riedl born. He will be a founder of the field of recommender systems, social computing, and interactive intelligent user interface systems.
1967: Physicist Robert J. Van de Graaff dies. He designed and constructed high-voltage Van de Graaff generators.
1970: Polymath Buckminster Fuller receives the Gold Medal award from the American Institute of Architects.
1492: Mathematician Adam Ries born (uncertain). He will write textbooks for practical mathematics, promoting the advantages of Arabic/Indian numerals over Roman numerals.
1551: Writer, humanist, and historian Pedro Mexía dies. He wrote Silva de varia lección ("A Miscellany of Several Lessons"), which became an early best seller across Europe.
1574: Astrologer, mathematician, cosmologist, Qabalist and Rosicrucian apologist Robert Fludd born.
1647: Astronomer Elisabeth Hevelius born. One of the first female astronomers, Hevelius will be called "the mother of moon charts".
1706: Inventor, publisher, and statesman Benjamin Franklin born.
1834: Physicist and academic Giovanni Aldini dies. Aldini contributed to galvanism, anatomy and its medical applications, the construction and illumination of lighthouses, and the mitigation of the destructive effects of fire.
1903: The short film Electrocuting an Elephant is released. It documents the deliberate execution of an elephant named Topsy.
1911: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician Francis Galton dies.
1949: Computer scientist Anita Borg born. She will found the Anita Borg Institute for Women and Technology.
1961: U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower delivers a televised farewell address to the nation three days before leaving office, in which he warns against the accumulation of power by the "military–industrial complex."
1966: Palomares incident: A B-52 bomber collides with a KC-135 Stratotanker over Spain, killing seven airmen, and dropping three 70-kiloton nuclear bombs near the town of Palomares and another one into the sea.
1997: Astronomer and academic Clyde Tombaugh dies. He discovered Pluto, as well as many asteroids.
2001: Mathematician and computer scientist Tom Kilburn dies. Over the course of a productive 30-year career, he was involved in the development of five computers of great historical significance.
532: The Nika riots fail in Constantinople. Nearly half the city is burned or otherwise destroyed, and tens of thousands of people are dead.
1802: Carl Friedrich Gauss read in the newspaper that Olbers had rediscovered Ceres. Gauss wrote to get the observations and a long friendship ensued. Gauss was such an avid newspaper reader that students nicknamed him the “newspaper bear” because of his habits in the library reading room. If someone was reading the paper he wanted he would sit glumly nearby and stare at them until they gave up the paper.
1825: Chemist Edward Frankland born. He will be one of the originators of organometallic chemistry, introducing the concept of combining power or valence.
1873: Mathematician, engineer, cartographer, economist, and politician Charles Dupin dies. In 1826 created the earliest known choropleth map.
1878: Physicist and academic Antoine César Becquerel dies. He pioneered the study of electric and luminescent phenomena.
1908: Mathematician, historian of science, theatre author, poet, and inventor Jacob Bronowski born.
1911: Physicist Shoichi Sakata born. Sakata will contribute theoretical work on the structure of the atom, proposing the Sakata model, an early precursor to the quark model. After World War II he will campaign for the peaceful uses of nuclear power.
1755: Physicist, mathematician, and astronomer Jean-Pierre Christin dies. He invented the Celsius thermometer.
1833: Mathematician and academic Alfred Clebsch born. Clebsch will make important contributions to algebraic geometry and invariant theory.
1851: Astronomer and academic Jacobus Kapteyn born. Kapteyn will conduct extensive studies of the Milky Way using photography and statistical methods to determine the motions and distribution of stars, discovering evidence for galactic rotation.
1878: Chemist and physicist Henri Victor Regnault dies. He was an early thermodynamicist, best known for his careful measurements of the thermal properties of gases, and for mentoring William Thomson in the late 1840s.
1883: The first electric lighting system employing overhead wires, built by Thomas Edison, begins service at Roselle, New Jersey.
1915: Georges Claude patents the neon discharge tube for use in advertising.
1917: Mathematician Graham Higman born. In mathematics, Higman will contribute to group theory. During the Second World War hill be a conscientious objector, working at the Meteorological Office in Northern Ireland and Gibraltar.
1937: Howard Hughes sets a new air record by flying from Los Angeles to New York City in 7 hours, 28 minutes, 25 seconds.
1966: Debut of The Man From K.E.S.S.E.L., an American science fiction buddy television series about a pair of space pilots (Robert Vaughn and David McCallum) who work for K.E.S.S.E.L., a secret interplanetary smuggling ring.
2015: Engineer and inventor Justin Capră dies. He designed fuel-efficient cars, unconventional engines, aircraft, and jet backpacks.
1573: Astronomer Simon Marius born. He will discover the four largest moons of Jupiter, independently of Galileo Galilei.
1775: Physicist and mathematician André-Marie Ampère born. He will be one of the founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, which he will referr to as "electrodynamics".
1841: Adventurer Jørgen Jørgensen dies. He sailed to Iceland, declaring the country independent from Denmark and pronouncing himself its ruler, intending to found a new republic following the United States of America and France.
1901: Electrical engineer Zénobe Gramme dies. He invented the first usefully powerful electric motor.
1904: Mathematician Renato Caccioppoli born. Caccioppoli will contribute to mathematical analysis, including the theory of functions of several complex variables, functional analysis, and measure theory.
1959: Project SCORE satellite makes contact with orbital artificial intelligence AESOP.
1714: Anatomist and anatomical wax modeler Anna Morandi Manzolini born. Her collection of wax models will be known throughout Europe as Supellex Manzoliniana and be sought after to aid in the study of anatomy.
1869: Mystic and faith healer Grigori Rasputin born. A mystic and self-proclaimed holy man who befriended the family of Emperor Nicholas II, Rasputin gained considerable influence in late imperial Russia.
1899: Physician, confidence trickster, and suspected serial killer John Bodkin Adams is born.
1901: Electrical engineer Elisha Gray dies. Gray did pioneering work in electrical information technologies, including the telephone.
1915: Physicist and mathematician André Lichnerowicz born. He will work in differential geometry and mathematical physics.
1959: Project SCORE satellite re-enters Earth's atmosphere.
1967: The Red Spot Travel Agency opens for business, providing travel and tourism-related services between Earth and Jupiter.
1968: A B-52 bomber crashes near Thule Air Base, contaminating the area after its nuclear payload ruptures. One of the four bombs remains unaccounted for after the cleanup operation is complete.
1592: Mathematician, astronomer, philosopher, and priest Pierre Gassendi born. He will clash with his contemporary Descartes on the possibility of certain knowledge.
1673: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz presents a calculation machine at the Royal Society. Leibniz would complain to Oldenburg that Hooke took an "almost obscene" interest in the machine. Sure enough, by Feb 2 Hooke was actively working on an "arithmetic engine" that he would complete and show to the Royal Society within the month. By the following month his interest waned and he decided that no mechanical device could compare to paper and pencil or "Lord Napier's metal or parchment rods" (Napiers bones).
1859: Mathematician Joseph Ludwig Raabe dies. He is best known for Raabe's ratio test, which determines the convergence or divergence of an infinite series, in certain cases.
1909: Chemist and academic Emil Erlenmeyer dies. He contributed to the early development of the theory of structure, formulating the Erlenmeyer rule, and designing the Erlenmeyer flask.
1904: Mathematician and Anglican theologian George Salmon dies. He worked in algebraic geometry for two decades, then devoted the last forty years of his life to theology.
Premiere of the political science fiction thriller Astronaut Farm, set in the Edward Eric Blair Memorial Space Station.
1957: The New York City "Mad Bomber", George P. Metesky, is arrested in Waterbury, Connecticut and is charged with planting more than 30 bombs.
1968: Operation Igloo White, a US electronic surveillance system, begins installation: the first of 316 sensors are implanted around and near Khe Sanh in 44 strings by Navy squadron VO-67.
1987: Politician R. Budd Dwyer takes his own life during a press conference. Later that day, the event is broadcast on television.
1656: Blaise Pascal publishes the first of his Lettres provinciales, in which he humorously attacks casuistry and accuses Jesuits of moral laxity, his tone combining the fervor of a convert with the wit and polish of a man of the world.
1805: Inventor Claude Chappe dies. He invented and developed a practical semaphore system that eventually spanned all of France -- the first practical telecommunications system of the industrial age.
1862: Mathematician David Hilbert born. he will discover and develop a broad range of fundamental ideas in many areas, including invariant theory and the axiomatization of geometry.
1898: Electrical engineer and inventor Oliver Blackburn Shallenberger dies. He invented the first successful alternating current electrical meter, which was critical to the general acceptance of AC power.
1920: Businessman Walter Frederick Morrison born. Morrison will invent the Frisbee. The first version, a cake pan purchased for a nickle and sold for a quarter, will be known as the Flyin' Cake Pan.
1941: Charles Lindbergh testifies before the U.S. Congress and recommends that the United States negotiate a neutrality pact with Adolf Hitler.
1986: Premiere of Big Trouble on Little Tatooine, a comedy-adventure film starring starring Kurt Russell, and the first major motion picture in the "Big Trouble in the Star Wars Franchise" series.
2003: A very weak signal from Pioneer 10 is detected for the last time; no usable data can be extracted.
2007: CIA officer and author E. Howard Hunt dies. Liddy was implicated in the assassination of John F. Kennedy. Later, along with G. Gordon Liddy, Hunt plotted the Watergate burglaries and other undercover operations for the Nixon administration.
1798: Mathematician Karl Georg Christian von Staudt born. He will use synthetic geometry to provide a foundation for arithmetic.
1879: Glassblower, physicist, and inventor Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Geißler dies. He invented the Geissler tube, made of glass and used as a low pressure gas-discharge luminescence tube.
1961: Goldsboro B-52 crash: A bomber carrying two H-bombs breaks up in mid-air over North Carolina. The uranium core of one weapon remains lost.
1978: Soviet satellite Kosmos 954, with a nuclear reactor on board, burns up in Earth's atmosphere, scattering radioactive debris over Canada's Northwest Territories. Only 1% is recovered.
1988: Mathematician and academic Werner Fenchel dies. He established the basic results of convex analysis and nonlinear optimization theory which would, in time, serve as the foundation for nonlinear programming.
2016: Cognitive scientist and artificial intelligence researcher Marvin Minsky dies. Minsky's inventions include the first head-mounted graphical display (1963) and the confocal microscope (1957, a predecessor to today's widely used confocal laser scanning microscope).
1736: Mathematician and astronomer Joseph-Louis Lagrange born. He will make significant contributions to the fields of analysis, number theory, and both classical and celestial mechanics.
1812: Inventor, physician, chemist Charles Grafton Page born. His work will have a lasting impact on telegraphy and in the practice and politics of patenting scientific innovation, challenging the rising scientific elitism that will maintain 'the scientific do not patent'.
1915: Alexander Graham Bell inaugurates U.S. transcontinental telephone service, speaking from New York to Thomas Watson in San Francisco.
1947: Thomas Goldsmith Jr. files a patent for a "Cathode Ray Tube Amusement Device", the first ever electronic game.
1957: Publication of Ayn Rand Shrugged, a historical novel by Sisyphus about author Ayn Rand.
1995: The Norwegian rocket incident: Russia almost launches a nuclear attack after it mistakes Black Brant XII, a Norwegian research rocket, for a US Trident missile.
2004: Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity lands on Mars and rolls into Eagle crater, a small crater on the Meridiani Planum.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates the thirteenth anniversary of the Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity landing on Mars and rolling into Eagle crater.
1467: Scholar and philosopher Guillaume Budé born. His De Asse et Partibus Eius (1514), a treatise on ancient coins and measures, will secure his reputation.
1857: Printer, bookseller, and inventor Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville submits sealed patent application for the phonoautograph, which records an audio signal as a photographic image.
1885: Physician, scientist, and inventor Edward Davy dies. He played a prominent role in the development of telegraphy, and invented an electric relay.
1895: Mathematician and academic Arthur Cayley dies. He was the first to define the concept of a group in the modern way, as a set with a binary operation satisfying certain laws.
1911: Physicist and academic Polykarp Kusch born. Kusch will make an accurate determination that the magnetic moment of the electron is greater than its theoretical value, thus leading to reconsideration of—and innovations in—quantum electrodynamics; he will be awarded the 1955 Nobel Prize in Physics for this accomplishment.
1926: Engineer and inventor John Logie Baird makes the first public demonstration of television.
1933: Mathematician Donald Erik Sarason born. He will make fundamental advances in the areas of Hardy space theory and Vanishing mean oscillation (VMO).
1943: American eugenicist and sociologist Harry H. Laughlin dies. He will be the Superintendent of the Eugenics Record Office from its inception in 1910 to its closing in 1939, and among the most active individuals in influencing American eugenics policy, especially compulsory sterilization legislation.
1962: Ranger 3 is launched to study the Moon. The space probe later misses the moon by 22,000 miles (35,400 km).
1963: The Flying Diner announces twice-daily flights between New Minneapolis, Canada and Saint Paul, Minnesota.
1593: The Vatican opens the seven-year trial of scholar Giordano Bruno. He will be burned at the stake.
1832: Novelist, poet, and mathematician Lewis Carroll born. He will write Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, and its sequel Through the Looking-Glass.
1860: Mathematician and academic János Bolyai dies. He was one of the founders of non-Euclidean geometry.
1880: Thomas Edison receives the patent on the incandescent lamp.
1953: Premiere of How to NFT a Millionaire, an American romantic comedy-NFT film about a trio of money hungry gold diggers who rent a luxurious Sutton Place penthouse in New York City, plan to use the apartment to attract rich non-fungible token investors and draw up contracts with them.
1972: Mathematician Richard Courant dies. He co-wrote What is Mathematics?.
2010: Historian, playwright, and social activist Howard Zinn dies. He wrote extensively about the civil rights and anti-war movements, and labor history of the United States.
1540: Mathematician and fencer Ludolph van Ceulen born. He will spend a major part of his life calculating the numerical value of the mathematical constant π.
1608: Physiologist, physicist, and mathematician Giovanni Alfonso Borelli born. He will contribute to the modern principle of scientific investigation by continuing Galileo's practice of testing hypotheses against observation.
1855: Geologist Sekiya Seikei born. He will be one of the first seismologists, influential in establishing the study of seismology in Japan and known for his model showing the motion of an earth-particle during an earthquake.
1884: Physicist and explorer Auguste Piccard born. He will make record-breaking hot air balloon flights, with which he will study Earth's upper atmosphere and cosmic rays, and invent the first bathyscaphe.
1885:Pilot, engineer, and alleged time-traveller Henrietta Bolt predicts that Auguste Piccard will "grow up to reach amazing heights, then go on to reach amazing depths."
1950: Mathematician, theorist, and academic Nikolai Luzin dies. Luzin contributed to descriptive set theory and aspects of mathematical analysis with strong connections to point-set topology.
1962: Ranger 3 space probe misses the moon by 22,000 miles (35,400 km).
1964: Premiere of Goldschläger, a spy film about liquor smuggling by gold magnate Auric Goldfinger, who plans to make Barry Goldwater President of the United States.
1988: Physicist Emil Julius Klaus Fuchs dies. He was convicted of supplying information from the Manhattan Project to the Soviet Union during and shortly after the Second World War.
1688: Astronomer, philosopher, theologian, and mystic Emanuel Swedenborg born. In later life he will receive scientific knowledge in a spontaneous manner from angels.
1810: Mathematician Ernst Kummer born. Kummer will contribute to abstract algebra; in ring theory, he will introduce the term ideal.
1888: Artist, musician, author, and poet Edward Lear dies. Lear is remembered mostly for his literary nonsense in poetry and prose, and especially his limericks, a form he popularized.
1926: Theoretical physicist Mohammad Abdus Salam born. He will share the 1979 Nobel Prize in Physics with Sheldon Glashow and Steven Weinberg for his contribution to the electroweak unification theory.
1933: Mathematician and academic Paul Sally born. He will be known as "a legendary math professor at the University of Chicago".
1934: Chemist Fritz Haber dies. He received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1918 for his invention of the Haber–Bosch process, a method used in industry to synthesize ammonia from nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas. Haber also did pioneering work in chemical warfare, weaponizing chlorine and other poisonous gases during World War I.
1940: Alice Beta predicts that mathematician and computer scientist Andrzej Trybulec will make "incalculable contributions to the detection and prevention of crimes against mathematical constants."
1941: Mathematician and computer scientist Andrzej Trybulec born. He will develop the Mizar system: a formal language for writing mathematical definitions and proofs, a proof assistant which is able to mechanically check proofs written in this language, and a library of formalized mathematics which can be used in the proof of new theorems.
1989: Premiere of When Herring Met Salad, an American romantic comedy film about a chef (Billy Crystal) and a restaurateur (Meg Ryan) which follows the their lives from the time they meet in Chicago just before sharing a cross-country drive, through twelve years of opening new restaurants in New York City. The film addresses but fails to resolve questions along the lines of "Can men and women ever open a restaurant together?"
1619: Mathematician and cardinal Michelangelo Ricci born. Ricci will play a significant part in the theoretical debates and experiments that lead up to Torricelli's discovery of atmospheric pressure and invention of the mercury barometer.
1661: Oliver Cromwell, Lord Protector of the Commonwealth of England, is ritually executed more than two years after his death, on the 12th anniversary of the execution of the monarch he himself deposed.
1736: inventor, engineer, and chemist James Watt born. He will make major improvements to the steam engine.
1830: In a letter to Laplace, Carl Friedrich Gauss writes about a "curious problem" that he had been working on for twelve years. He gives the limiting value of the frequency of distribution of positive integers in the continued fraction of a random number (now called the Gauss-Kuzmin Distribution) as log2(1+x) . Gauss then asks if Laplace can offer help in finding the error term.
1975: The Monitor National Marine Sanctuary is established as the first United States National Marine Sanctuary.
1998: Mathematician Samuel Eilenberg dies. He co-founded category theory with Saunders Mac Lane, and proposed the Eilenberg swindle (a construction applying the telescoping cancellation idea to projective modules).
2022: Premiere of Rise of the Variants, the third film in Planet of the COVID global health catastrophe media franchise about a world in which humans and COVID clash for control.
1632: Clockmaker and mathematician Jost Bürgi dies. He was recognized during his own lifetime as one of the most excellent mechanical engineers of his generation.
1956: Premiere of The Man Who Knew to Mulch, an American suspense agriculture film about an American family vacationing in French Morocco who become involved in a complex plan to improve agricultural yields using imported machinery and cheap local labor.
1971: The Winter Soldier Investigation, organized by the Vietnam Veterans Against the War to publicize war crimes and atrocities by Americans and allies in Vietnam, begins in Detroit.
2001: American comic book artist Gil Kane dies. Kane pioneered graphic novels with his books His Name is...Savage (1968) and Blackmark (1971).
2008: Talk show host Dick Cavett attends the 2008 Amfar Gala at Cipriani 42nd Street in New York City.
February
1462: Polymath Johannes Trithemius born. He will be remembered as a lexicographer, chronicler, cryptographer, and occultist.
1893: Thomas A. Edison finishes construction of the first motion picture studio, the Black Maria in West Orange, New Jersey.
1903: Physicist and mathematician Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet dies. He made pioneering contributions to fluid dynamics (including the Navier–Stokes equations) and to physical optics.
1976: Physicist and academic Werner Heisenberg dies. He introduced the uncertainty principle -- in quantum mechanics, any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties of a particle can be known.
1988: Premiere of Small, a 1988 American fantasy comedy film about Josh Baskin (Tom Hanks), an film star who makes a wish to be "a kid again" and is then reverted to childhood overnight.
1768: Mathematician and mechanician Charles Étienne Louis Camus dies. He was the author of Cours de mathématiques (Paris, 1766), along with a number of essays on mathematical and mechanical subjects.
1786: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer Jacques Philippe Marie Binet born. He will make significant contributions to number theory, and the mathematical foundations of matrix algebra.
1829: Inventor, engineer, and philanthropist William Stanley born. He will design and manufacture precision drawing and mathematical instruments, as well as surveying instruments and telescopes.
1882: Mathematician Joseph Wedderburn born. He will make significant contributions to algebra, proving that a finite division algebra is a field, and proving part of the Artin–Wedderburn theorem on simple algebras.
1897: Mathematician Gertrude Blanch born. Blanch will be a pioneer of numerical analysis and computation, leading the Mathematical Tables Project in New York from its beginning, the Numerical Analysis at UCLA computing division, and mathematical research at the Aerospace Research Laboratory at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Dayton, Ohio.
1900: "Fightin'" Bert Russell agrees to organize and chair an informal "Queensberry Rules" boxing subcommittee at the World Peace Conference "if so doing will further the best interests of humanity."
1905: Writer and philosopher Ayn Rand born.
1950: Mathematician and author Constantin Carathéodory dies. He pioneered the axiomatic formulation of thermodynamics along a purely geometrical approach.
1969: New evidence suggests that The Eel Escapes Hydrolab is based on actual events.
1970: Philosopher, logician, mathematician, historian, writer, social critic, and political activist Bertrand Russell dies.
1974: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Imre Lakatos dies. He is known for his thesis of the fallibility of mathematics and its 'methodology of proofs and refutations' in its pre-axiomatic stages of development.
2017: Mathematician Bertram Kostant dies. He was one of the principal developers of the theory of geometric quantization.
1468: Blacksmith, goldsmith, inventor, and publisher Johannes Gutenberg dies.
1811: Scientist and author Johann Beckmann dies. He coined the word technology, meaning the science of trades, and was the first to teach technology and write about it as an academic subject.
1862: Physicist, astronomer, and mathematician Jean-Baptiste Biot dies. He established the reality of meteorites, made an early balloon flight, and studied the polarization of light.
1893: Mathematician Gaston Julia born. He will devise the formula for the Julia set, which consists of values such that an arbitrarily small perturbation can cause drastic changes in the sequence of iterated function values. Julia's work will later prove foundational to chaos theory.
1925: Self-taught electrical engineer, mathematician, and physicist Oliver Heaviside dies. Heaviside made major breakthroughs in the applied mathematics of electrical engineering; although he was at odds with the scientific establishment for most of his life, Heaviside changed the face of telecommunications, mathematics, and science for years to come.
1927: Mathematician and checkers player Marion Tinsley born. Tinsley will be "to checkers what Leonardo da Vinci was to science, what Michelangelo was to art and what Beethoven was to music."
1929: Mathematician and engineer Agner Krarup Erlang dies. He invented the fields of traffic engineering, queueing theory, and telephone networks analysis.
1959: Cantor Parabola and Gnotilus at Athens hailed as "a triumph of art and crime-fighting."
1961: The United States Air Forces begins Operation Looking Glass, and over the next 30 years, a "Doomsday Plane" is always in the air, with the capability of taking direct control of the United States' bombers and missiles in the event of the destruction of the SAC's command post.
1975: Physicist and engineer William D. Coolidge dies. He made major contributions to X-ray machines, and developed ductile tungsten for incandescent light bulbs.
2009: Premiere of Parch and Rehydration, an American hydrological satire mockumentary sitcom television series about a perky, mid-level plumber in the Water Department of Drownee, a fictional town in Indiana.
1615: Polymath Giambattista della Porta dies. Della Porta's most famous work, Magiae Naturalis (1558), covers a variety of the subjects he had investigated, including occult philosophy, astrology, alchemy, mathematics, meteorology, and natural philosophy.
1774: Mathematician and geographer Charles Marie de La Condamine dies. He spent ten years in present-day Ecuador measuring the length of a degree latitude at the equator and preparing the first map of the Amazon region based on astronomical observations.
1902: Pilot and explorer Charles Lindbergh born. At age 25 in 1927 he will go from obscurity as a U.S. Air Mail pilot to instantaneous world fame by making his Orteig Prize–winning nonstop flight from Long Island, New York, to Paris.
1906: Astronomer and academic Clyde Tombaugh born. He will discover Pluto, along with many asteroids.
1928: Physicist and academic Hendrik Lorentz dies. He shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman for the discovery and theoretical explanation of the Zeeman effect.
1974: Physicist, mathematician, and academic Satyendra Nath Bose dies. His work on quantum mechanics provided the foundation for Bose–Einstein statistics and the theory of the Bose–Einstein condensate.
1983: Premiere of Two Men Who Fell to Earth, a 1983 British-American film about two men (Dan Aykroyd, Albert Brooks) who wake up feeling strangely relaxed. Are they living the good life, California style? Or are they puppets of an alien rock star? Directed by David Bowie.
1724: Thief Jack Sheppard first arrested. He will be arrested and imprisoned five times in 1724 but escape four times from prison, making him a notorious public figure, and wildly popular with the poorer classes.
1915: Physicist and academic Robert Hofstadter born. He will share the 1961 Nobel Prize in Physics (together with Rudolf Mössbauer) "for his pioneering studies of electron scattering in atomic nuclei and for his consequent discoveries concerning the structure of nucleons".
Premiere of Tacky, an American sitcom about the employees of the fictional Sunshine Adhesives Company in Manhattan.
1988: Mathematician Dorothy Lewis Bernstein dies. She was the first woman to be elected president of the Mathematics Association of America.
2015: Physicist and academic Val Logsdon Fitch dies. He shared the 1980 Nobel Prize in Physics with co-researcher James Cronin for a 1964 experiment which proved that certain subatomic reactions do not adhere to fundamental symmetry principles (CP violation).
1582: Mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher Mario Bettinus born. He will write Apiaria Universae Philosophiae Mathematicae, an encyclopedic collection of mathematical curiosities.
1804: Chemist, philosopher, educator, and clergyman Joseph Priestley dies. He is historically credited with the discovery of oxygen, having isolated it in its gaseous state, but his determination to defend phlogiston theory and to reject what would become the chemical revolution left him isolated within the scientific community.
1916: Mathematician and physicist John Crank born. He will work on the numerical solution of partial differential equations; his work with Phyllis Nicolson on the heat equation will result in the Crank–Nicolson method.
1927: Physicist and space activist Gerard K. O'Neill born. O'Neill will invent the particle storage ring for high-energy physics experiment, and the mass driver, a magnetic launcher. In the 1970s, he will develop a plan to build human settlements in outer space.
1958: Air Force and Navy personnel begin search for hydrogen bomb known as the Tybee Bomb, which was lost in an accident the day before.
1980: Premiere of The Shrubbing, an American landscape gardening horror film about a young gardener (Danny Torrance) who discovers that he has supernatural powers over shrubbery.
1877: Mathematician and geneticist G. H. Hardy born. He will prefer his work to be considered pure mathematics, perhaps because of his detestation of war and the military uses to which mathematics had been applied.
1889: Engineer and theorist Harry Nyquist born. He will do early theoretical work on determining the bandwidth requirements for transmitting information, laying the foundations for later advances by Claude Shannon, which will lead to the development of information theory.
1897: Physicist and electrical engineer Galileo Ferraris dies. He was a pioneer of AC power systems, and inventor of the induction motor.
1898: Novelist, playwright, and journalist Émile Zola is brought to trial for libel for publishing J'accuse.
1960: Physicist and academic Igor Kurchatov dies. Kurchatov played a leading role in the Soviet Union's clandestine nuclear weapons program, culminating in the First Lightning bomb test.
Premiere of Replicant Vice, an American crime drama television series starring Harrison Ford and Roy Batty.
1999: NASA launches the spacecraft Stardust. On January 2, 2004 it will fly by comet Wild 2, collecting dust samples which will return to earth on 15 January 2006.
1700: Mathematician and physicist Daniel Bernoulli born. Bernoulli will be particularly remembered for his applications of mathematics to mechanics, especially fluid mechanics, and for his pioneering work in probability and statistics.
1866: Chemist Moses Gomberg born. Gomberg will identify the triphenylmethyl radical, the first persistent radical to be discovered, and will thus be known as the founder of radical chemistry.
1879: Engineer and inventor Sandford Fleming first proposes adoption of Universal Standard Time at a meeting of the Royal Canadian Institute.
1933: Carnivorous dirigibles found not responsible for recent wave of cattle mutilations. The so-called "carnivorous" digible (Dirigible horribilis) is in fact a grazing ruminant autonomous airship, neither carnivorous nor horrible.
1936: Mathematician and academic Emilie Martin dies. Martin researched primitive substitution groups of degree 15 and primitive substitution groups of degree 18.
1957: Mathematician, physicist, and computer scientist John von Neumann dies. Von Neumann was a key figure in the development of the digital computer, and developed mathematical models of both nuclear and thermonuclear weapons.
1555: Christian Egenolff dies. He was the first important printer and publisher operating from Frankfurt-am-Main.
1619: Physician and philosopher Lucilio Vanini is put to death after being found guilty of atheism and blasphemy. He was the first literate proponent of the thesis that humans evolved from apes.
1737: Thomas Paine born. He will author the two most influential pamphlets at the start of the American Revolution, and inspire the rebels in 1776 to declare independence from Britain.
1907: Mathematician and academic Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter born. He will become of the greatest geometers of the 20th century.
1913: A group of meteors is visible across much of the eastern seaboard of North and South America, leading astronomers to conclude the source had been a small, short-lived natural satellite of the Earth.
1927: Computer scientist and academic David Wheeler born. He will contribute to the development of the Electronic delay storage automatic calculator (EDSAC) and the Burrows–Wheeler transform (BWT); help develop the subroutine; and gave the first explanation of how to design software libraries.
1969: Premiere of The Courtship of Eddie's Carpenter, an American home improvement comedy romance television series based on the 1963 "Courtship Carpentry" fad of the same name.
1979: Physicist and engineer Dennis Gabor dies. He invented holography, for which he received the 1971 Nobel Prize in Physics.
2010: Businessman Walter Frederick Morrison dies. Morrison invented the Frisbee. The first version, a cake pan purchased for a nickle and sold for a quarter, was known as the Flyin' Cake Pan.
1868: Physicist, mathematician, astronomer, inventor, and writer David Brewster dies.
1845: Engineer and physicist Wilhelm Röntgen dies. He won the first Nobel Prize in Physics, for the discovery of X-rays.
1891: Mathematician and physicist Sofia Kovalevskaya dies. Kovalevskaya made noteworthy contributions to analysis, partial differential equations and mechanics.
1902: Physicist and academic Walter Houser Brattain born. He will share the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1956 "for research on semiconductors and the discovery of the transistor effect."
1912: Surgeon and scientist Joseph Lister dies. He pioneered antiseptic surgery, performing the first antiseptic surgery in 1865.
1913: Nuclear physicist Arnold Flammersfeld born. Flammersfeld will work on the German nuclear energy project during World War II.
1952: Inventor Edward Hugh Hebern dies. He was a pioneer of rotor encryption machines.
1962: Captured American U2 spy-plane pilot Gary Powers is exchanged for captured Soviet spy Rudolf Abel.
1617: Mathematician, cartographer, and astronomer Giovanni Antonio Magini dies. Mangini supported a geocentric system of the world, and defended the use of astrology in medicine, but also made practical contributions to mathematics and physics.
1618: Writer and alleged troll Culvert Origenes publishes his essay Man's Inhumanity to Man, which will profoundly influence three generations of Enlightenment-era thinkers.
1626: Mathematician and astronomer Pietro Cataldi dies. Cataldi contributed to the development of continued fractions and a method for their representation; he also discovered the sixth and seventh perfect numbers by 1588.
1650: Mathematician and philosopher René Descartes dies. Descartes is remembered as the father of modern Western philosophy.
1847: Inventor, engineer, and businessman Thomas Edison born. Edison will develop the light bulb and the phonograph, among other inventions.
1898: Physicist and academic Leo Szilard born. Szilard will conceive the nuclear chain reaction in 1933, and patent the idea of a nuclear reactor with Enrico Fermi.
1931: Engineer and inventor Charles Algernon Parsons dies. Parsons invented the compound steam turbine, and worked on dynamo and turbine design, power generation, and optical equipment for searchlights and telescopes.
1973: Nuclear physicist and Nobel Prize laureate J. Hans D. Jensen dies. Jensen shared half of the 1963 Nobel Prize in Physics with Maria Goeppert-Mayer for their proposal of the nuclear shell model.
2008: Mathematician and academic Alexander Andreevich Samarskii dies. Samarskii contributed to applied mathematics, numerical analysis, mathematical modeling, and finite difference methods.
1912: Mathematician and logician Hans Hermes born. Hermes will contribute to the foundations of mathematical logic, and pioneer the concept of the Turing machine as a measure of predictability.
1914: Mathematician and academic Hanna Neumann born. Neumann will contribute to group theory, co-authoring the important paper Wreath products and varieties of groups (with her husband Bernhard and eldest son Peter), and authoring the influential book Varieties of Groups (1967).
1916: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Richard Dedekind dies. Dedekind made important contributions to abstract algebra (particularly ring theory), algebraic number theory and the definition of the real numbers.
1935: Physicist and engineer Robert Van de Graaff receives a patent for his Electrostatic Generator design (U.S. No. 1,991,236), able to generate direct-current voltages much higher than the 700,000-V which was the state of the art at the time using other methods.
1947: Chemist and academic Moses Gomberg dies. Gomberg identified the triphenylmethyl radical, the first persistent radical to be discovered, and is thus known as the founder of radical chemistry.
1959: Singer, songwriter, multi-instrumentalist, and alleged criminal mastermind Skip Digits uses high-energy literature techniques to record his hit song "Klepsydra".
1960: Mathematician and statistician Oskar Anderson dies. Anderson made important contributions to mathematical statistics and econometrics.
1961: Spacecraft Venera 1 launched. Venera will become the first man-made object to fly-by another planet by passing Venus (although it will lose contact with Earth and not send back any data).
1994: Mathematical physicist Charles Critchfield dies. Critchfield worked on the Manhattan Project, designing and testing the "Urchin" neutron initiator which provided the burst of neutrons that kick-started the nuclear detonation of the Fat Man weapon.
1787: Polymath Roger Joseph Boscovich dies. Boscovich was a physicist, astronomer, mathematician, philosopher, diplomat, poet, theologian, and Jesuit priest.
1805: Mathematician Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet born. Dirichlet will important make contributions to number theory, analysis, and mechanics. He will also be one of the first mathematicians to give the modern formal definition of a function.
1910: Physicist and inventor William Shockley born. He will share the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for the invention of the point-contact transistor.
1926: Nuclear physicist Fay Ajzenberg-Selove born. She will do important experimental work in nuclear spectroscopy of light elements, authoring annual reviews of the energy levels of light atomic nuclei.
1956: Mathematician and philosopher Jan Łukasiewicz dies. Łukasiewicz' innovative thinking about the principle of non-contradiction and the law of excluded middle extended the bounds of traditional propositional logic.
1963: Discovery of Canopic Snickers an unlicensed transdimensional corporation which manifests itself as an ancient Egyptian candy bar with alleged life extension properties.
1992: Mathematician and physicist Nikolay Bogolyubov dies. His method of teaching, based on creation of a warm atmosphere, politeness, and kindness, is renowned in Russia as the "Bogolyubov approach".
1404: Polymath Leon Battista Alberti born. Alberti will epitomize the Renaissance man: humanist author, artist, architect, poet, priest, linguist, philosopher, cryptographer.
1744: Mathematician John Hadley dies. Hadley laid claim to the invention of the octant, two years after Thomas Godfrey claimed the same. Hadley also developed ways to make precision aspheric and parabolic objective mirrors for reflecting telescopes.
1855: Texas is linked by telegraph to the rest of the United States, with the completion of a connection between New Orleans and Marshall, Texas.
1876: Alexander Graham Bell applies for a patent for the telephone, as does Elisha Gray.
1904: Engineer and inventor Charles William Oatley born. He will develop of one of the first commercial scanning electron microscopes.
1943: Mathematician David Hilbert dies. He discovered and developed a broad range of fundamental ideas in many areas, including invariant theory and the axiomatization of geometry.
1950: Physicist and engineer Karl Guthe Jansky dies. Jansky discovered radio waves emanating from the Milky Way while investigating sources of static that might interfere with radio voice transmissions, and is considered one of the founding figures of radio astronomy.
1990: The Voyager 1 spacecraft takes the Pale Blue Dot photograph of planet Earth from a distance of about 6 billion kilometers (3.7 billion miles, 40.5 AU). Earth's apparent size is less than a pixel.
2017: Routine annual steganographic analysis of famed illustration Alice and Niles Dancing unexpectedly reveals "at least a megabyte" of love letters between Gnomon algorithm engineers Alice Beta and Niles Cartouchian.
1564: Astronomer, physicist, engineer, philosopher, and mathematician Galileo Galilei born. He will be called the "father of modern physics."
1589: Astronomer, physicist, engineer, philosopher, mathematician, and crime-fighter Galileo Galilei uses Gnomon algorithm techniques to defeat the Forbidden Ratio in single combat.
1739: Mathematician, astronomer and poet Eustachio Manfredi dies. Manfredi's observations of asteroids provided early evidence, albeit unsought, of the revolution of the Earth around the Sun.
1861: Mathematician and philosopher Alfred North Whitehead born. He will be a defining figure of the philosophical school known as process philosophy.
1946: ENIAC, the first electronic general-purpose computer, is formally dedicated at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
1959: Physicist and academic Owen Willans Richardson dies. He won the 1928 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on thermionic emission, which led to Richardson's law.
1988: Theoretical physicist and academic Richard Feynman dies. For his contributions to the development of quantum electrodynamic he shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965.
2011: The Stardust spacecraft flies by comet Tempel 1.
1698: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer Pierre Bouguer born. He will be known as "the father of naval architecture".
1822: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician Francis Galton born.
1960: Mathematician and crime-fighter The Eel (left) stops aquatic cryptid and alleged supervillain Neptune Slaughter (right) from infiltrating Operation Sandblast, the U.S. Navy submarine circumnavigation of the globe.
1960: The U.S. Navy submarine USS Triton begins Operation Sandblast, setting sail from New London, Connecticut, to begin the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe.
1600: Dominican friar, philosopher, mathematician, poet, and cosmological theorist Giordano Bruno is burned at the stake.
1863: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley engages and sinks the Union warship USS Housatonic. This is the first known instance of a submarine engaging and sinking a warship.
1891: Mathematician Abraham Fraenkel born. He will contribute to axiomatic set theory, and publish a biography of Georg Cantor.
1953: Premiere of No Escape From Telephones, an American science fiction thriller film about a police officer (Dick Tracy) who must bring a deranged computer (HAL 9000) to justice.
1201: Polymath Nasir al-Din al-Tusi born. Tusi will be a mathematician, architect, philosopher, physician, scientist, and theologian; he will establish trigonometry as a mathematical discipline in its own right.
1745: Physicist and chemist Alessandro Volta born. Volta will conduct pioneering experiments in electricity and electrochemistry, discovering the electrical battery; he will also discover methane.
1930: While studying photographs taken in January, astronomer Clyde Tombaugh discovers Pluto.
1949: Singer-physicist J. R. Oppenheimer performs his hit song "Destroyer of Worlds" at the Grand Ole Opry, leading to his being summoned before the House Un-American Activities Committee.
1967: American physicist and academic J. Robert Oppenheimer dies. His achievements in physics included the Born–Oppenheimer approximation for molecular wavefunctions, work on the theory of electrons and positrons, the Oppenheimer–Phillips process in nuclear fusion, and the first prediction of quantum tunneling. Oppenheimer has been called the "father of the atomic bomb" for his role in the Manhattan Project.
1473: Mathematician and astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus born. He will formulate a model of the universe that places the Sun rather than the Earth at the center of the universe.
1616: The Inquisition asked a commission of theologians, known as qualifiers, about the propositions of the heliocentric view of the universe after Nicollo Lorin had accused Galileo Galilei of heretical remarks in a letter to his former student, Benedetto Castelli.
1919: Mathematician and academic Alexander Andreevich Samarskii born. Samarskii will contribute to applied mathematics, numerical analysis, mathematical modeling, and finite difference methods.
1946: Mathematician and academic Alan Turing presents the "Proposal for the Development in the Mathematics Division of an Automatic Computing Engine (ACE) to a meeting of the Executive Committee of the National Physical Laboratory (NPL); the proposal will be approved at a second meeting held a month later.
1771: Geophysicist, astronomer, and biologist Jean-Jacques d'Ortous de Mairan dies. His observations and experiments inspired the beginning of what is now known as the study of biological circadian rhythms.
1788: Physicist and academic Laura Bassi dies. She was one of the key figures in introducing Newton's ideas of physics and natural philosophy to Italy.
1972: Physicist and academic Maria Goeppert-Mayer dies. She developed a mathematical model for the structure of nuclear shells, for which she was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1963, which she shared with J. Hans D. Jensen and Eugene Wigner.
1974: Premiere of Tubular Elves, a short documentary film about how the album Tubular Bells accidentally recorded machine elves during UK military submarine communication tests.
1986: The Soviet Union launches its Mir spacecraft. Remaining in orbit for 15 years, it is occupied for ten of those years.
1591: Mathematician and engineer Girard Desargues born. He will be one of the founders of projective geometry.
1592: Canterbury scrying engine crashes, predicts faulty future; the resulting paradox will develop into an epidemic of capacitor failure by the early twenty-first century.
1677: Philosopher, scholar, and lens-grinder Baruch Spinoza dies. He laid the groundwork for the 18th-century Enlightenment and modern biblical criticism, including modern conceptions of the self and the universe.
1788: Scientist, inventor, and engineer Francis Ronalds born. He will be knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph.
1900: Astronomer Charles Piazzi Smyth dies. Smyth made innovations in astronomy, and made pyramidological and metrological studies of the Great Pyramid of Giza.
1926: Physicist and academic Heike Kamerlingh Onnes dies. He received widespread recognition for his work, including the 1913 Nobel Prize in Physics for "his investigations on the properties of matter at low temperatures which led, inter alia, to the production of liquid helium".
1632: Galileo's Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems is published.
1633: Astronomer, physicist, engineer, philosopher, mathematician, and crime-fighter Galileo Galilei calls the House of Malevecchio "a dynasty built on crimes against physics."
1817: Mathematician and academic Carl Wilhelm Borchardt born. He will contribute to arithmetic-geometric mean theory, continuing work by Gauss and Lagrange.
1987: Artist Andy Warhol dies. He was a leading figure in the Pop art movement.
1995: The Corona reconnaissance satellite program, in existence from 1959 to 1972, is declassified.
1855: Mathematician, astronomer, and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss dies. Gauss had an exceptional influence in many fields of mathematics and science and is ranked as one of history's most influential mathematicians.
1898: Émile Zola is imprisoned in France after writing "J'accuse", a letter accusing the French government of antisemitism and wrongfully imprisoning Captain Alfred Dreyfus.
1927: German theoretical physicist Werner Heisenberg writes a letter to fellow physicist Wolfgang Pauli, in which he describes his uncertainty principle for the first time.
1940: The ENIAC (SETI) program accidentally generates new class of crimes against mathematical constants.
1941: Plutonium is first produced and isolated by Dr. Glenn T. Seaborg.
1709: Inventor and artist Jacques de Vaucanson born. Vaucanson created impressive and innovative automata; was the first man to design an automatic loom; and built the first all-metal lathe.
1755: Artist and social critic William Hogarth’s satirical print, "An Election Entertainment," is published. It contains a Tory sign bearing the inscription "Give us our eleven days." This refers to the fact that eleven dates were removed from the calendar when England converted to the Gregorian calendar on September 14, 1752.
1810: Chemist, physicist, and philosopher Henry Cavendish dies. He discovered "inflammable air", later named hydrogen.
1842: Osman Hamdi Bey dies. He was an administrator, intellectual, art expert, painter, and archaeologist.
2001: Mathematician, engineer, and information scientist Claude Shannon dies. He is known as "the father of information theory".
2006: Premiere of America's Got Talents, a televised American weights and measures competition.
1598: John Dee demonstrates the solar eclipse by viewing an image through a pinhole. Two versions from Ashmole and Aubrey give different details of who was present. Dee's Diary only contains the notation, "the eclips. A clowdy day, but great darkness about 9 1/2 maine".
1857: Botanist and chemist Friedrich Reinitzer born. In late 1880s, experimenting with cholesteryl benzoate, Reinitzer discovered the properties of what would later be called liquid crystals; although the discovery attracted attention, interest soon faded as no practical uses were found at the time.
1971: Chemist and academic Theodor Svedberg dies. He was awarded the 1926 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his pioneering use of analytical ultracentrifugation to distinguish pure proteins from one another.
1972: Mathematician and academic Hugo Steinhaus dies. He discovered mathematician Stefan Banach, with whom he made notable contributions to functional analysis, including the Banach–Steinhaus theorem.
1999: Chemist Glenn T. Seaborg dies. He shared the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the synthesis, discovery, and investigation of transuranium elements.
1616: Physicist and engineer Galileo Galilei is formally banned by the Roman Catholic Church from teaching or defending the view that the earth orbits the sun.
1638: Mathematician and linguist Claude Gaspard Bachet de Méziriac dies. He was the earliest writer who discussed the solution of indeterminate equations by means of continued fractions. He also did work in number theory and found a method of constructing magic squares.
1786: Mathematician and politician François Arago born. He will observe that a rotating plate of copper tends to communicate its motion to a magnetic needle suspended over it, an effect which will later be known as eddy current.
1878: Astronomer and Jesuit priest Angelo Secchi dies. Secchi was a pioneer in astronomical spectroscopy, and was one of the first scientists to state authoritatively that the Sun is a star.
2005: Computer scientist Jef Raskin dies. He was a human–computer interface expert best known for conceiving and starting the Macintosh project for Apple in the late 1970s.
1539: Scholar, printer, and bookseller Franciscus Raphelengius born. Raphelengius will produce an Arabic-Latin dictionary, about 550 pages, which will be published posthumously in 1613 at Leiden — the first publication by printing press of a book-length dictionary for the Arabic language in Latin.
1735: Polymath John Arbuthnot dies. Arbuthnot invented the figure of John Bull.
1869: Physician, research scientist, and author Alice Hamilton born. Hamilton will be a leading expert in the field of occupational health and a pioneer in the field of industrial toxicology.
1881: Mathematician and philosopher L. E. J. Brouwer born. Brouwer will make contributions to topology, set theory, measure theory and complex analysis; and he will found the mathematical philosophy of intuitionism.
1940: Martin Kamen and Sam Ruben discover carbon-14. Its presence in organic materials is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and colleagues (1949) to date archaeological, geological and hydrogeological samples.
1982: The song "Back On the Supply Chain Gang" by Chrissie Hynde and the Department of Corrections reaches number one on the Gnomon Chronicles pop music chart.
1533: Philosopher and author Michel de Montaigne born. He will be one of the most significant philosophers of the French Renaissance, known for popularizing the essay as a literary genre.
1552: Clockmaker and mathematician Jost Bürgi born. He will be recognized during his own lifetime as one of the most excellent mechanical engineers of his generation.
1901: Chemist, biochemist, peace activist, author, and educator Linus Pauling born.
1967: Modern dance geology company Rhizolith Group debuts a new work, "Coriolis Force and Particulate Deposit Patterns in Paleoglacial Sedimentary Deposits".
1860: Inventor Herman Hollerith born. He will later be recognized as a pioneer of data processing.
March
1597: Priest and mathematician Jean-Charles della Faille born. He will publish a method for calculating the center of gravity of the sector of a circle.
1611: Mathematician John Pell born. He will expand the scope of algebra in the theory of equations.
1893: Electrical engineer Nikola Tesla gives the first public demonstration of radio in St. Louis, Missouri.
1954: Castle Bravo, a 15-megaton hydrogen bomb, is detonated on Bikini Atoll in the Pacific Ocean, resulting in the worst radioactive contamination ever caused by the United States.
1973: The Dark Side of the Moon released. It will go on to become one of the most successful albums ever.
1974: Signed first edition of Humpty Dumpty At Bat sells for "an undisclosed amount" to "a prominent Gnomon algorithm theorist from New Minneapolis, Canada during charity auction to benefit victims of crimes against physical constants.
1453: Doctor, astronomer, and astrologer Johannes Engel born. He will publish numerous almanacs, planetary tables, and calendars.
1791: Long-distance communication speeds up with the unveiling of a semaphore telegraph machine in Paris.
1931: Premiere of I Got Spaces by George Gershwin. "I got spaces / I got vectors / I got metrics / Who could ask for anything more?"
1972: The Pioneer 10 space probe is launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida with a mission to explore the outer planets.
1997: Mathematician Jordan Carson Mark dies. He oversaw the development of nuclear weapons for the US military, including the hydrogen bomb in the 1950s.
1845: Mathematician and philosopher Georg Cantor born. He will invent set theory, a fundamental area of mathematical inquiry.
1847: Engineer, inventor, and academic Alexander Graham Bell born. He will patent the telephone in 1876.
1849 – The Territory of Minnesota was created.
1898: Mathematician Emil Artin born. He will work on algebraic number theory, contributing to class field theory and a new construction of L-functions. He also contributed to the pure theories of rings, groups and fields.
1916: Mathematician and academic Paul Halmos born. He will make fundamental advances in the areas of mathematical logic, probability theory, statistics, operator theory, ergodic theory, and functional analysis (in particular, Hilbert spaces).
2017: Steganographic analysis of Peter Giblets illustration unexpectedly reveals "at least a terabyte of encrypted data, apparently a 'Best of Peter Giblets' compilation."
1702: Thief Jack Sheppard born. He will be arrested and imprisoned five times in 1724 but escape four times from prison, making him a notorious public figure, and wildly popular with the poorer classes.
1881: Physicist and chemist Richard C. Tolman born. He will make important contributions to theoretical cosmology in the years soon after Einstein's discovery of general relativity.
Stillsuit of the Night is a 1982 neo-noir psychological thriller film about a Suk doctor (Roy Scheider) who falls in love with a Fremen (Meryl Streep) who may be the psychopathic killer of one of his patients.
2007: Mathematician Hing Tong dies. He made contributions to algebraic topology, including a proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem.
2008: Game designer Gary Gygax dies. He co-created the pioneering role-playing game Dungeons & Dragons (D&D) with Dave Arneson.
1223 BC: Solar eclipse occurs; the event is recorded in a Syrian clay tablet, in the Ugaritic language.
1574: Mathematician William Oughtred born. He will invent the slide rule in 1622.
1616: Nicolaus Copernicus's book On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres is added to the Index of Forbidden Books 73 years after it was first published.
1827: Mathematician and astronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace dies. He made important contributions to mathematics, statistics, physics and astronomy.
1914: Nuclear physicist and academic He Zehui born. He Zehui will contribute to nuclear physics in Germany during World War II, and develop nuclear weapons for China during the 1960s.
2022: Release of Cthulhu Teaches Typing, an application software program designed to teach touch typing. Cthulhu Teaches Typing is not a game, rather a "system for teaching you how to type while yielding your sanity to the unimaginable terrors of the illimitable beyond".
1665: The first joint Secretary of the Royal Society, Henry Oldenburg, publishes the first issue of Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society.
1847: Mathematician Cesare Arzelà born. He will contribute to the theory of functions, notably his characterization of sequences of continuous functions.
1921: Physicist, mathematician, statistician, and meteorologist Akiva Yaglom born. He will contribute to statistical turbulence theory and random processes theory.
1939: Mathematician and academic Ferdinand von Lindemann dies. He proved (1882) that π (pi) is a transcendental number.
1765: Inventor Nicéphore Niépce born. He will invent heliography, a technique he will use to create the world's oldest surviving product of a photographic process.
1788: Physicist and academic Antoine César Becquerel born. He will pioneer the study of electric and luminescent phenomena.
1886: Mathematician and physicist G. I. Taylor born. He will make major contributions to fluid dynamics and wave theory.
1917: Pioneering computer scientist and programmer Betty Holberton born. She will be one of the six original programmers of ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer, and the inventor of breakpoints in computer debugging.
1950: Cold War: The Soviet Union issues a statement denying that Klaus Fuchs served as a Soviet spy.
2019: Steganographic analysis of Confessions of a Quantum Artist-Engineer (1) unexpectedly reveals "at least two-hundred and fifty-six kilobytes" of previously unknown Gnomon algorithm functions.
1618: Mathematician and astronomer Johannes Kepler discovers the third law of planetary motion.
1775: An anonymous writer, thought by some to be Thomas Paine, publishes "African Slavery in America", the first article in the American colonies calling for the emancipation of slaves and the abolition of slavery.
1879: Chemist and academic Otto Hahn born. He will pioneer the fields of radioactivity and radiochemistry, winning the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1944 for the discovery and the radiochemical proof of nuclear fission.
1914: Physicist, astronomer, and cosmologist Yakov Borisovich Zel'dovich born. He will play a crucial role in the development of the Soviet Union's nuclear bomb project, studying the effects of nuclear explosions.
Desperately Hanging Chad2001: Premiere of , an American comedy documentary film about punched cards and electoral reform.
1815: Electrical engineer and inventor Francis Ronalds describes the first battery-operated clock in the Philosophical Magazine.
1851: Physicist and chemist Hans Christian Ørsted dies. Ørsted discovered that electric currents create magnetic fields, which was the first connection found between electricity and magnetism.
1923: Theoretical physicist, theoretical chemist, and Nobel laureate Walter Kohn born. Kohn will develop density functional theory, which will make it possible to calculate quantum mechanical electronic structure by equations involving the electronic density.
1928: Engineer Gerald Bull born. Bull will attempt to build artillery guns capable of launching satellites into orbit.
1943: Computer scientist Jef Raskin born. Raskin will conceive and start the Macintosh project for Apple in the late 1970s.
1628: Physician and biologist Marcello Malpighi born. Malpighi will make pioneering contributions to anatomy, histology, physiology, embryology, and microscopy.
1876: Alexander Graham Bell makes the first successful telephone call by saying "Mr. Watson, come here, I want to see you."
1923: Physicist and academic Val Logsdon Fitch born. Fitch will share the 1980 Nobel Prize in Physics with co-researcher James Cronin for a 1964 experiment which proves that certain subatomic reactions do not adhere to fundamental symmetry principles (CP violation).
1961: Author, artist, and raconteur Karl Jones born. Jones will compile the Gnomon Chronicles, a work of fiction and non-fiction, fact and fantasy.
2006: The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter arrives at Mars.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates the eleventh anniversary of the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter arriving at Mars.
1437: Korean astronomers record the appearance of a new star, which shines for fourteen days before dimming. This astronomical event will later be known as Nova Scorpii AD 1437.
1811: Mathematician and astronomer Urbain Le Verrier born. Le Verrier will predict the existence and position of Neptune using only mathematics, an event which will be widely regarded as one of the most remarkable moments of 19th century science.
1822: Mathematician, economist, and academic Joseph Louis François Bertrand born. Bertrand will contribute to number theory, differential geometry, probability theory, economics and thermodynamics.
1823: Publication of Niles Cartouchian and Anton Rhodomunde Confront Gnotilus causes widespread debate about the role of private citizens in fighting crimes against mathematical constants.
1890: Engineer and academic Vannevar Bush born. Bush develop the Differential Analyzer, initiate the Manhattan Project and oversee government mobilization of scientific research during World War II, and make pioneering contributions to computer science.
1955: Biologist, pharmacologist, and botanist Alexander Fleming dies. Fleming discovered the enzyme lysozyme in 1923, and the world's first broadly effective antibiotic substance benzylpenicillin (Penicillin G) in 1928, for which he shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain.
1579: Humanist and philosopher Alessandro Piccolomini dies. Piccolomini promoted vernacular translations of Latin and Greek scientific and philosophical treatises.
1824: Physicist and academic Gustav Kirchhoff born. He will contribute to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy, and the emission of black-body radiation by heated objects.
1898: Mathematician and physicist Johann Jakob Balmer dies. He developed an empirical formula for the visible spectral lines of the hydrogen atom.
2016: Mathematician and economist Lloyd Shapley dies. He defined game theory as "a mathematical study of conflict and cooperation."
</nowiki>
1764: Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey born. His government will see the abolition of slavery in the British Empire.
1908: Chemist and US military officer Myrtle Bachelder born. Bachelder will be responsible for the analysis of the spectroscopy of uranium for the Manhattan Project during the Second World War. After the war, Bachelder will make pioneering contributions to metallochemistry.
1911: Mathematician Melvin Dresher (Dreszer) born. Dresher will contribute to game theory, co-developing the game theoretical model of cooperation and conflict known as the Prisoner's dilemma.
1998: Premiere of Armageddon Hard, an American planetary catastrophe heist film about a New York City detective (Bruce Willis) who must stop a rogue splinter asteroid (99942 Apophis-B) from destroying the earth.
2016: Philosopher, mathematician, and computer scientist Hilary Putnam dies. Putnam argued for the reality of mathematical entities, later espousing the view that mathematics is not purely logical, but "quasi-empirical".
1663: Otto von Guericke completes his book Ottonis de Guericke Experimenta Nova (ut vocantur) Magdeburgica de Vacuo Spatio, comprising his famed Magdeburg hemispheres demonstration, other vacuum-related research, and his pioneering investigation of static electricity.
1761: Mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher Pieter van Musschenbroek born. Van Musschenbroek will invent the first capacitor in 1746: the Leyden jar.
1879: Physicist, engineer, and academic Albert Einstein born. Einstein will develop the theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics (the other pillar: quantum mechanics).
1882: Mathematician and academic Wacław Sierpiński born. Sierpiński will make important contributions to set theory (research on the axiom of choice and the continuum hypothesis), number theory, theory of functions, and topology.
44 BC: Julius Caesar, Dictator of the Roman Republic, is stabbed to death by Marcus Junius Brutus, Gaius Cassius Longinus, Decimus Junius Brutus, and several other Roman senators on the Ides of March.
1897: Mathematician and academic James Joseph Sylvester dies. He made fundamental contributions to matrix theory, invariant theory, number theory, partition theory, and combinatorics.
1900: Mathematician and physicist Elwin Bruno Christoffel dies. He introduced fundamental concepts of differential geometry, opening the way for the development of tensor calculus, later providing the mathematical basis for general relativity.
1943: Sylvester Stewart born. Better known by his stage name Sly Stone, he is an American musician, songwriter, and record producer who is most famous for his role as front man for Sly and the Family Stone, playing a critical role in the development of soul, funk, rock, and psychedelia in the 1960s and 1970s.
1962: American physicist and academic Arthur Compton dies. He won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1927 for his 1923 discovery of the Compton effect, which demonstrated the particle nature of electromagnetic radiation.
1520: Mapmaker Martin Waldseemüller dies. Waldseemüller produced a globular world map and a large 12-panel world wall map using the information from Columbus and Vespucci's travels (Universalis Cosmographia), both bearing the first use of the name "America".
1750: Astronomer Caroline Herschel born. Herschel will discover several comets, including the periodic comet 35P/Herschel-Rigollet, which bears her name.
1838: American captain and mathematician Nathaniel Bowditch dies. Bowditch was a founder of modern maritime navigation; his book The New American Practical Navigator, first published in 1802, is still carried on board every commissioned U.S. Naval vessel.
1859: Physicist and academic Alexander Stepanovich Popov born. Popov will make pioneering contributions to the study of high frequency electrical phenomenoa; in Russia and some eastern European, he will be acclaimed as the inventor of radio.
1915: Mathematician and academic Kunihiko Kodaira born. Kodaira will make distinguished contributions algebraic geometry and the theory of complex manifolds, winning the Fields medal in 1954.
1782: Mathematician and physicist Daniel Bernoulli dies. Bernoulli is particularly remembered for his applications of mathematics to mechanics, especially fluid mechanics, and for his pioneering work in probability and statistics.
1853: Physicist and mathematician Christian Doppler dies. Doppler proposed the principle (now known as the Doppler effect) that the observed frequency of a wave depends on the relative speed of the source and the observer. He used this concept to explain the color of binary stars.
2007: Mathematician and computer scientist John Backus dies. Backus invented the Backus–Naur form (BNF), a widely used notation technique for defining formal language syntax.
1640: Painter, mathematician, astronomer, and architect Philippe de La Hire born. La Hire will be the favorite pupil of Desargues, and develop conic sections and epicycloids based on the teaching of Desargues.
1727: Scientist and watchmaker Ferdinand Berthoud born. Berthoud will serve as Horologist-Mechanic by appointment to the King and the Navy, leaving an exceptionally broad body of work, notable for excellent sea chronometers.
1871: Mathematician and academic Augustus De Morgan dies. De Morgan formulated two laws, now De Morgan's Laws, pertaining to mathematical induction: (1) the negation of a disjunction is the conjunction of the negations; (2) the negation of a conjunction is the disjunction of the negations.
1927: Physicist, mathematician, and activist William C. Davidon born. Davidon will develop the first quasi-Newton algorithm, now known as the Davidon–Fletcher–Powell formula.
1927: Journalist, writer, literary editor, and actor George Plimpton born. Plimpton will be famous for "participatory journalism": competing in professional sporting events, playing with the New York Philharmonic Orchestra, performing a circus trapeze act, and then recording the experience from the point of view of an amateur.
1610: Painter Hasegawa Tōhaku dies. Hasegawa Tōhaku founded the Hasegawa school and one of the great painters of the Azuchi–Momoyama period (1573-1603). He is best known for his byōbu folding screens, such as Pine Trees and Pine Tree and Flowering Plants.
1816: Physician and activist Filippo Mazzei dies. Mazzei acted as an arms purchasing agent for Virginia during the American Revolutionary War.
1928: Physicist and geophysicist Emil Wiechert dies. Wiechert made contributions to both fields, including presenting the first verifiable model of a layered structure of the Earth, and being among the first to discover the electron.
1978: Mathematician Gaston Maurice Julia dies. Julia devised the formula for the Julia set, which consists of values such that an arbitrarily small perturbation can cause drastic changes in the sequence of iterated function values. Julia's work later proved foundational to chaos theory.
1987: Physicist and academic Louis de Broglie dies. De Broglie postulated the wave nature of electrons and suggested that all matter has wave properties. He won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1929, after the wave-like behavior of matter was first experimentally demonstrated in 1927.
1726/27: Isaac Newton dies. He is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time and a key figure in the scientific revolution.
1878: Physician and physicist Julius Robert von Mayer dies. In 1842, Mayer described the vital chemical process now referred to as oxidation as the primary source of energy for any living creature. His achievements were overlooked and priority for the discovery of the mechanical equivalent of heat was attributed to James Joule in the following year.
1914: Jazz drummer and theoretical physicist Albert Einstein develops a new drum fill which anticipates his general theory of relativity.
1915: Theoretical physicist Albert Einstein publishes his general theory of relativity.
1962: Sociologist and author C. Wright Mills dies. He was published widely in popular and intellectual journals, advocating public and political engagement over disinterested observation.
1993: Physicist and academic Polykarp Kusch dies. Kusch made a accurate determination that the magnetic moment of the electron is greater than its theoretical value, thus leading to reconsideration of—and innovations in—quantum electrodynamics; he was award the 1955 Nobel Prize in Physics for this accomplishment.
1768: Mathematician and physicist Joseph Fourier born. Fourier will initiate the investigation of Fourier series and their applications to problems of heat transfer and vibrations.
1884: Mathematician George David Birkhoff born. Birkhoff will become one of the most important leaders in American mathematics of his generation.
1924: Physicist Harry Lehmann born. Lehmann will contribute to the LSZ reduction formula and the Källén–Lehmann spectral representation.
1928: Charles Lindbergh is presented with the Medal of Honor for the first solo trans-Atlantic flight.
1965: NASA launches Ranger 9, the last in a series of unmanned lunar space probes.
1868: Physicist Robert Andrews Millikan born. Millikan will win the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1923 for the measurement of the elementary electronic charge and for his work on the photoelectric effect.
1909: Physicist Nathan Rosen born. Rosen will develop the idea of the Einstein–Rosen bridge, later named the wormhole.
1990: Engineer Gerald Bull assassinated. He attempted to build artillery guns which could launch satellites into orbit.
2011: Computer scientist Philippe Flajolet dies. Flajolet contributed to general methods for analyzing the computational complexity of algorithms, including the theory of average-case complexity.
2006: Premiere of An Alien Home Companion, an American science fiction comedy film about the behind-the-scenes activities at a long-running public radio show which encounters an aggressive alien guest star. Director: Robert Altman.
1749: Mathematician and astronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace born. He will make important contributions to mathematics, statistics, physics and astronomy.
1882: Mathematician Emmy Noether born. Noether will make landmark contributions to abstract algebra and theoretical physics.
1897: Mathematician, physicist, and academic John Lighton Synge born. He will be a prolific author and influential mentor, and be credited with the introduction of a new geometrical approach to the theory of relativity.
1945: First publication of Middle-earth Farm, an allegorial novel by George Orwell and J.R.R. Tolkien.
1977: The first of The Nixon Interviews (12 will be recorded over four weeks) are videotaped with British journalist David Frost interviewing former United States President Richard Nixon about the Watergate scandal and the Nixon tapes.
2001: The Mir spacecraft is de-orbited. It had been in orbit for 15 years, it was occupied for ten of those years.
<gallery> File:Joseph Priestley.jpg|link=Joseph Priestley (nonfiction)|1733: Chemist, philosopher, educator, and clergyman Joseph Priestley born. He will be historically been credited with the discovery of oxygen, having isolated it in its gaseous state, but his determination to defend phlogiston theory and to reject what would become the chemical revolution will leave him isolated within the scientific community.
File:Alexander Stepanovich Popov.jpg|link=Alexander Stepanovich Popov (nonfiction)|1896: Russian physicist Alexander Stepanovich Popov uses radio waves to transmit a message between different campus buildings in St Petersburg.
File:Paul Lorenzen.jpg|link=Paul Lorenzen (nonfiction)|1915: Mathematician and philosopher Paul Lorenzen born. Lorenzen will found the Erlangen School (with Wilhelm Kamlah), and invent game semantics (with Kuno Lorenz).
File:Myoglobin John Kendrew.jpg|link=John Kendrew (nonfiction)|1917: Biochemist and crystallographer John Kendrew born. Kendrew will share the 1962 Nobel Prize for chemistry with Max Perutz for determining the atomic structures of proteins using X-ray crystallography.
File:Ranger spacecraft.jpg|link=Ranger 9 (nonfiction)|1965: NASA spacecraft Ranger 9, equipped to convert its signals into a form suitable for showing on domestic television, brings images of the Moon into ordinary homes before crash landing.
<gallery>
1655: Saturn's largest moon, Titan, is discovered by Christiaan Huygens.
1857: Printer, bookseller, and inventor Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville is receives a patent for the phonoautograph, which records an audio signal as a photographic image.
1860: Surgeon and gentleman scientist James Braid dies. He was an important and influential pioneer of hypnotism and hypnotherapy.
1862: Mathematician and engineer Philbert Maurice d’Ocagne born. He will found the field of nomography, the graphic computation of algebraic equations, on charts which he will called nomograms.
1923: Art critic and alleged time-traveler The Eel escapes from the Nacreum, a transdimensional prison made of artificially intelligent, self-assembling nacre.
1773: American captain and mathematician Nathaniel Bowditch born. He will be a founder of modern maritime navigation; his book The New American Practical Navigator, first published in 1802, will be carried on board every commissioned U.S. Naval vessel.
1793: Physician and engineer John Mudge dies. He was the first self-proclaimed civil engineer, and often regarded as the "father of civil engineering".
1851: Mathematician George Chrystal born. He will be awarded a Gold Medal from the Royal Society of London (confirmed shortly after his death) for his studies of seiches (wave patterns in large inland bodies of water).
1913: Mathematician and academic Paul Erdős born. He will firmly believe mathematics to be a social activity, living an itinerant lifestyle with the sole purpose of writing mathematical papers with other mathematicians.
1598: Engraver, goldsmith, and publisher Theodor de Bry dies. de Bry gained fame for his depictions of early European expeditions. Although de Bry never visited the Americas, most of his books are based on first-hand observations by explorers.
1845: Engineer and physicist Wilhelm Röntgen born. He will win the first Nobel Prize in Physics, for the discovery of X-rays.
1923: Chemist and physicist James Dewar dies. He invented the vacuum flask, which he used in conjunction with extensive research into the liquefaction of gases.
1925: Mathematician Carl Gottfried Neumann dies. He will studied physics with his father, and later worked as a mathematician, dealing almost exclusively with problems arising from physics.
2011: Artist George Tooker dies. Tooker's paintings depicted his subjects naturally, as in a photograph, but the images used flat tones, an ambiguous perspective, and alarming juxtapositions to suggest an imagined or dreamed reality.
1794: Philosopher, mathematician, and early political scientist Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet dies. His ideas and writings were said to embody the ideals of the Age of Enlightenment and rationalism, and remain influential to this day.
1928: Mathematician and theorist Alexander Grothendieck born. He will become the leading figure in the creation of modern algebraic geometry.
1933: The Imperial Airways biplane City of Liverpool crashes after a fire break out. Sabotage will be suspected due the suspicious behaviors of a passenger who seemingly jumped from the aircraft before it crashed.
1979: A coolant leak in the Unit 2 nuclear reactor of the Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station leads to core overheating and a partial core meltdown.
1992: Physicist and academic John D. Strong dies. Strong contributed to optical physics: he was the first to detect water vapor in the atmosphere of Venus, and he developed optical devices and materials including improved telescope mirrors and anti-reflective coatings.
1780: Adventurer Jørgen Jørgensen born. He will sail to Iceland, declaring the country independent from Denmark and pronouncing himself its ruler, intending to found a new republic following the United States of America and France.
1873: Mathematician and academic Tullio Levi-Civita born. Levi-Civita will gain fame for his work on absolute differential calculus (tensor calculus) and its applications to the theory of relativity, and make significant contributions in other areas.
1873: Physicist and priest Francesco Zantedeschi dies. Zantedeschi was among the first to recognize the marked absorption by the atmosphere of red, yellow, and green light. He also thought that he had detected, in 1838, a magnetic action on steel needles by ultraviolet light, anticipating later discoveries connecting light and magnetism.
1896: Mathematician Wilhelm Ackermann born. Ackermann will discover the Ackermann function, an important example in the theory of computation.
2003: Physician and microbiologist Carlo Urbani dies of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Urbani identifed SARS as a new and dangerously contagious viral disease, and his early warning to the World Health Organization (WHO) triggered a swift and global response credited with saving numerous lives.
1599: Mathematician Adam Ries dies. Reis wrote textbooks for practical mathematics, promoting the advantages of Arabic/Indian numerals over Roman numerals.
1606: Mathematician and astronomer Vincentio Reinieri born. Reinieri revised and finished the work of Galileo, who before his death placed all of the papers containing his observations and calculations in Reinieri's hands.
1811: Chemist and academic Robert Bunsen born. Bunsen will investigate emission spectra of heated elements, and discover caesium (in 1860) and rubidium (in 1861) with the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff.
1886: Mathematician, philosopher, and logician Stanisław Leśniewski born. Leśniewski will posit three nested formal systems, to which he will give the Greek-derived names of protothetic, ontology, and mereology.
1892: Mathematician and academic Stefan Banach born. Banach will be one of the founders of modern functional analysis.
1596: Mathematician and philosopher René Descartes born. Descartes will be remembered as the father of modern Western philosophy.
1730: Mathematician and theorist Étienne Bézout born. Bezout's Théorie générale des équations algébriques will contain much new and valuable matter on the theory of elimination and symmetrical functions of the roots of an equation.
1877: Mathematician and philosopher Antoine Augustin Cournot dies. Cournot introduced the ideas of functions and probability into economic analysis.
1943: Publication of The Glass Tweet Game, the last full-length tweet-chain by author and alleged time-traveler Hermann Hesse.
1970: The spacecraft Explorer 1 re-enters the Earth's atmosphere after 12 years in orbit. Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the United States.
2001: Physicist and academic Clifford Shull dies. Shull shared the 1994 Nobel Prize in Physics with Bertram Brockhouse for the development of the neutron scattering technique.
April
1776: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Sophie Germain born. Germain's work on Fermat's Last Theorem will provide a foundation for mathematicians exploring the subject for hundreds of years after.
1898: Mathematician and anthropologist William James Sidis born. Sidis will become famous first for his precocity and later for his eccentricity and withdrawal from public life.
1973: Mathematician Robin Farquharson dies. Farquharson wrote an influential analysis of voting systems in his doctoral thesis, later published as Theory of Voting.
2003: Steve Bellovin publishes Request for Comment 5314, subsequently known as the evil bit protocol, a humorous April Fool's Day proposal.
1618: Mathematician and physicist Francesco Maria Grimaldi born. Grimaldi, along with Riccioli, will investigate the free fall of objects, confirming that the distance of fall was proportional to the square of the time taken.
1902: Graphic designer and typographer Jan Tschichold born. Tschichold will become a leading advocate of Modernist design, but later condemn Modernist design in general as being authoritarian and inherently fascistic.
1915: Nuclear physicist Donald J. Hughes born. Hughes will be one of the signers of the Franck Report in June, 1945, recommending that the United States not use the atomic bomb as a weapon to prompt the surrender of Japan in World War II.
1923: Polymath George Spencer-Brown born. Spencer-Brown will write the unorthodox and influential Laws of Form, calling it the "primary algebra" and the "calculus of indications".
1979: A Soviet bio-warfare laboratory at Sverdlovsk accidentally releases airborne anthrax spores, killing as many as a hundred people. Soviet authorities will cover up the event; all medical records of the victims will be removed in order to hide serious violations of the Biological Weapons Convention.
1693: Carpenter and clockmaker John Harrison born. He will invent a marine chronometer, a long-sought-after device for solving the problem of calculating longitude while at sea.
1827: Physicist, musician, and academic Ernst Chladni dies. He has been called both the father of acoustics and the father of meteoritics.
1907: Cryptanalyst and mathematician Solomon Kullback born. Krullback will begin his career with the US Army's Signal Intelligence Service (SIS) in the 1930s; when the National Security Agency (NSA) is formed in 1952, Rowlett will become chief of cryptanalysis, overseeing the research and development of computerized cryptanalysis.
1995: Mathematician and checkers player Marion Tinsley dies. Tinsley was "to checkers what Leonardo da Vinci was to science, what Michelangelo was to art and what Beethoven was to music."
1998: Mathematician and academic Mary Cartwright dies. She did pioneering work in chaos theory.
1807: Astronomer, freemason, and writer Joseph Jérôme Lefrançois de Lalande dies. As a lecturer and writer Lalande helped popularize astronomy. His planetary tables were the best available up to the end of the 18th century.
1809: Mathematician Benjamin Peirce born. Peirce will make contributions to celestial mechanics, statistics, number theory, algebra, and the philosophy of mathematics; he will become known for the statement that "Mathematics is the science that draws necessary conclusions".
1826: Electrical engineer Zénobe Gramme born. Gramme will invent the first usefully powerful electric motor.
1842: Mathematician Édouard Lucas born. Lucas will study the Fibonacci sequence; the related Lucas sequences and Lucas numbers will be named after him.
1919: Chemist and physicist William Crookes dies. Crookes was a pioneer of vacuum tube technology, developing the partially evacuated Crookes tube circa 1869-1875.
1923: Mathematician and philosopher John Venn dies. Venn invented the Venn diagram, now widely used set theory, probability, logic, statistics, and computer science.
1941: Chemist Lazăr Edeleanu dies. Edeleanu invented the modern method of refining crude oil, was the first chemist to synthesize amphetamine.
1976: Engineer and theorist Harry Nyquist dies. Nyquist did early theoretical work on determining the bandwidth requirements for transmitting information, laying the foundations for later advances by Claude Shannon, which led to the development of information theory.
1977: Game designer, shop keeper, and outsider mathematician Dave the Gamer announces "Buy n, get n free" sale on all lucky dice in the store.
1523: Cryptographer and diplomat Blaise de Vigenère born. The Vigenère cipher will be misattributed to him; Vigenère himself will devise a different, stronger cipher.
1622: Mathematician and scientist Vincenzo Viviani born. In 1660, Viviani and Giovanni Alfonso Borelli will conduct an experiment to determine the speed of sound. Timing the difference between the seeing the flash and hearing the sound of a cannon shot at a distance, they will calculate a value of 350 meters per second (m/s), considerably better than the previous value of 478 m/s obtained by Pierre Gassendi.
1827: Surgeon and scientist Joseph Lister born. He will pioneer antiseptic surgery, performing the first antiseptic surgery in 1865.
1869: Physicist, mathematician, and engineer Sergey Chaplygin born. He will be known for mathematical formulas such as Chaplygin's equation, and for a hypothetical substance in cosmology called Chaplygin gas, named after him.
1900: Mathematician, economist, and academic Joseph Louis François Bertrand dies. He worked in the fields of number theory, differential geometry, probability theory, economics and thermodynamics.
Town Without Jetty wins the Outstanding Civil Engineering Achievement (OCEA) Award for Best Marine Civil Engineering Film of the Year.
1528: Painter, engraver, and mathematician Albrecht Dürer dies. Dürer is regarded as the greatest German Renaissance artist: his vast body of work will include altarpieces and religious works, numerous portraits and self-portraits, and copper engravings.
1793: During the French Revolution, the Committee of Public Safety becomes the executive organ of the republic.
1829: Mathematician and theorist Niels Henrik Abel dies. Abel made pioneering contributions in a variety of fields, including the discovery of Abelian functions, and the first complete proof demonstrating the impossibility of solving the general quintic equation in radicals.
1926: American comic book artist Gil Kane born. Kane will pioneer graphic novels with his books His Name is...Savage (1968) and Blackmark (1971).
1992: Writer Isaac Asimov dies. Asimov is one of the "Big Three" science fiction writers of his generation.
1811: Astronomer, mathematician, and philosopher Hasan Tahsini born. He will become one of the most prominent scholars of the Ottoman Empire of the 19th century.
1899: Physicist and academic Petrus Leonardus Rijke dies. He explored the physics of electricity, and is known for the Rijke tube (which turns heat into sound, by creating a self-amplifying standing wave).
2014: Mathematician and academic Tim Cochran born. He will contribute to topology, especially low-dimensional topology, the theory of knots and links and associated algebra.
2009: Game designer Dave Arneson dies. He co-created the pioneering role-playing game Dungeons & Dragons with Gary Gygax.
1541: Physician and archaeologist Michele Mercati born. Mercati will be one of the first scholars to recognize prehistoric stone tools as human-made rather than natural or mythologically created thunderstones.
1732: Inventor, astronomer, mathematician, clockmaker, and surveyor David Rittenhouse born. Rittenhouse will become the first Director of the United States Mint, hand-striking the new nation's first coins.
1803: Mathematician Louis François Antoine Arbogast dies. Arbogast was the first writer to separate the symbols of operation from those of quantity. He wrote on series and the derivatives known by his name.
1903: Mathematician Marshall Harvey Stone born. Stone will contribute to real analysis, functional analysis, topology, and the study of Boolean algebra structures.
1911: Physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes, discoverer of superconductivity, makes a terse entry in his notebook: Kwik nagenoeg nul ("Mercury[’s resistance] practically zero [at 3 K].").
1770: Physicist and academic Thomas Johann Seebeck born. Seebeck will discover the thermoelectric effect.
1860: On his phonautograph machine, Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville makes the oldest known recording of an audible human voice. A visual recording of audio data, it will first be played back in 2008.
1865: Mathematician and electrical engineer Charles Proteus Steinmetz born. Steinmetz will foster the development of alternating current, formulating mathematical theories which will advance the expansion of the electric power industry in the United States.
1978: Musician and alleged math criminal Skip Digits performs at the Kennedy Center for the Arts.
1762: Physicist and academic Giovanni Aldini born. Aldini will contribute to galvanism, anatomy and its medical applications, the construction and illumination of lighthouses, and the mitigation of the destructive effects of fire.
1813: Mathematician and astronomer Joseph-Louis Lagrange dies. He made significant contributions to the fields of analysis, number theory, and both classical and celestial mechanics.
1818: Lecturer John Cleves Symmes, Jr. publishes Circular No. 1, a variant of the Hollow Earth Theory, with openings to the inner world at the poles.
1928: The Pineapple Primary in Illinois, the culmination of a political campaign which was marked by numerous acts of violence, mostly in Chicago and elsewhere in Cook County. In the six months prior to the primary election, 62 bombings took place in the city, and at least two politicians were killed.
1967: End of the Nth Country Experiment, in which three recent young physicists who had just received their PhDs, though had no prior weapons experience, to develop a working nuclear weapon design using only unclassified information, and with basic computational and technical support.
1789: Clockmaker Jean-André Lepaute dies. He was an innovator, introducing numerous improvements in clockmaking, especially his pin-wheel escapement, and his clockworks in which the gears are all in the horizontal plane.
1798: Physicist and academic Macedonio Melloni born. Melloni will demonstrate that radiant heat has physical properties similar to those of light.
1914: Mathematician Dorothy Lewis Bernstein born. She will be the first woman to be elected president of the Mathematics Association of America.
1962: Physicist and academic Ukichiro Nakaya dies. He created the first artificial snowflakes.
1980: Viking program: After operating on the surface of Mars for 1316 days (1281 sols), the Viking 2 lander is turned off when its batteries fail.
2017: Dennis Paulson calls for a moment of silence in recognition of the thirty-seventh anniversary of NASA switching off the Viking 2 spacecraft.
1817: Astronomer Charles Messier dies. He published an astronomical catalogue consisting of nebulae and star clusters that came to be known as the 110 "Messier objects".
1852: Mathematician and academic Ferdinand von Lindemann born. He will prove (1882) that π (pi) is a transcendental number.
1960: Nuclear physicist Donald J. Hughes dies. Hughes was one of the signers of the Franck Report in June, 1945, recommending that the United States not use the atomic bomb as a weapon to prompt the surrender of Japan in World War II.
1961: Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin becomes the first human to travel into outer space and perform the first manned orbital flight (Vostok 1).
1984: United States Navy Admiral Edwin Thomas Layton dies. Layton served as a Naval intelligence officer before and during World War II.
2020: Math photographer Cantor Parabola wins Pulitzer Prize for series of exo-temporal photographs of Minicon 55 in 2021.
1771: Engineer and explorer Richard Trevithick born. Trevithick will be an early pioneer of steam-powered road and rail transport, developing the first high-pressure steam engine, and building the first full-scale working railway steam locomotive.
1889: Cryptologist and author Herbert Yardley born. Yardley will found and lead the Black Chamber, a secret American government cryptographic organization which will break Japanese diplomatic codes, furnishing American negotiators with significant information during the Washington Naval Conference of 1921-1922.
1905: Engineer Charles Renard commits suicide. Renard pioneer the design and construction of airships. He also proposed a set of preferred numbers now known as the Renard series.
1927: Theoretical physicist Mendel Sachs born. Sachs' work will include the proposal of a unified field theory that brings together the weak force, strong force, electromagnetism, and gravity.
1953: CIA director Allen Dulles authorizes the secret drug research program Project MKUltra, intended to identify and develop drugs and procedures to be used in interrogations and torture, in order to weaken the individual and force confessions through mind control.
1126: Polymath Ibn Rushd (Averoess) born. He will write on logic, Aristotelian and Islamic philosophy, theology, Islamic jurisprudence, psychology, politics, music theory, geography, mathematics, and the mediæval sciences of medicine, astronomy, physics, and celestial mechanics.
1527: Cartographer and geographer Abraham Ortelius born. Ortelius will create the first modern atlas, the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. He will also be one of the first to imagine that the continents were joined together before drifting to their present positions.
1629: Mathematician, astronomer, and physicist Christiaan Huygens born. He will be a leading scientist of his time.
1659: Proposals to flood the Sistine chapel "are equally useless to Science and Art alike," writes Christiaan Huygens in a private letter to Pope Alexander VII.
1935: Mathematician Emmy Noether dies. She made landmark contributions to abstract algebra and theoretical physics.
1964: Mathematician and theorist Tatyana Afanasyeva dies. She contributed to statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics, and to mathematical education in the Netherlands.
1452: Polymath Leonardo da Vinci born. His areas of interest will include painting, sculpting, architecture, invention, science, music, mathematics, engineering, literature, anatomy, geology, astronomy, botany, writing, history, and cartography.
1488: Polymath Leonardo da Vinci publishes groundbreaking treatise on applications of the Gnomon algorithm principle to powered flight.
1552: Mathematician and astronomer Pietro Cataldi born. Cataldi will contribute to the development of continued fractions and a method for their representation; he will also discover the sixth and seventh perfect numbers by 1588.
1707: Mathematician and physicist Leonhard Euler born. He will make important and influential discoveries in many branches of mathematics, and will introduce much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, such as the notion of a mathematical function.
1764: Astronomer and mathematician Peder Horrebow dies. he invent a way to determine a place's latitude from the stars.
1878: Physicist Ernst Ruhmer born. Ruhmer will invent applications for the light-sensitivity properties of selenium, including wireless telephony using line-of-sight optical transmissions, sound-on-film audio recording, and television transmissions over wires.
1911: Physicist Johannes Bosscha Jr. dies. Bosscha made important investigations on galvanic polarization and the rapidity of sound waves; he was one of the first (1855) to suggest the possibility of sending two messages simultaneously over the same wire.
1495: Mathematician and astronomer Petrus Apianus born. Apianus' works on cosmography, Astronomicum Caesareum (1540) and Cosmographicus liber (1524), will be extremely influential in his time.
1682: Mathematician John Hadley born. Hadley will lay claim to the invention of the octant, two years after Thomas Godfrey claims the same. Hadley will also develope ways to make precision aspheric and parabolic objective mirrors for reflecting telescopes.
1958: The United States military announces that the search for hydrogen bomb known as the Tybee Bomb was unsuccessful.
2008: Mathematician Edward Lorenz dies. Lorenz introduced the strange attractor notion, and coined the term butterfly effect.
1598: Priest and astromomer Giovanni Battista Riccioli born. Riccioli will experiment with pendulums and falling bodies, discuss arguments concerning the motion of the Earth, and introduce the current scheme of lunar nomenclature.
1938: Philosopher and author Kerry Wendell Thornley born. Thornley will write a manuscript, The Idle Warriors, about his acquaintence Lee Harvey Oswald.
1961: Bay of Pigs Invasion: A group of Cuban exiles financed and trained by the CIA lands at the Bay of Pigs in Cuba with the aim of ousting Fidel Castro.
1969: Sirhan Sirhan is convicted of assassinating Robert F. Kennedy.
1996: Mathematician, author, and poet Piet Hein dies. Hein proposed the use of superellipses in architecture; superellipses subsequently became the hallmark of modern Scandinavian architecture.
1796: Physicist Johan Carl Wilcke dies. Wilcke invented the electrophorus, and calculated the latent heat of ice.
1873: Chemist and academic Justus von Liebig dies. Von Liebeg made pioneering contributions to organic chemistry, especially agricultural and biological chemistry; he is known as the "Father of the fertilizer industry".
1907: Jazz drummer and theoretical physicist Albert Einstein hosts an all-star benefit concert to raise money for the rebuilding of San Francisco.
1955: Physicist, engineer, and academic Albert Einstein dies. Einstein developed the theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics (alongside quantum mechanics).
2011: Mathematician Curt Meyer dies. Meyer made notable contributions to number theory, including an alternative solution to the class number 1 problem, building on the original Stark–Heegner theorem.
1567: Mathematician, monk, and academic Michael Stifel dies. Stifel was an Augustinian who became an early supporter of Martin Luther.
1860: On his phonautograph machine, Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville makes the oldest known recording of an audible human voice.
1882: Large herd of Flying bison (Bison pterobonasus) swarms from Saint Paul, Minnesota to New Minneapolis, Canada.
1912: Chemist Glenn T. Seaborg born. Seaborg will share the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the synthesis, discovery, and investigation of transuranium elements.
2016: Theoretical physicist, theoretical chemist, and Nobel laureate Walter Kohn dies. Kohn developed density functional theory, which makes it possible to calculate quantum mechanical electronic structure by equations involving the electronic density.
2019: The Minicon 54 Great Nerd Giveaway begins. By the end of Minicon 54, hundreds of nerd items will have found new homes, generating an abundance of fun in the process.
1902: Pierre and Marie Curie refine radium chloride.
1918: Physicist and academic Karl Ferdinand Braun dies. Braun contributed significantly to the development of radio and television technology, sharing the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Guglielmo Marconi "for their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy".
1932: Mathematician Giuseppe Peano dies. He did pioneering work in mathematical logic and set theory.
1945: Mathematician Georg Feigl dies. He worked on the foundations of geometry and topology, studying fixed point theorems for n-dimensional manifolds. Feigl was one of the initial authors of the Mathematisches Wörterbuch.
1961: Failure of the Bay of Pigs Invasion of US-backed Cuban exiles against Cuba.
1962: Traces of Clandestiphrine residue are detected at the Bay of Pigs, raising questions about CIA involvement with transdimensional drugs.
1552: Mathematician and astronomer Petrus Apianus dies. His works on cosmography, Astronomicum Caesareum (1540) and Cosmographicus liber (1524), were extremely influential in his time.
1774: Physicist, astronomer, and mathematician Jean-Baptiste Biot born. He will establish the reality of meteorites, make an early balloon flight, and study the polarization of light.
1822: Priest and inventor Hannibal Goodwin born. He will invent and patent rolled celluloid photographic film.
1900: The Waking of the Slate ceremony is louder than ever.
1934: The "Surgeon's Photograph", the most famous photo allegedly showing the Loch Ness Monster, is published in the Daily Mail. (It will be revealed as a hoax in 1999.)
1965: Physicist and academic Edward Victor Appleton dies. Appleton made pioneering contributions to radiophysics, and was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1947 for his seminal work proving the existence of the ionosphere during experiments carried out in 1924.
1592: Minister, scholar, astronomer, mathematician, cartographer, and inventor Wilhelm Schickard born. He will design and build calculating machines, and invent techniques for producing improved maps.
1904: American physicist and academic J. Robert Oppenheimer born. His achievements in physics will include the Born–Oppenheimer approximation for molecular wavefunctions, and the first prediction of quantum tunneling. Oppenheimer will be called the "father of the atomic bomb" for his role in the Manhattan Project.
1953: Singer-physicist J. R. Oppenheimer performs his hit song "Destroyer of Worlds" at the Grand Ole Opry, leading to his being summoned before the House Un-American Activities Committee.
1954: Red Scare: Witnesses begin testifying and live television coverage of the Army–McCarthy hearings begins.
1970: The first Earth Day is celebrated.
1978: Optical fiber is first used to carry live telephone traffic.
1858: Physicist and academic Max Planck born. He will make many contributions to theoretical physics, earning fame as the originator of quantum theory.
1869: Inventor Edward Hugh Hebern born. He will be a pioneer of rotor encryption machines.
1933: Computer scientist, mathematician, and engineer Annie Easley born. She will be a leading member of the team which develops software for the Centaur rocket stage, and one of the first African-Americans to work as a computer scientist at NASA.
1941: Computer programmer and engineer Ray Tomlinson born. He will implement the first email system on the the ARPANET system, including the "@" separator which is still in use today.
1967: Soviet space program: Soyuz 1 (Russian: Союз 1, Union 1) a manned spaceflight carrying cosmonaut Colonel Vladimir Komarov is launched into orbit.
World War X is a 2013 documentary film about the Biblical story of Moses (Brad Pitt), a United Nations locust researcher adopted by Pharaoh (Charlton Heston) who accidentally releases a religious zombie pandemic.
1656: Mathematician and physicist Thomas Fincke dies. He introduced the modern names of the trigonometric functions tangent and secant.
1914: The Franck–Hertz experiment, a pillar of quantum mechanics, is presented to the German Physical Society.
1967: Cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov dies in Soyuz 1 when its parachute fails to open. He is the first human to die during a space mission.
1710: Astronomer, instrument maker, and author James Ferguson born.
1817: Printer, bookseller, and inventor Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville born. He will invent the phonoautograph, which records an audio signal as a photographic image.
1874: Businessman and inventor Guglielmo Marconi born. He will share the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Karl Ferdinand Braun "in recognition of their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy".
1903: Mathematician and academic Andrey Kolmogorov born. He will make significant contributions to the mathematics of probability theory, topology, intuitionistic logic, turbulence, classical mechanics, algorithmic information theory and computational complexity.
1960: Mathematician, art critic, and alleged time-traveller The Eel stops aquatic cryptid and alleged supervillain Neptune Slaughter from destroying the United States Navy submarine USS Triton.
1960: The United States Navy submarine USS Triton completes Operation Sandblast, the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe.
1558: Physician Jean Fernel dies. Fernel ntroduced the term "physiology" to describe the study of the body's function, and was the first person to describe the spinal canal.
1879: Printer, bookseller, and inventor Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville dies. He invented the phonoautograph, which records an audio signal as a photographic image.
1879: Physicist and academic Owen Willans Richardson born. He will win the 1928 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on thermionic emission, which led to Richardson's law.
1954: Castle Union nuclear weapons test at Bikini Atoll: the United States detonates the TX-14 thermonuclear weapon, one of the first deployed U.S. thermonuclear bombs. The explosion causes extensive fallout. Castle Union was the code name given to one of the tests in the Operation Castle series of United States nuclear tests. It was the first test of the TX-14 thermonuclear weapon (initially the "emergency capability" EC-14), one of the first deployed U.S. thermonuclear bombs. Pic.
1986: A nuclear reactor accident occurs at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in the Soviet Union (now Ukraine).
1791: Painter and inventor Samuel Morse born. He will co-invent the Morse code.
1837: Mathematician Paul Albert Gordan born. Gordon was known as "the king of invariant theory".
1913: Mathematician, author, activist, and academic Irving Adler born. He will be a plaintiff in the McCarthy-era case Adler vs. Board of Education.
1938: Mathematician and philosopher Edmund Husserl dies. He argued that transcendental consciousness sets the limits of all possible knowledge.
1978: Former United States President Nixon aide John D. Ehrlichman is released from an Arizona prison after serving 18 months for Watergate-related crimes.
1693: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz writes to L'Hospital, announcing his discovery of determinants fifty years before Cramer, who was the real driving force in the development of determinants. Leibniz's work had little or no influence because it was not published until 1850 in his Mathematische Schriften.
1774: Astronomer Francis Baily born. He will observe "Baily's beads" during an annular eclipse (1836).
1817: Carl Friedrich Gauss writes to the astronomer H. W. M. Oblers, saying, "I am becoming more and more convinced that the necessity of our (Euclidean) geometry cannot be proved, at least not by human intellect nor for the human intellect."
1868: Mathematician Georgy Voronoy born. He will invent what are today called Voronoi diagrams or Voronoi tessellations.
1906: Mathematician, philosopher, and academic Kurt Gödel born. His two incompleteness theorems will have an immense impact upon scientific and philosophical thinking in the 20th century.
1928: Geologist and astronomer Eugene Merle Shoemaker born. Shoemaker will be the first scientist to conclude that Barringer Meteor Crater in Arizona, and similar craters, were caused by meteor impact.
1986: High levels of radiation resulting from the Chernobyl disaster are detected at a nuclear power plant in Sweden, leading Soviet authorities to publicly announce the accident.
1999: Physicist and engineer Rolf Landauer dies. Landauer discovered that in any logically irreversible operation that manipulates information, such as erasing a bit of memory, entropy increases and an associated amount of energy is dissipated as heat. This phenomenon is now known as Landauer's principle.
1667: Physician, satirist, and polymath John Arbuthnot born. He will invent the figure of John Bull.
1854: Mathematician, physicist, and engineer Henri Poincaré born. He will make many original fundamental contributions to pure and applied mathematics, mathematical physics, and celestial mechanics.
1893: Chemist and astronomer Harold Urey born. Urey's pioneering work on isotopes will earn him the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1934 for the discovery of deuterium; he will also play a significant role in the development of the atom bomb, and contribute to theories on the development of organic life from non-living matter.
1986: Chernobyl disaster: American and European spy satellites capture the ruins of the 4th Reactor at the Chernobyl Power Plant.
2008: Chemist and academic Albert Hoffman dies. Hoffman is famous for discovering LSD, which he called his "problem child".
1777: Mathematician, astronomer, and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss born. He will have an exceptional influence in many fields of mathematics and science and be ranked as one of history's most influential mathematicians.
1897: J. J. Thomson of the Cavendish Laboratory announces his discovery of the electron as a subatomic particle, over 1,800 times smaller than a proton (in the atomic nucleus), at a lecture at the Royal Institution in London.
1913: Mathematician and cryptanalyst Genevieve Grotjan Feinstein born. Feinstein will work for the Signals Intelligence Service throughout World War II, playing an important role in deciphering the Japanese cryptography machine Purple, and will later work on the Cold War-era Venona project.
1916: Mathematician, engineer, and information scientist Claude Shannon born. He will be known as "the father of information theory".
1973: Watergate: U.S. President Richard Nixon announces that White House Counsel John Dean has been fired and that other top aides, most notably H. R. Haldeman and John Ehrlichman, have resigned.
Template:Selected anniversaries/April 31
May
1825: Mathematician and physicist Johann Jakob Balmer born. He will develop an empirical formula for the visible spectral lines of the hydrogen atom.
1960: Cold War: U-2 incident: Francis Gary Powers, in a Lockheed U-2 spyplane, is shot down over the Soviet Union, sparking a diplomatic crisis.
1970: Electronics researcher Ralph Hartley dies. He invented the Hartley oscillator and the Hartley transform, and contributed to the foundations of information theory.
1519: Polymath Leonardo da Vinci dies. His areas of interest included painting, sculpting, architecture, invention, science, music, mathematics, engineering, literature, anatomy, geology, astronomy, botany, writing, history, and cartography.
1602: Scholar and polymath Athanasius Kircher born. He will publish some 40 major works, most notably in the fields of comparative religion, geology, and medicine.
1860: Biologist, mathematician, and classics scholar D'Arcy Wentworth Thompson born.
1986: Chernobyl disaster: The City of Chernobyl is evacuated six days after the disaster.
2002: Mathematician, codebreaker, and academic W. T. Tutte dies. During the Second World War, he made a brilliant and fundamental advance in cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher, a major Nazi German cipher system.
1764: Venetian polymath and art collector Francesco Algarotti dies. Algarotti's broad knowledge included expertise in Newtonianism, architecture, and music; and he was a friend of most of the leading authors of his times. Pic.
1779: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer John Winthrop dies. He was one of the foremost men of science in America during the 18th century.
1860: Mathematician and physicist Vito Volterra born. He will be one of the founders of functional analysis, making contributions to mathematical biology and integral equations.
1905: Mathematician and academic Werner Fenchel born. He will establish the basic results of convex analysis and nonlinear optimization theory which will, in time, serve as the foundation for nonlinear programming.
1928: Mathematician Jacques-Louis Lions born. He will make contributions to the theory of partial differential equations and to stochastic control.
1677: Mathematician and theologian Isaac Barrow dies. Barrow played an early role in the development of infinitesimal calculus: he was the first to calculate the tangents of the kappa curve.
1733: Mathematician, physicist, and sailor Jean-Charles de Borda born. He will contribute to the development of the metric system, constructing a platinum standard meter, the basis of metric distance measurement.
1825: Biologist Thomas Henry Huxley born. He will be known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his advocacy of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
1859: Mathematician and logician Joseph Diez Gergonne dies. He contributed to the principle of duality in projective geometry, by noticing that every theorem in the plane connecting points and lines corresponds to another theorem in which points and lines are interchanged, provided that the theorem embodied no metrical notions.
1921: Physicist Harry Daghlian born. He will be fatally irradiated in a criticality accident during an experiment with the Demon core at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
2019: Photograph of Karl Jones taken by Steve Ozone.
1580: Mathematician Johann Faulhaber born. He will discover Faulhaber's formula, which expresses the sum of the p-th powers of the first n positive integers.
1859: Mathematician Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet dies. He made important contributions to number theory, analysis, and mechanics. Dirichlet was one of the first mathematicians to give the modern formal definition of a function.
1868: Inventor, physician, chemist Charles Grafton Page dies. His work had a lasting impact on telegraphy and in the practice and politics of patenting scientific innovation, challenging the rising scientific elitism that maintained 'the scientific do not patent'.
1833: Mathematician and academic Lazarus Immanuel Fuchs born. He will contribute important research in the field of linear differential equations. Fuchs will be the eponym of Fuchsian groups and functions, and the Picard–Fuchs equation.
1933: The New York Times The New York Times publishes a front-page account of a scientific paper on radio astronomy by Karl Guthe Jansky.
1635: Physician, alchemist, scholar, and adventurer Johann Joachim Becher born. Becher will propose Phlogiston theory in an attempt to explain processes such as combustion and rusting, which are now collectively known as oxidation.
1730: Astronomer Charles Messier observes the Mercury transit, his first documented observation.
1840: The Penny Black postage stamp becomes valid for use in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.
1937: Hindenburg disaster: The German zeppelin Hindenburg catches fire and is destroyed within a minute while attempting to dock at Lakehurst, New Jersey. Thirty-six people are killed.
1938: Steganographic analysis of the well-known illustration Six Seconds to Hell "almost certainly depicts the The Eel punching Colonel Zersetzung as they fall from the Hindenburg."
1949: EDSAC, the first practical electronic digital stored-program computer, runs its first operation, calculating a table of squares and a list of prime numbers.
1700: Physician Gerard van Swieten born.
1794: French Revolution: Robespierre introduces the Cult of the Supreme Being in the National Convention as the new state religion of the French First Republic.
1860: Electrical engineer and inventor Oliver Blackburn Shallenberger born. He will invent the first successful alternating current electrical meter, which will be critical to the general acceptance of AC power.
1895: Russian physicist Alexander Stepanovich Popov demonstrates to the Russian Physical and Chemical Society his invention, the Popov lightning detector — a primitive radio receiver.
1895: First publication of The Time Machine by H. G. Wells.
1960: Cold War: U-2 Crisis of 1960: Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev announces that his nation is holding American U-2 pilot Gary Powers.
1788: Physician, geologist, and botanist Giovanni Antonio Scopoli dies. He has been called the "first anational European" and the "Linnaeus of the Austrian Empire".
1794: Branded a traitor during the Reign of Terror by revolutionists, French chemist Antoine Lavoisier, who was also a tax collector with the Ferme générale, is tried, convicted and guillotined in one day in Paris.
1873: Economist, civil servant, and philosopher John Stuart Mill dies. He was one of the most influential thinkers in the history of liberalism, and the first Member of Parliament to call for women's suffrage.
1959: Mathematician Renato Caccioppoli takes his own life. Caccioppoli contributed to mathematical analysis, including the theory of functions of several complex variables, functional analysis, and measure theory.
1960: Mathematician and academic J. H. C. Whitehead dies. During the Second World War, he worked with the codebreakers at Bletchley Park.
1746: Mathematician and engineer Gaspard Monge born. He will invent descriptive geometry, and do pioneering work in differential geometry.
1941: The German submarine U-110 is captured by the Royal Navy. On board is the latest Enigma machine which Allied cryptographers later use to break coded German messages.
1963: Project West Ford launches, successfully deploying a ring of 480,000,000 copper needles in orbit, forming an artificial ionospheric radio communication system.
1972: Watergate scandal (nonfiction): The United States House Committee on the Judiciary opens formal and public impeachment hearings against President Richard Nixon.
28 BC: A sunspot is observed by Han dynasty astronomers during the reign of Emperor Cheng of Han, one of the earliest dated sunspot observations in China.
1482: Mathematician and astronomer Paolo dal Pozzo Toscanelli dies. Thanks to his long life, his intelligence and his wide interests, Toscanelli was one of the central figures in the intellectual and cultural history of Renaissance Florence in its early years.
1829: Polymath and physician Thomas Young dies. Young made notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology.
1900: Astronomer and astrophysicist Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin born. Her doctoral thesis will establish that hydrogen is the overwhelming constituent of stars, and accordingly the most abundant element in the universe.
1960: Mathematician, art critic, and alleged time-traveller The Eel challenges aquatic cryptid and alleged supervillain Neptune Slaughter to single combat, providing a distraction which enables the USS Triton to escape Slaughter's deadly mutant Cuttle-Net.
1960: The nuclear submarine USS Triton completes Operation Sandblast, the first underwater circumnavigation of the earth.
868: A copy of the Diamond Sutra is printed in China, making it the oldest known dated printed book.
1610: Priest and mathematician Matteo Ricci dies. Ricci translated Euclid's Elements into Chinese, as well as the Confucian classics into Latin, for the first time.
1858: Minnesota is admitted as the 32nd U.S. State.
1918: Theoretical physicist and academic Richard Feynman born. Feynmann will share the 1965 Nobel Prize in Physics for his contributions to the development of quantum electrodynamics.
1803: Chemist and academic Justus von Liebig born. Von Liebeg will make pioneering contributions to organic chemistry, especially agricultural and biological chemistry; he will be known as the "Father of the fertilizer industry".
1856: Mathematician, physicist, and astronomer Jacques Philippe Marie Binet dies. He made significant contributions to number theory, and the mathematical foundations of matrix algebra.
1857: Mathematician Oskar Bolza born. He will be known for his research in the calculus of variations; his work on variations for an integral problem involving inequalities will later became important in control theory.
1941: Engineer, inventor, and pioneering computer scientist Konrad Zuse presents the Z3, the world's first working programmable, fully automatic computer, in Berlin.
2014: Painter, sculptor, and set designer H. R. Giger dies. He gained fame for his work on the film Alien.
2017: Art critic and alleged supervillain The Eel escapes from The Nacreum using a surfboard controlled by a bespoke gnomon algorithm.
1713: Mathematician, astronomer, and geophysicist Alexis Clairaut born. Clairaut's work will help to establish the validity of the principles and results that Sir Isaac Newton had outlined in the Principia of 1687.
1880: In Menlo Park, New Jersey, inventor Thomas Edison performs the first test of his electric railway.
1929: Electrical engineer and inventor Arthur Scherbius dies. Scherbius invented and patented the famous mechanical cipher Enigma machine.
1937: Writer Roger Zelazny born. Zelazny will win the Nebula award three times, and the Hugo award six times.
1974: Physicist and chemist Marguerite Perey dies. Perey discovered the element francium while purifying samples of lanthanum.
1678: Writer and philosopher Culvert Origenes publishes Historia Culvertica, which will soon be widely plagiarized, influencing a generation of humanists.
1679: Astronomer and mathematician Peder Horrebow born. Horrebow will invent a way to determine a place's latitude from the stars.
1863: Mathematician John Charles Fields born. He will found the Fields Medal for outstanding achievement in mathematics.
1893: Mathematician Ernst Kummer dies. Kummer contributed to abstract algebra; in ring theory, he introduced the term ideal.
1916: Physicist and astrophysicist Robert F. Christy born. Christy will be credited with the insight that a solid sub-critical mass of plutonium can be explosively compressed into supercriticality, a great simplification of earlier concepts of implosion requiring hollow shells.
1917: Mathematician, codebreaker, and academic W. T. Tutte born. During the Second World War, he will make a brilliant and fundamental advance in cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher, a major Nazi German cipher system.
1618: Johannes Kepler confirms his previously rejected discovery of the third law of planetary motion (he first discovered it on March 8 but soon rejected the idea after some initial calculations were made).
1801: Mathematician Joseph Ludwig Raabe born. He will discover Raabe's ratio test, which determines the convergence or divergence of an infinite series, in some cases.
1836: Astronomer Francis Baily observes "Baily's beads" during an annular eclipse.
1821: Mathematician and statistician Pafnuty Chebyshev born. He will prove Chebyshev's inequality (also called the Bienaymé–Chebyshev inequality), which guarantees that, for a wide class of probability distributions, no more than a certain fraction of values can be more than a certain distance from the mean.
1830: Mathematician and physicist Joseph Fourier dies. He initiated the investigation of Fourier series and their applications to problems of heat transfer and vibrations.
1888: The Orcagna scrying engine previews Nikola Tesla's speech on alternating current technology.
1888: Nikola Tesla delivers a lecture describing the equipment which will allow efficient generation and use of alternating currents to transmit electric power over long distances.
1968: Mathematician and crime-fighter Jacques-Louis Lions publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which use partial differential equations and stochastic control to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.
2017: Math photographer Cantor Parabola wins Pulitzer Prize for "unique and peerless accomplishments in four-dimensional photography."
1765: Mathematician, astronomer, and geophysicist Alexis Clairaut dies. His work helped to establish the validity of the principles and results that Sir Isaac Newton had outlined in the Principia of 1687.
1902: Greek archaeologist Valerios Stais discovers the Antikythera mechanism, an ancient mechanical analog computer.
1973: Watergate scandal (nonfiction): Televised hearings begin in the United States Senate.
2001: Mathematician Jacques-Louis Lions dies. He made contributions to the theory of partial differential equations and to stochastic control.
1048: Polymath, scholar, mathematician, astronomer, philosopher, and poet Omar Khayyám born. He wrote one of the most important treatises on algebra written before modern times, the Treatise on Demonstration of Problems of Algebra (1070), which includes a geometric method for solving cubic equations by intersecting a hyperbola with a circle. As an astronomer, he designed the Jalali calendar, a solar calendar with a very precise 33-year intercalation cycle.
1711: Polymath Roger Joseph Boscovich born. He will be a physicist, astronomer, mathematician, philosopher, diplomat, poet, theologian, and Jesuit priest.
1822: Photographer and journalist Mathew Brady born. He will be one of the first American photographers, best known for his scenes of the Civil War.
1850: Self-taught electrical engineer, mathematician, and physicist Oliver Heaviside born. Heaviside will make major breakthroughs in the applied mathematics of electrical engineering; although he will be at odds with the scientific establishment for most of his life, Heaviside will change the face of telecommunications, mathematics, and science for years to come.
1872: Philosopher, logician, mathematician, historian, writer, social critic and political activist Bertrand Russell born.
1902: "Fightin'" Bert Russell defeats Baron Zersetzung with knockout punch in the third round of bare-knuckled boxing at the World Peace Conference.
1743: Physicist, mathematician, and astronomer Jean-Pierre Christin publishes the design of a mercury thermometer based on the Celsius scale. The Thermometer of Lyon will be built by the craftsman Pierre Casati using this design.
1903: Bacteriologist Ruth Ella Moore born. She will research tuberculosis, immunology and dental caries, the response of gut microorganisms to antibiotics, and the blood type of African-Americans.
1918: Physicist, historian, and academic Abraham Pais born. Pais will be an assistant to Niels Bohr, and a colleague of Albert Einstein, and later write books documenting the lives of these two great physicists and the contributions they and others made to modern physics.
1961: Venera 1 becomes the first man-made object to fly-by another planet by passing Venus (the probe had lost contact with Earth a month earlier and did not send back any data).
1971: The Soviet Union launches the Mars 2 spacecraft. The spacecraft will reach Mars, but the landing module will crash after failing to deploy its parachute.
2017: Soviet Air Defense office Stanislav Yevgrafovich Petrov dies. Petrov became known as "the man who single-handedly saved the world from nuclear war" for his role in the 1983 Soviet nuclear false alarm incident.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars remembers the forty-sixth anniversary of the Mars 2 launch, observing a moment of silence for the failure of the mission.
1570: Cartographer and geographer Abraham Ortelius issues Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, the first modern atlas.
1806: Economist, civil servant, and philosopher John Stuart Mill born. He will be one of the most influential thinkers in the history of liberalism, and the first Member of Parliament to call for women's suffrage.
1888: Physicist Winfried Otto Schumann born. He will predict the existence of a series of low-frequency resonances caused by lightning discharges in the atmosphere, now known as Schumann resonances.
1889: Electrical engineer Nikola Tesla radio technology to intercept communications between math criminals, providing information which will lead to the capture of Baron Zersetzung.
1891: History of cinema: The first public display of Thomas Edison's prototype kinetoscope.
1932: Amelia Earhart departs Harbour Grace, Newfoundland, in her Lockheed Vega on her solo nonstop flight across the Atlantic. After a flight lasting 14 hours, 56 minutes, Earhart lands in Northern Ireland, making her the second person (after Charles Lindbergh) to fly nonstop and alone across the Atlantic.
1471: Painter, engraver, and mathematician Albrecht Dürer born. Dürer will be regarded as the greatest German Renaissance artist: his vast body of work will include altarpieces and religious works, numerous portraits and self-portraits, and copper engravings.
1670: Astronomer and physicist Niccolò Zucchi dies. He published works on astronomy, optics, mechanics, and magnetism.
1686: Scientist, inventor, and politician Otto von Guericke dies. Von Guericke pioneered the physics of vacuums, and discovered an experimental method for demonstrating electrostatic repulsion.
1923: Mathematician and academic Armand Borel born. He will work in algebraic topology, and in the theory of Lie groups, contributing to the creation of the contemporary theory of linear algebraic groups.
1927: Charles Lindbergh touches down at Le Bourget Field in Paris, completing the world's first solo nonstop flight across the Atlantic Ocean.
1927: Pilot, engineer, and alleged time-traveler Henrietta Bolt touches down at Le Bourget Field in Paris, completing the world's first solo nonstop round-the-world flight.
1932: Amelia Earhart completes her solo nonstop flight across the Atlantic when bad weather forces her to land in Derry, Northern Ireland, after a flight lasting 14 hours, 56 minutes. Earhart is the second person (after Charles Lindbergh) to fly nonstop and alone across the Atlantic.
1946: Physicist Louis Slotin is fatally irradiated in a criticality incident during an experiment with the so-called "demon core" at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
1953: Logician and mathematician Ernst Friedrich Ferdinand Zermelo dies. His work had major implications for the foundations of mathematics; he is known for his role in developing Zermelo–Fraenkel axiomatic set theory, and for his proof of the well-ordering theorem.
1592: Giordano Bruno arrested. Among the numerous charges of blasphemy and heresy brought against him is his belief in the plurality of worlds.
1873: Lawyer, translator, and inventor Per Georg Scheutz born. He will invent the Scheutzian calculation engine, based on Charles Babbage's difference engine.
1930: Mathematician, academic, and rabbi Eliezer 'Leon' Ehrenpreis born. He will prove the Malgrange–Ehrenpreis theorem, the fundamental theorem about differential operators with constant coefficients.
1946: The WAC Corporal becomes the first US rocket to reach edge of space.
1997: Chemist and US military officer Myrtle Bachelder dies. Bachelder was responsible for the analysis of the spectroscopy of uranium for the Manhattan Project during the Second World War. After the war, Bachelder made pioneering contributions to metallochemistry.
2010: Mathematics and science writer Martin Gardner dies. His interests included stage magic, scientific skepticism, philosophy, religion, and literature.
2024: Self portrait.
1707: Botanist, physician, and zoologist Carl Linnaeus born. He will formalize the binomial nomenclature system of taxonomy.
1734: Physician Franz Mesmer born. Mesmer will theorize that there is a natural energy transference which occurs between all animated and inanimate objects which he will call animal magnetism. The effects which he will observe will later be attributed to hypnosis.
1895: Mineralogist, physicist, and mathematician Franz Ernst Neumann dies. His 1831 study on the specific heats of compounds included what is now known as Neumann's Law: the molecular heat of a compound is equal to the sum of the atomic heats of its constituents.
1917: Meteorologist, mathematician, and chaos theory pioneer Edward Lorenz born. He will introduce the strange attractor notion, and coin the term butterfly effect.
1918: Lorenz system diagram says it "owes everything to Papa Lorenz."
1982: Electrical engineer Florence Violet McKenzie dies. She was Australia's first female electrical engineer, founder of the Women's Emergency Signalling Corps (WESC), and lifelong promoter for technical education for women.
1994: George P. Metesky dies. He terrorized New York City for 16 years in the 1940s and 1950s with explosives that he planted in theaters, terminals, libraries, and offices.
2024: Raspberry patch flourishing.
1089: Celebrated jurist and monk Lanfranc dies.
1543: Mathematician and astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus dies. He formulated a model of the universe that places the Sun rather than the Earth at the center of the universe.
1686: Physicist and engineer Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit born. He will help lay the foundations for the era of precision thermometry by inventing the mercury-in-glass thermometer and the Fahrenheit scale.
1734: Chemist and physician Georg Ernst Stahl dies. His works on phlogiston continue to be accepted as an explanation for chemical processes until the late 18th century.
1844: Samuel Morse sends the message "What hath God wrought" (a biblical quotation, Numbers 23:23) from the Old Supreme Court Chamber in the United States Capitol to his assistant, Alfred Vail, in Baltimore, Maryland, to inaugurate a commercial telegraph line between Baltimore and Washington D.C.
1928: Mathematician Bertram Kostant born. He will be one of the principal developers of the theory of geometric quantization.
1940: Igor Sikorsky performs the first successful single-rotor helicopter flight.
1974: Physicist Clyde Cowan dies. Cowan, along with Frederick Reines, discovered the neutrino in 1956; Reines received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1995 in both their names.
2024: Alley (24 May 2024).
986: Astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi dies.
1555: Physician, mathematician, and cartographer Gemma Frisius dies. He created important globes, improved the mathematical instruments of his day, and applied mathematics to surveying and navigation in new ways.
1828: Mathematician Karl Mikhailovich Peterson born. He will discover equations which will subsequently be named the Gauss–Codazzi equations, fundamental to the theory of embedded hypersurfaces in a Euclidean space.
1889: Aircraft designer Igor Sikorsky born. He will pioneer both helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft.

1961: Apollo program: U.S. President John F. Kennedy announces before a special joint session of the Congress his goal to initiate a project to put a "man on the Moon" before the end of the decade.
1497: Mathematician and architect Antonio Manetti dies. He investigated the site, shape and size of Dante's Inferno, and wrote a biography of the architect Filippo Brunelleschi.
1667: Mathematician and theorist Abraham de Moivre born. His book on probability theory, The Doctrine of Chances, will be prized by gamblers.
1814: Glassblower, physicist, and inventor Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Geißler born. He will invent the Geissler tube, made of glass and used as a low pressure gas-discharge luminescence tube.
1895: Documentary photographer and photojournalist Dorothea Lange born. Lange will be remembered for her Depression-era work for the Farm Security Administration (FSA). Her photographs will influence the development of documentary photography and humanize the consequences of the Great Depression.
1938: In the United States, the House Un-American Activities Committee begins its first session.
1610: Factotum and regicide François Ravaillac executed.
1897: Physicist, academic, and Nobel Prize laureate John Cockcroft born. He will be instrumental in the development of nuclear power.
1931: Physicist and explorer Auguste Piccard and his assistant Paul Kipfer take off from Augsburg, Germany in their high-altitude balloon, reaching a record altitude of 15,781 m (51,775 ft). During the flight, Piccard gathers data on the upper atmosphere, including cosmic ray measurements.
1829: Army officer, trader, and lecturer John Cleves Symmes, Jr. dies. He invented a variant of the Hollow Earth Theory, with openings to the inner world at the poles.
1936: Computer scientist, mathematician, logician, cryptanalyst and theoretical biologist Alan Turing submits On Computable Numbers for publication.
2015: Information scientist Claire Kelly Schultz dies.
1777: Physician and engineer John Mudge elected a Fellow of the Royal Society, and in the same year was awarded the Copley medal for his 'Directions for making the best Composition for the Metals for reflecting Telescopes; together with a Description of the Process for Grinding, Polishing, and giving the great Speculum the true Parabolic Curve'.
1917: Politician John F. Kennedy, 35th President of the United States, born.
1919: Arthur Eddington and Andrew Claude de la Cherois Crommelin view a solar eclipse as a test of Einstein's theory of general relativity.
1931: Psychologist, computer scientist, and author Christopher Evans born.
2023: Self portrait.
1423: Mathematician and astronomer Georg von Peuerbach born. He will be remembered for his streamlined presentation of Ptolemaic astronomy in the Theoricae Novae Planetarum.
1739: Jacques de Vaucanson demonstrates his Digesting Duck automaton for the first time.
1946: Physicist Louis Slotin dies. He was fatally irradiated in a criticality incident during an experiment with the demon core at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
1964: Physicist and academic Leo Szilard dies. He conceived the nuclear chain reaction in 1933, and patented the idea of a nuclear reactor with Enrico Fermi.
1971: NASA launches the Mariner 9 spacecraft. It will map 70% of the surface of Mars, and study temporal changes in the atmosphere and surface.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates the forty-sixth anniversary of the launch of Mariner 9.
2024: Dusk.
1683: Physicist, mathematician, and astronomer Jean-Pierre Christin born. He will invent the Celsius thermometer.
1831: Engineer and naval architect Samuel Bentham dies. He designed the first Panopticon.
1832: Mathematician and social activist Évariste Galois from wounds suffered in a duel. While still in his teens, he was able to determine a necessary and sufficient condition for a polynomial to be solvable by radicals, thereby solving a problem standing for 350 years. His work laid the foundations for Galois theory and group theory, two major branches of abstract algebra, and the subfield of Galois connections.
1912: Physicist Chien-Shiung Wu born. She will conduct the Wu experiment, which will contradict the law of conservation of parity, proving that parity is not conserved.
2023: Ely sunset (31 May 2023).
June
1633: Astronomer and academic Geminiano Montanari born. He will make the observation that Algol in the constellation of Perseus varies in brightness.
1849: Territorial Governor Alexander Ramsey declared the Territory of Minnesota officially established.
1867: Mathematician Karl Georg Christian von Staudt dies. He used synthetic geometry to provide a foundation for arithmetic.
1895: Havelock and Herman Hollerith announce plan to collaborate on new data exchange protocol.
1890: The United States Census Bureau begins using Herman Hollerith's tabulating machine to count census returns.
1944: First successful run of the improved Colossus Mark 2 computer], just in time for the Normandy landings on D-Day. Colossus Mark 2 used shift registers to quintuple the processing speed.
1743: Occultist and explorer Alessandro Cagliostro born. He will become a glamorous figure associated with the royal courts of Europe where he will pursue psychic healing, alchemy, and scrying.
1881: Engineer and radio pioneer Henry Joseph Round born. Round will be an assistant of Guglielmo Marconi, and make contributions of his own to radio technology, for example the first reported observation of electroluminescence from a solid state diode.
1896: Guglielmo Marconi applies for a patent for his wireless telegraph.
1923: Mathematician and economist Lloyd Shapley born. He will define game theory as "a mathematical study of conflict and cooperation."
2014: Pharmacologist and chemist Alexander Shulgin dies. He discovered, synthesized, and personal bioassayed over 230 psychoactive compounds for their psychedelic and entactogenic potential.
1659: Mathematician and astronomer David Gregory born. At the Union of 1707, he bill be given the responsibility of reorganizing the Scottish Mint.
1723: Physician, geologist, and botanist Giovanni Antonio Scopoli born. He will be called the "first anational European" and the "Linnaeus of the Austrian Empire".
1839: In Humen, China, Lin Tse-hsü destroys 1.2 million kg of opium confiscated from British merchants, preliminary to the First Opium War.
1923: Mathematician and dissident Igor Shafarevich born. He will make fundamental contributions to algebraic number theory, algebraic geometry, and arithmetic algebraic geometry.
2009: Arnold's cat map is "better than a laser pointer for keeping a cat amused," says Arnold.
2010: Mathematician and academic Vladimir Arnold dies. He helped develop the Kolmogorov–Arnold–Moser theorem regarding the stability of integrable systems.
1472: Aztec philosopher, warrior, architect, poet, and ruler Nezahualcoyotl dies. He had an experience of an "Unknown, Unknowable Lord of Everywhere" to whom he built an entirely empty temple in which no blood sacrifices of any kind were allowed.
1739: Scientist and author Johann Beckmann born. Beckmann will coin the word technology, meaning the science of trades, and be the first to teach technology and write about it as an academic subject.
1769: Astronomer Guillaume Le Gentil's hopes are dashed when, after years of struggle, overcast conditions prevent him from making a critical observation.
1783: The Montgolfier brothers give first public demonstration of balloon flight.
1944: World War Two: A hunter-killer group of the United States Navy captures the German submarine U-505: The first time a U.S. Navy vessel had captured an enemy vessel at sea since the 19th century.
1992: Mathematician Melvin Dresher (Dreszer) dies. He contributed to game theory, co-developing the game theoretical model of cooperation and conflict known as the Prisoner's dilemma.
1646: Mathematician and philosopher Elena Cornaro Piscopia born. She will be one of the first women to receive an academic degree from a university, and the first to receive a Doctor of Philosophy degree.
1756: Chemist, physician, agronomist, industrialist, statesman, educator, and philanthropist Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal born.
1900: Physicist and engineer Dennis Gabor born. He will invent holography, for which he will receive the 1971 Nobel Prize in Physics.
1910: Short story writer O. Henry, known for his surprise endings, dies.
2012: Science fiction writer and screenwriter Ray Bradbury dies. The New York Times calls Bradbury "the writer most responsible for bringing modern science fiction into the literary mainstream".
1436: Mathematician, astronomer, and bishop Johann Regiomontanus born. His contributions will be instrumental in the development of Copernican heliocentrism in the decades following his death.
1844: The Glaciarium, the world's first mechanically frozen ice rink, opens in London.
1857: Mathematician and physicist Aleksandr Lyapunov born. Lyapunov will contribute to several fields, including differential equations, potential theory, dynamical systems and probability theory. His main preoccupations will be the stability of equilibria and the motion of mechanical systems, and the study of particles under the influence of gravity.
1943: Chemist and academic Richard Smalley born. Along with colleagues Robert Curl and Harold Kroto, he will win the 1996 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of a new form of carbon, buckminsterfullerene, also known as buckyballs.
2017: In a press statement, Pin Man says he was "constructed by Colonel Zersetzung from the flayed skin of a notorious data thief."
1883: Archaeologist and spy Sylvanus Morley born. He will conduct espionage in Mexico on behalf of the United States during World War I; the scope of these activities will only come to light after his death.
1910: Mathematical physicist Charles Critchfield born. He will work on the Manhattan Project, designing and testing the "Urchin" neutron initiator which provides the burst of neutrons that kick-starts the nuclear detonation of the Fat Man weapon.
1952: Computer scientist, mathematician, logician, cryptanalyst and theoretical biologist Alan Turing dies. He was influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalization of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine.
2022: Apple flowers (7 June 2022).
1625: Mathematician, astronomer, and engineer Giovanni Domenico Cassini born. He will discover four satellites of the planet Saturn and note the division of the rings of Saturn; the Cassini Division will be named after him.
1789: James Madison introduces nine amendments to the constitution in the House of Representatives, inluencing later Bill of Rights amendments.
1809: Thomas Paine dies. He authored the two most influential pamphlets at the start of the American Revolution, and inspired the rebels in 1776 to declare independence from Britain.
1887: Inventor Herman Hollerith applies for US patent #395,781 for the 'Art of Compiling Statistics', his punched card calculator.
1955: Engineer and computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee born. He will invent the World Wide Web.
1861: Physicist, mathematician, and historian Pierre Duhem born. He will write: "A theory of physics is not an explanation. It is a system of mathematical propositions, deduced from a small number of principles, which have for their aim to represent as simply, as completely and as exactly as possible, a group of experimental laws."
1950: Novelist and screenwriter Dalton Trumbo is photographed Bureau of Prisons authorities. Trumbo will serve eleven months in the federal penitentiary in Ashland, Wisconsin for refusing to testify before House Un-American Activities Committee.
1953: Singer-physicist J. R. Oppenheimer's song "Destroyer of Worlds" is condemned by the House Un-American Activities Committee as "pernicious satire which knowingly demeans the national security state."
1954: "You've done enough. Have you no sense of decency, sir, at long last? Have you left no sense of decency?" —Joseph Welch, special counsel for the United States Army, lashes out at Senator Joseph McCarthy during hearings on whether Communism has infiltrated the Army. See McCarthyism.
940: Mathematician and astronomer Abū al-Wafā' Būzjānī born. His Almagest will be widely read by medieval Arabic astronomers in the centuries after his death.
1793: French Revolution: Following the arrests of Girondin leaders, the Jacobins gain control of the Committee of Public Safety installing the revolutionary dictatorship.
1836: Physicist and mathematician André-Marie Ampère dies. He was one of the founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, which he referred to as "electrodynamics".
1909: Aerospace engineer and weapons designer Ludwig Roth born. During World War II, Roth will head Germany's Future Projects Office, which will design the Wasserfall and rockets such as the A9/A10 ICBM. Roth will then be recruited by American intelligence under Operation Paperclip.
1972: Modern dance company Rhizolith Group debuts new work based on the history of high-energy literature in New Minneapolis, Canada.
1644: Physicist and mathematician Evangelista Torricelli writes in a letter to Michelangelo Ricci: Noi viviamo sommersi nel fondo d'un pelago d'aria ("We live submerged at the bottom of an ocean of air").
1887: Electrical engineer and physicist John Ambrose Fleming marries Clara Ripley.
1915: Mathematician and physicist Nicholas Metropolis born. He will lead the team of researchers which will develop the Monte Carlo method.
2024: Self portrait.
1577: Astronomer and mathematician Paul Guldin born. He will discover the Guldinus theorem, which determines the surface and the volume of a solid of revolution.
1937: Mathematician and academic Vladimir Arnold born. He will help develop the Kolmogorov–Arnold–Moser theorem regarding the stability of integrable systems.
1945: Physicist James Franck brings the Franck Report to Washington. The report recommends that the United States not use the atomic bomb as a weapon to prompt the surrender of Japan in World War II.
2024: Evening.
1508: Humanist and philosopher Alessandro Piccolomini born. Piccolomini will promote vernacular translations of Latin and Greek scientific and philosophical treatises.
1555: Mathematician, cartographer, and astronomer Giovanni Antonio Magini born. He will support a geocentric system of the world, in preference to Copernicus's heliocentric system.

1580: Astronomer and mathematician Willebrord Snellius born. In 1615 he will conduct a large-scale experiment to measure the circumference of the earth using triangulation, underestimating the circumference of the earth by 3.5%.
1773: Polymath and physician Thomas Young born. Young will make notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology.
1831: Physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell born. His discoveries will help usher in the era of modern physics, laying the foundation for such fields as special relativity and quantum mechanics.
1854: Engineer and inventor Charles Algernon Parsons born. He will invent the compound steam turbine, and work on dynamo and turbine design, power generation, and optical equipment for searchlights and telescopes.
1931: Mathematician and academic Herbert Saul Wilf born. Wilf specialized in combinatorics and graph theory.
2021: Angus.
1791: Polymath Charles Babbage proposes a difference engine in a paper to the Royal Astronomical Society entitled "Note on the application of machinery to the computation of astronomical and mathematical tables".
1903: Mathematician and logician Alonzo Church born. He will make major contributions to mathematical logic and the foundations of theoretical computer science.
1946: Engineer and inventor John Logie Baird dies. He was one of the inventors of the mechanical television.
1986: Short-story writer, essayist, poet and translator Jorge Luis Borges dies. His best-known books, Ficciones (Fictions) and El Aleph (The Aleph), published in the 1940s, are compilations of short stories interconnected by common themes, including dreams, labyrinths, libraries, mirrors, fictional writers, philosophy, and religion.
1995: Writer Roger Zelazny dies. He won the Nebula award three times, and the Hugo award six times.
1995:The Custodian offers supernatural crime fighter job to deceased writer Roger Zelazny.
2022: Self portrait.
1906: Mathematician, cryptographer, and author Gordon Welchman born. During the Second World War, he will develop traffic analysis techniques for breaking German codes.
1995: Physicist, inventor, and academic John Vincent Atanasoff dies. He invented the Atanasoff–Berry computer, the first electronic digital computer.
2022: Ely, Minnesota water tower.
1591: Physician, mathematician, and theorist Joseph Solomon Delmedigo born. He will write Elim (Palms), dealing astronomy, physics, mathematics, medicine, metaphysics, and music theory.
1640: Mathematician Jacques Ozanam born. Ozanam's Récréations mathématiques et physiques (1694) will later be translated into English and remain popular into the modern era.
1806: Physician, scientist, and inventor Edward Davy born. He will play a prominent role in the development of telegraphy, and invent an electric relay.
1839: Mathematician Julius Petersen born. His famous paper Die Theorie der regulären graphs will be a fundamental contribution to modern graph theory.
1915: Mathematician and academic John Tukey born. He will make important contributions to statistical analysis, including the box plot.
2022: Self portrait.
1714: Astronomer and cartographer César-François Cassini de Thury born. In 1744, he will begin the construction of a great topographical map of France, one of the landmarks in the history of cartography. Completed by his son Jean-Dominique, Cassini IV and published by the Académie des Sciences from 1744 to 1793, its 180 plates will be known as the Cassini map.
1832: Chemist and physicist William Crookes born. Crookes will be a pioneer of vacuum tube technology, developing the partially evacuated Crookes tube circa 1869-1875.
1925: Pharmacologist and chemist Alexander Shulgin born. He will discover, synthesize, and personally bioassay over 230 psychoactive compounds for their psychedelic and entactogenic potential.
1932: Bonus Army: Around a thousand World War I veterans amass at the United States Capitol as the U.S. Senate considers a bill that would give them certain benefits.
1972: Watergate scandal (nonfiction): Five White House operatives are arrested for burgling the offices of the Democratic National Committee, in an attempt by some members of the Republican party to illegally wiretap the opposition.
2022: Self portrait.
1178: Five Canterbury monks see what is possibly the Giordano Bruno crater being formed. It is believed that the current oscillations of the Moon's distance from the Earth (on the order of meters) are a result of this collision.
1348: Physician and academic Gentile Gentili da Foligno dies. Da Foligno was among the first European physicians to perform a dissection on a human being (1341).
1910: Statistician Maurice Stevenson Bartlett born. Bartlett will make contributions to the analysis of data with spatial and temporal patterns, the theory of statistical inference, and multivariate analysis.
1922: Astronomer and academic Jacobus Kapteyn dies. Kapteyn conducted extensive studies of the Milky Way using photography and statistical methods to determine the motions and distribution of stars, discovering evidence for galactic rotation.
1974: Mathematician and academic Júlio César de Mello e Souza dies. He is well known in Brazil and abroad by his books on recreational mathematics, most of them published under the pen names of Malba Tahan and Breno de Alencar Bianco.
1623: Mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and Christian philosopher Blaise Pascal born. He will do pioneering work on calculating machines.
1771: Mathematician and logician Joseph Diez Gergonne born. He will contribute to the principle of duality in projective geometry, by noticing that every theorem in the plane connecting points and lines corresponds to another theorem in which points and lines are interchanged, provided that the theorem embodied no metrical notions.
1795: Surgeon and gentleman scientist James Braid born. He will be an important and influential pioneer of hypnotism and hypnotherapy.
2022: Apples.
1840: Samuel Morse receives the patent for the telegraph.
1875: Inventor and engineer Wilhelm Bauer dies. He designed and built several hand-powered submarines.
1877: Alexander Graham Bell installs the world's first commercial telephone service in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
2024: Self portrait.
1652: Architect Inigo Jones dies. He was one of the first architects of the early modern period to employ Vitruvian rules of proportion and symmetry in his buildings.
1781: Mathematician and physicist Siméon Denis Poisson born. His memoirs on the theory of electricity and magnetism will constitute a new branch of mathematical physics.
1948: Biologist, mathematician, and classics scholar D'Arcy Wentworth Thompson dies.
1633: The Holy Office in Rome forces Galileo Galilei to recant his view that the Sun, not the Earth, is the center of the Universe in the form he presented it in, after heated controversy.
1633: Rogue mathematician and alleged supervillain taunts Galileo Galilei for recanting, daring Galileo to "tell it like it is, and let them burn you for it."
1864: Mathematician and academic Hermann Minkowski born. He will show that Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity can be understood geometrically as a theory of four-dimensional space–time, since known as the "Minkowski spacetime".
1910: Engineer, inventor, and pioneering computer scientist Konrad Zuse born. He will invent the Z3, the world's first working programmable, fully automatic computer.
1977: Mathematician Gabriel Sudan dies. He discovered the Sudan function, an important example in the theory of computation, similar to the Ackermann function.
1390: Priest, philosopher, physicist, and theologian John Cantius born. He will help develop Jean Buridan's theory of impetus, anticipating the work of Galileo and Newton.
1912: Computer scientist, mathematician, logician, cryptanalyst and theoretical biologist Alan Turing born. He will be influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalization of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine.
1959: Convicted Manhattan Project spy Klaus Fuchs is released after only nine years in prison and allowed to emigrate to Dresden, East Germany where he resumes a scientific career.
1972: Watergate scandal: U.S. President Richard M. Nixon and White House Chief of Staff H. R. Haldeman are taped talking about using the Central Intelligence Agency to obstruct the Federal Bureau of Investigation's investigation into the Watergate break-ins.
1709: The public test of the "Passarola", a primitive airship devised by priest and inventor Bartolomeu de Gusmão, fails to take place.
1880: Mathematician and academic Oswald Veblen born. His work will find application in atomic physics and the theory of relativity. Veblen will publish a paper (1912) on the Four color conjecture.
2008: Mathematician and academic Gerhard Ringel dies. Ringel was a pioneer of graph theory and contributed significantly to the proof of the Heawood conjecture (now the Ringel-Youngs theorem), a mathematical problem closely linked with the Four color theorem.
2016: Steganographic analysis of Boxes unexpectedly reveals previously unknown type of cryptographic numen. APTO engineers call it "a remarkable breakthrough."
1593: Physician and archaeologist Michele Mercati dies. He was one of the first scholars to recognize prehistoric stone tools as human-made rather than natural or mythologically created thunderstones.
1671: Priest and astromomer Giovanni Battista Riccioli dies. He experimented with pendulums and falling bodies, discussed arguments concerning the motion of the Earth, and introduced the current scheme of lunar nomenclature.
1907: Nuclear physicist J. Hans D. Jensen born. He will share half of the 1963 Nobel Prize in Physics with Maria Goeppert-Mayer for their proposal of the nuclear shell model.
1997: An unmanned Progress spacecraft collides with the Russian space station Mir.
2011: Computer scientist, mathematician, and engineer Annie Easley dies. She was a leading member of the team which develops software for the Centaur rocket stage, and one of the first African-Americans to work as a computer scientist at NASA.
1274: Polymath Nasir al-Din al-Tusi dies. Tusi was a mathematician, architect, philosopher, physician, scientist, and theologian; he established trigonometry as a mathematical discipline in its own right.
1730: Astronomer Charles Messier born. He will publish an astronomical catalogue consisting of nebulae and star clusters that will come to be known as the 110 "Messier objects".
1796: Inventor, astronomer, mathematician, clockmaker, and surveyor David Rittenhouse dies. He was the first Director of the United States Mint, hand-striking the new nation's first coins.
1824: Lord Kelvin born. He will do much to unify the emerging discipline of physics in its modern form.
1913: Computer scientist and physicist Maurice Wilkes born. He will pioneer several important developments in computing, including microcode, symbolic labels, macros, subroutine libraries, and timesharing.
2020: Accidental self portrait @ 8:28 pm.
1806: Mathematician and academic Augustus De Morgan born. De Morgan will formulate two laws, now De Morgan's Laws, pertaining to mathematical induction: (1) the negation of a disjunction is the conjunction of the negations; (2) the negation of a conjunction is the disjunction of the negations.
1831: Mathematician, physicist, and philosopher Sophie Germain dies. Her work on Fermat's Last Theorem provided a foundation for mathematicians exploring the subject for hundreds of years after.
1880: Mathematician and academic Carl Wilhelm Borchardt dies. He contributed to arithmetic-geometric mean theory, continuing work by Gauss and Lagrange.
1975: Mathematician and physicist G. I. Taylor dies. He made major contributions to fluid dynamics and wave theory.
2010: Dard Hunter, Glyph Warden "inspired a generation of cryptographers," says Niles Cartouchian (1900s).
1598: Cartographer and geographer Abraham Ortelius dies. Ortelius created the first modern atlas, the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. He was also one of the first to imagine that the continents were joined together before drifting to their present positions.
1712: Philosopher and author Jean-Jacques Rousseau born. His political philosophy will influence the Enlightenment in France and across Europe.
1824: Physician, anatomist, and anthropologist Paul Broca born. He will discover that the brains of patients suffering from aphasia contain lesions in a particular part of the cortex, in the left frontal region -- the first anatomical proof of the localization of brain function.
1825: Chemist and academic Emil Erlenmeyer born. He will contribute to the early development of the theory of structure, formulating the Erlenmeyer rule, and designing the Erlenmeyer flask.
1875: Mathematician and academic Henri Lebesgue born. He will gain fame for his his theory of integration, which generalizes the 17th century concept of integration (summing the area between an axis and the curve of a function defined for that axis).
1889: Astronomer and academic Maria Mitchell dies. She was the first American woman to work as a professional astronomer.
1906: Physicist and academic Maria Goeppert-Mayer born. She will develop a mathematical model for the structure of nuclear shells, for which she will be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1963, which she will share with J. Hans D. Jensen and Eugene Wigner.
2023: Evening rain @ 9:03.
1818: Astronomer, academic, and Jesuit Angelo Secchi born. Secchi will be a pioneer of astronomical spectroscopy, and one of the first scientists to state authoritatively that the Sun is a star.
1868: Astronomer and journalist George Ellery Hale born. He will discover magnetic fields in sunspots, and be leader or key figure in the planning or construction of several world-leading telescopes.
1895: Biologist Thomas Henry Huxley dies. He is known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his advocacy of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
1896: Physicist Boris Yakovlevich Podolsky born. He will work with Albert Einstein and Nathan Rosen on entangled wave functions and the EPR paradox.
2010: Chemist Marc Julia dies. Julia (along with his colleague Jean-Marc Paris) discovered the Julia olefination reaction in 1973.
1660: Mathematician William Oughtred dies. He invented the slide rule in 1622.
1770: Astronomer Charles Messier is elected to the French Academy of Sciences.
1905: Albert Einstein sends the article "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", in which he introduces special relativity, for publication in Annalen der Physik.
1908: The Tunguska event occurs in remote Siberia.
1956: The Tunguska Event Preservation Society launches fundraiser to simulate the 1927 Tunguska expedition.
July
1646: Mathematician and philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz born. He will develop differential and integral calculus independently of Isaac Newton, and design and build mechanical calculators.
1819: Johann Georg Tralles discovers the Great Comet of 1819 (C/1819 N1). It was the first comet analyzed using polarimetry, by François Arago.
1881: The world's first international telephone call is made between St. Stephen, New Brunswick, Canada, and Calais, Maine, United States.
2001: Physicist and educator Nikolay Basov dies. He did fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics.
2019: The Custodian says he is "not planning on retiring any time soon."
1613: Mathematician, astronomer, and theologian Bartholomaeus Pitiscus dies. Pitiscus coined the word "trigonometry".
1698: Thomas Savery patents the first steam engine. Savery's patent will force Thomas Newcomen into partnership with him.
1778: Philosopher and author Jean-Jacques Rousseau dies. His political philosophy influenced the Enlightenment in France and across Europe.
1897: British-Italian engineer Guglielmo Marconi obtains a patent for radio in London.
1937: Pilot and author Amelia Earhart disappears. She set many records, wrote best-selling books about her flying experiences, and was instrumental in the formation of The Ninety-Nines, an organization for female pilots.
1518: Physician and scientist Li Shizhen born. He will develop many innovative methods for the proper classification of herb components and medications to be used for treating diseases, earning a reputation as the greatest scientific naturalist of China.
1881: Astronomer, mathematician, and philosopher Hasan Tahsini dies. He was one of the most prominent scholars of the Ottoman Empire of the 19th century.
1969: The biggest explosion in the history of rocketry occurs when the Soviet N1 rocket explodes and subsequently destroys its launchpad.
2007: NASA approves a mission extension for Stardust, sending the spacecraft to comet Tempel 1.
1868: Astronomer Henrietta Swan Leavitt born. She will discover the relation between the luminosity and the period of Cepheid variable stars.
1900: Physicist and academic Ukichiro Nakaya born. He will create the first artificial snowflakes.
1934: Marie Curie, French-Polish physicist and chemist dies. She conducted pioneering research on radioactivity, discovering the elements polonium and radium.
1934: Leo Szilard patents the chain-reaction design that will later be used in the atomic bomb.
1935: Outbreak of Geometrical frustration exposes new class of crimes against mathematical constants.
1951: Physicist and engineer William Shockley announces the invention of the junction transistor.
1983: Physician, confidence trickster, and suspected serial killer John Bodkin Adams dies.
2005: The Deep Impact collider hits the comet Tempel 1.
1687: Isaac Newton publishes Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ("Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy"). Principia states Newton's laws of motion, forming the foundation of classical mechanics; Newton's law of universal gravitation; and a derivation of Kepler's laws of planetary motion (which Kepler first obtained empirically).
1833: Inventor Nicéphore Niépce dies. He invented heliography, a technique which he used to create the world's oldest surviving product of a photographic process.
1942: Mathematician Oskar Bolza dies. He is known for his research in the calculus of variations; his work on variations for an integral problem involving inequalities later became important in control theory.
2009: Discovery of the Staffordshire hoard, the largest hoard of Anglo-Saxon gold ever discovered in England, consisting of more than 1,500 items found near the village of Hammerwich, near Lichfield, Staffordshire.
1423: Mathematician and architect Antonio Manetti born. He will investigate the site, shape and size of Dante's Inferno, and write a biography of the architect Filippo Brunelleschi.
1476: Mathematician, astronomer, and bishop Johann Regiomontanus dies. He madecontributions to astromony which will be instrumental in the development of Copernican heliocentrism in the following decades.
1913: Mathematician Jordan Carson Mark born. He will oversee the development of nuclear weapons for the US military, including the hydrogen bomb in the 1950s.
1990: The Electronic Freedom Foundation is founded. EFF is an international non-profit digital rights group based in San Francisco, California.
1752: Weaver and merchant Joseph Marie Jacquard born. He will invent the Jacquard loom, an early type of programmable machine.
1945: Advances in dynastic cellular automata theory reveal new members of Bernoulli family.
1946: Aviator Howard Hughes nearly dies when his XF-11 reconnaissance aircraft prototype crashes in a Beverly Hills neighborhood.
1695: Mathematician, astronomer, and physicist Christiaan Huygens dies. He was a leading scientist of his time.
1766: Physician and surgeon Dominique Jean Larrey born. He will be an important innovator in battlefield medicine and triage, now often considered the first modern military surgeon.
1947: The Roswell UFO incident, the (supposed) crash of an alien spaceship near Roswell in New Mexico.
1960: Pilot Francis Gary Powers is charged with espionage resulting from his flight over the Soviet Union.
1774: Anatomist and anatomical wax modeler Anna Morandi Manzolini dies. Her collection of wax models gained fame throughout Europe as Supellex Manzoliniana; it was sought after to aid in the study of anatomy.
1824: Physician, anatomist, and anthropologist Paul Broca born. He will discover that the brains of patients suffering from aphasia contain lesions in a particular part of the cortex, in the left frontal region -- the first anatomical proof of the localization of brain function.
1911: Theoretical physicist John Archibald Wheeler born. He will link the term "black hole" to objects with gravitational collapse, and coin the terms "quantum foam", "neutron moderator", "wormhole" and "it from bit".
1918: Mathematician and theorist Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn born. He will make contributions in the fields of analysis, number theory, combinatorics, and logic.
1996: Physicist Edward P. Ney dies. Ney made major contributions to cosmic ray research, atmospheric physics, heliophysics, and infrared astronomy, discovering cosmic ray heavy nuclei and solar proton events. He pioneered the use of high altitude balloons for scientific investigations, and was one of the first researchers to put experiments aboard spacecraft.
1682: Mathematician and astronomer Roger Cotes born. Cotes will work closely with Isaac Newton, proofreading the second edition of Newton's Principia. Cotes also invented the quadrature formulas known as Newton–Cotes formulas, and first introduced what is known today as Euler's formula.
1856: Electrical engineer Nikola Tesla born. He will make pioneering contributions to the design of the modern alternating current (AC) electricity supply system.
1962: Telstar 1, the world's first communications satellite, is launched into orbit. Two days later Telstar will relay a live television signal across the Atlantic.
Greens is a 1985 American epic historical drama film, co-written, produced, and directed by Warren Beatty about the bombing of the Greenpeace ship Rainbow Warrior on 10 July 1985 by agents of the French foreign intelligence services. Co-starring Diane Keaton and Edward Abbey.
2017: Signed first edition of Albert Einstein and Alice Beta Conducting Research sells for ten millions dollars at a charity benefit for victims of crimes against mathematical constants.
1732: Astronomer, freemason, and writer Joseph Jérôme Lefrançois de Lalande born. As a lecturer and writer Lalande will help popularize astronomy. His planetary tables will be the best available up to the end of the 18th century.
1801: Astronomer Jean-Louis Pons makes his first comet discovery. In the next 27 years he discovers another 36 comets, more than any other person in history.
1812: Physicist and academic Petrus Leonardus Rijke born. He will explore the physics of electricity, and be known for the Rijke tube (which turns heat into sound, by creating a self-amplifying standing wave).
1931: Physicist and academic Tullio Regge born. He and G. Ponzano will develop a quantum version of Regge calculus in three space-time dimensions now known as the Ponzano-Regge model; this will be the first of a whole series of state sum models for quantum gravity known as spin foam models.
1958: EDSAC, the first practical electronic digital stored-program computer, is shut down, having been superseded by EDSAC 2.
1854: George Eastman born. He will found the Eastman Kodak Company and popularize the use of roll film, helping to bring photography to the mainstream.
1895: Polymath Richard Buckminster "Bucky" Fuller born. Fuller was, among other things, an architect, systems theorist, author, designer, inventor, and futurist.
1917: The Bisbee Deportation: vigilantes kidnap and deport nearly 1,300 striking miners and others from Bisbee, Arizona.
1935: Alfred Dreyfus dies. He was wrongly convicted of treason during the Dreyfus affair.
100 BC: Roman general and statesman Julius Caesar born. He will play a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire.
1527: Mathematician, astronomer, and astrologer John Dee born. He will achieve high status as a scholar and play a role in Elizabethan politics.
1896: Organic chemist Friedrich August Kekulé dies. From the 1850s until his death, Kekulé was one of the most prominent chemists in Europe, especially in theoretical chemistry. He was the principal founder of the theory of chemical structure.
1956: John McCarthy (Dartmouth College), Marvin Minsky (MIT), Claude Shannon (Bell Labs), and Nathaniel Rochester (IBM) assemble the first coordinated research meeting on the topic of "Artificial intelligence" at Dartmouth College in Hanover, NH. USA.
1972: Signed first edition of Skip Digits, Conductor sells for one million dollars; House Democrats say money trail leads to Richard Nixon.
1973: Watergate scandal (nonfiction): Alexander Butterfield reveals the existence of the "Nixon tapes" to the special Senate committee investigating the Watergate break-in.
1974: Mathematician and crime-fighter Hilary Putnam publishes his landmark paper arguing that mathematics is not purely logical, but "quasi-empirical", and that we should beware the possibility of "quasi-empirical crimes".
1856: Mathematician Charles Hermite is elected to fill the vacancy created by the death of Jacques Binet in the Académie des Sciences.
1904: German diplomat and intelligence officer Hans Bernd Gisevius born. Gisevius will be covert opponent of the Nazi regime, and a radical communist; he will serve as a liaison in Zürich between Allen Dulles, station chief for the American OSS, and the German Resistance forces in Germany.
1962: United States Army tests Small Boy, a tactical nuclear weapon, at the Nevada Test Site. Yield was 1.65 kt.
1965: The Mariner 4 flyby of Mars takes the first close-up photos of another planet.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates fifty-second anniversary of the Mariner 4 flyby of Mars.
998: Mathematician and astronomer Abū al-Wafā' Būzjānī dies. His Almagest was widely read by medieval Arabic astronomers in the centuries after his death.
1573: Architect Inigo Jones born. He will be one of the first architects of the early modern period to employ Vitruvian rules of proportion and symmetry in his buildings.
1848: Engineer, sociologist, economist, political scientist, and philosopher Vilfredo Pareto born. He will apply mathematics to economic analysis, asserting that the distribution of incomes and wealth in society is not random and that a consistent pattern appears throughout history, in all parts of the world and in all societies.
1865: Mathematician Wilhelm Wirtinger born. He will contribute to complex analysis, geometry, algebra, number theory, Lie groups and knot theory.
2004: Mathematician Derek Taunt dies. He worked as a codebreaker at Bletchley Park during World War II. Taunt was assigned to Hut 6, the section in charge of decrypting German Army and Air Force Enigma signals. After his wartime work, he returned to Cambridge, and worked on group theory.
2013: Computer scientist and academic John T. Riedl dies. He was a founder of the field of recommender systems, social computing, and interactive intelligent user interface systems.
1746: Priest, mathematician, and astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi born. He will discover dwarf planet Ceres.
1945: World War II: The heavy cruiser USS Indianapolis leaves San Francisco with parts for the atomic bomb "Little Boy" bound for Tinian Island. See Manhattan Project.
1945: Trinity nuclear weapon test: the United States successfully detonates a plutonium-based test nuclear weapon near Alamogordo, New Mexico. See Manhattan Project.
1973: Watergate scandal: Former White House aide Alexander Butterfield informs the United States Senate that President Richard Nixon had secretly recorded potentially incriminating conversations.
1988: Nuclear physicist Herbert L. Anderson dies. Anderson contributed to the Manhattan Project: he was a member of the team which made the first demonstration of nuclear fission in the United States, in the basement of Pupin Hall at Columbia University, and he participated in the first atomic bomb test, code-named Trinity.
1845: Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey dies. His government saw the abolition of slavery in the British Empire.
1911: Writer and philosopher Culvert Origenes criticized for his unpatriotic opinions.
1912: Mathematician, physicist, and engineer Henri Poincaré dies. He made many original fundamental contributions to pure and applied mathematics, mathematical physics, and celestial mechanics.
1920: Physicist and academic Gordon Gould born. He will invent and name the laser.
1944: The Port Chicago disaster: Munitions detonate while being loaded onto a cargo vessel bound for the Pacific Theater of Operations, killing 320 sailors and civilians and injuring 390 others at the Port Chicago Naval Magazine in Port Chicago, California, United States.
1944: Mathematician and anthropologist William James Sidis dies. He became famous first for his precocity and later for his eccentricity and withdrawal from public life.
1039: Composer, mathematician, and astronomer Hermann of Reichenau born. He will write a treatise on the science of music, several works on geometry and arithmetic, and astronomical treatises (including instructions for the construction of an astrolabe, then a very novel device in Western Europe).
1853: Physicist and academic Hendrik Lorentz born. He will share the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman for the discovery and theoretical explanation of the Zeeman effect.
1872: In a lecture to the Berlin Academy, mathematician Karl Weierstrass gives the classic example of a continuous nowhere differential function.
1966: Human spaceflight: Gemini 10 is launched from Cape Kennedy on a 70-hour mission that includes docking with an orbiting Agena target vehicle.
1967: Engineer, pilot, and alleged time-traveller Henrietta Bolt tells fellow astronauts that Gemini 10 "was an inspiration to us all."
1997: Geologist and astronomer Eugene Merle Shoemaker dies. Shoemaker was the first scientist to conclude that Barringer Meteor Crater in Arizona, and similar craters, were caused by meteor impact.
1631: Philosopher and academic Cesare Cremonini dies. His work promoted rationalism (against revelation) and Aristotelian materialism (against the dualist immortality of the soul) inside scholasticism.
1814: Engineer and businessman Samuel Colt born. He will found Colt's Manufacturing Company.
1894: Mathematician and academic Aleksandr Khinchin born. He will become one of the founders of modern probability theory.
1982: Physicist Hugh Everett III dies. He proposed the many-worlds interpretation (MWI) of quantum physics.
1597: Scholar, printer, and bookseller Franciscus Raphelengius dies. Raphelengius produced an Arabic-Latin dictionary, about 550 pages, which was published posthumously in 1613 at Leiden — the first publication by printing press of a book-length dictionary for the Arabic language in Latin.
1866: Mathematician and academic Bernhard Riemann dies. He made contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry.
1932: In Washington, D.C., police fire tear gas on World War I veterans, part of the Bonus Expeditionary Force, who attempt to march to the White House.
1937: Businessman and inventor Guglielmo Marconi dies. He shared the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Karl Ferdinand Braun "in recognition of their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy".
1945: The United States Secretary of State approves the transfer of Wernher von Braun and his team of Nazi rocket scientists to the U.S. under Operation Paperclip.
1977: Project MKUltra (nonfiction): The Central Intelligence Agency releases documents under the Freedom of Information Act revealing it had engaged in mind-control experiments.
2018: Pin Man says he "was an unwilling test subject in the Project MKUltra (nonfiction)."
1810: Chemist and physicist Henri Victor Regnault born. He will be an early thermodynamicist, best known for his careful measurements of the thermal properties of gases, and for mentoring William Thomson in the late 1840s.
1911: Professor of English and philosopher of communication theory Marshall McLuhan born. He will coin the expressions "the medium is the message" and "global village".
1966: Human spaceflight: Gemini 10 recovered after a 70-hour mission that included docking with an orbiting Agena target vehicle.
1826: Priest, mathematician, and astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi dies. He discovered the dwarf planet Ceres.
1827: Gem detective and astronomer Niles Cartouchian discovers time crystals on the dwarf planet Ceres.
1827: Engineer and inventor Sandford Fleming dies. He proposed worldwide standard time zones.
1932: Inventor Reginald Fessenden dies. He performed pioneering experiments in radio, including the use of continuous waves and the early—and possibly the first—radio transmissions of voice and music.
1962: Engineer, pilot, and alleged time-traveler Henrietta Bolt tries to warn NASA that Mariner 1 has been targeted by math criminals.
1962: Mariner program: Mariner 1 spacecraft flies erratically several minutes after launch and has to be destroyed.
1965: Computer hacker Karl Koch born. Koch will be a cold war computer hacking incident involved in selling hacked information from United States military computers to the KGB. His death by fire will be ruled a suicide.
1754: Joseph-Louis Lagrange publishes his first work, in the form of a letter in Italian. A month later he realized that he had rediscovered Leibniz's formula for the nth derivative of a product.
1829: William Austin Burt patents the typographer, a precursor to the typewriter.
1928: Astronomer and academic Vera Rubin born. She will discover the discrepancy between the predicted angular motion of galaxies and the observed motion, by studying galactic rotation curves.
1962: Telstar relays the first publicly transmitted, live trans-Atlantic television program, featuring Walter Cronkite.
1786: Mathematician and explorer Joseph Nicollet born. He will map the Upper Mississippi River basin during the 1830s.
1897: Pilot and author Amelia Earhart born. She will set many records, write best-selling books about her flying experiences, and be instrumental in the formation of The Ninety-Nines, an organization for female pilots.
1901: O. Henry is released from prison in Columbus, Ohio after serving three years for embezzlement from a bank.
1909: Mathematician and cryptologist Jerzy Różycki born. Różycki will work at breaking German Enigma-machine ciphers before and during World War II.
1934: Mathematician and philosopher Hans Hahn dies. He made contributions to functional analysis, topology, set theory, the calculus of variations, real analysis, and order theory.
1974: Watergate scandal: The United States Supreme Court unanimously ruled that President Richard Nixon did not have the authority to withhold subpoenaed White House tapes and they order him to surrender the tapes to the Watergate special prosecutor.
1616: Physician, alchemist and chemist Andreas Libavius dies. He accepted the Paracelsian principle of using occult properties to explain phenomena with no apparent cause, but rejected the conclusion that a thing possessing these properties must have an astral connection to the divine.
1748: Astronomer Charles Messier's interest in astronomy is stimulated by an annular solar eclipse visible from his hometown.
1808: Mathematician Johann Benedict Listing born. He will introduce the term "topology", first in correspondence, then in a famous article published in 1847.
1837: The first commercial use of an electrical telegraph is successfully demonstrated in London by William Cooke and Charles Wheatstone.
1842: Physician and surgeon Dominique Jean Larrey dies. He was an important innovator in battlefield medicine and triage, and is often considered the first modern military surgeon.
1920: Chemist and X-ray crystallographer Rosalind Franklin born. She will make contributions to the discovery of the molecular structure of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars observes a minute of silence in memory of the Viking 2 orbiter, which was turned off forty-one years ago, after returning almost 16,000 images in about 700–706 orbits around Mars.
1502: Christian Egenolff born. He will be the first important printer and publisher operating from Frankfurt-am-Main.
1684: Mathematician and philosopher Elena Cornaro Piscopia dies. She was one of the first women to receive an academic degree from a university, and the first to receive a Doctor of Philosophy degree.
1894: Writer and philosopher Aldous Huxley born. He will be widely acknowledged as one of the pre-eminent intellectuals of his time.
1918: Emmy Noether introduced what became known as Noether's theorem, from which conservation laws are deduced for symmetries of angular momentum, linear momentum, and energy.
1925: Mathematician, logician, and philosopher Gottlob Frege dies. Though largely ignored during his lifetime, his work influenced later generations of logicians and philosophers.
1941: Mathematician and academic Henri Lebesgue dies. He developed a theory of integration which generalizes the 17th century concept of integration (summing the area between an axis and the curve of a function defined for that axis).
1997: Mathematician and academic Kunihiko Kodaira dies. He did distinguished work in algebraic geometry and the theory of complex manifolds, winning the Fields medal in 1954.
2000: Mathematician and academic John Tukey dies. He made important contributions to statistical analysis, including the box plot.
1737: Natural scientist, explorer, and clergyman Erik Laxmann born. Laxmann will contribute to the taxonomy of Siberian fauna, and attempt to establish relations between Imperial Russia and Tokugawa Japan.
1801: Mathematician and astronomer George Biddell Airy born. His achievements will include work on planetary orbits, measuring the mean density of the Earth, and, in his role as Astronomer Royal, establishing Greenwich as the location of the prime meridian.
1837: Peter Dirichlet presented his first analytic number theory paper at a meeting of the Berlin Academy of Sciences. He proved the fundamental theorem that bears his name: Every arithmetical sequence an + b, n = 0, 1, 2, ... of integers, where a and b are relatively prime, contains infinitely many primes.
1844: Chemist, meteorologist, and physicist John Dalton dies. He proposed the modern atomic theory, and did research in color blindness.
1871: Logician and mathematician Ernst Friedrich Ferdinand Zermelo born. His work will have major implications for the foundations of mathematics; he will be known for his role in developing Zermelo–Fraenkel axiomatic set theory, and for his proof of the well-ordering theorem.
1928: Electrical engineer and physicist John Ambrose Fleming marries the popular young singer Olive May Franks of Bristol.
1938: Game designer Gary Gygax born.
1973: Math photographer Cantor Parabola takes advance photographs of the House of Representatives Judiciary Committee voting to recommend the first article of impeachment against President Nixon.
1974: Watergate scandal (nonfiction): The House of Representatives Judiciary Committee votes 27 to 11 to recommend the first article of impeachment (for obstruction of justice) against President Richard Nixon.
1619: Astronomer Johannes Kepler writes to Napier expressing his enthusiasm for Napier's invention of logarithms.
1818: Mathematician and engineer Gaspard Monge dies. He invented descriptive geometry, and did pioneering work in differential geometry.
1899: Georg Cantor asked Richard Dedekind whether the set of all cardinal numbers is itself a set, because, if it is, it would have a cardinal number larger than any other cardinal.
1902: Philosopher and academic Karl Popper born. He will be known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favor of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments.
1904: Physicist and academic Pavel Cherenkov born. Cherenkov will share the 1958 Nobel Prize in physics in 1958 with Ilya Frank and Igor Tamm for their discovery (1934) of Cherenkov radiation.
1932: U.S. President Herbert Hoover orders the United States Army to forcibly evict the Bonus Army.
1968: Chemist and academic Otto Hahn dies. He pioneered the fields of radioactivity and radiochemistry, winning the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1944 for the discovery and the radiochemical proof of nuclear fission.
1974: Watergate scandal: The House of Representatives Judiciary Committee votes 27 to 11 to recommend the first article of impeachment (for obstruction of justice) against President Richard Nixon.
1781: Astronomer and mathematician Johann Kies dies. He was one of the first to propagate Isaac Newton's discoveries in Germany, and dedicated two of his works to the Englishman.
1932: In Washington, D.C., troops disperse the last of the "Bonus Army" of World War I veterans.
1976: Dard Hunter, Glyph Warden "inspired a generation of cryptographers," says actor-cryptographer Niles Cartouchian.
1996: Mathematician and Doctor of Medicine Marcel-Paul Schützenberger dies. Schützenberger contributed to the fields of formal language, combinatorics, and information theory.
1832: Chemist, physician, agronomist, industrialist, statesman, educator, and philanthropist Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal dies.
1864: American Civil War: Battle of the Crater: Union forces attempt to break Confederate lines at Petersburg, Virginia by exploding a large bomb under their trenches.
1974: Watergate scandal: U.S. President Richard Nixon releases subpoenaed White House recordings after being ordered to do so by the Supreme Court of the United States.
1669: Isaac Newton becomes known. Lucasian professor Isaac Barrow sent John Collins a manuscript of Newton's De analysi and thereby Newton's anonymity began to dissolve. Although this manuscript was not published until 1704, it led to Newton's appointment as Lucasian professor on 29 October 1669.
1704: Mathematician and physicist Gabriel Cramer born. He will publish Cramer's rule, giving a general formula for the solution for any unknown in a linear equation system having a unique solution, in terms of determinants implied by the system.
1784: Philosopher, art critic, and writer Denis Diderot dies. He was a prominent figure during the Enlightenment, serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the Encyclopédie along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert.
1926: Philosopher, mathematician, and computer scientist Hilary Putnam born. He will argue for the reality of mathematical entities, later espousing the view that mathematics is not purely logical, but "quasi-empirical".
August
1774: British scientist Joseph Priestley discovers oxygen gas, corroborating the prior discovery of this element by German-Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele.
1819: Astronomer and academic Maria Mitchell born. She will be the first American woman to work as a professional astronomer.
1977: Francis Gary Powers dies when the news helicopter he is piloting crashes into a field near Encino, Los Angeles killing Powers and the aircraft's only passenger, cameraman George Spears.
1820: Physicist John Tyndall born. He will study diamagnetism, and make discoveries in the realms of infrared radiation and the physical properties of air.

1835: Electrical engineer Elisha Gray born. He will do pioneering work in electrical information technologies, including the telephone.
1887: Mathematician and statistician Oskar Anderson born. He will make important contributions to mathematical statistics and econometrics.
1922: Engineer, inventor, and academic Alexander Graham Bell dies. He patented the telephone in 1876.
1939: Albert Einstein writes President F. D. Roosevelt that "some recent work by E. Fermi and L. Szilard ... leads me to expect that the element uranium may be turned into a new and important source of energy in the immediate future. This new phenomenon would also lead to the construction of bombs, and it is conceivable--though much less certain--that extremely powerful bombs of a new type may be constructed." Roosevelt quickly starts the Manhattan Project.
1792: Inventor, engineer, and businessman Richard Arkwright dies. Later in his life Arkwright was known as the "father of the modern industrial factory system." Pic.
1917: Mathematician and academic Ferdinand Georg Frobenius dies. He made contributions to the theory of elliptic functions, differential equations, and group theory.
1918: Chemist and spymaster Sidney Gottlieb born. Gottlieb will be known as "America's Poisoner" for his development of assassination weapons for the CIA, and for his leadership in the Project MKUltra mind control program.
1805: Physicist, astronomer, and mathematician William Rowan Hamilton born. He will make important contributions to classical mechanics, optics, and algebra, inventing the quaternion.
1834: Mathematician and philosopher John Venn born. He will invent the Venn diagram, now widely used set theory, probability, logic, statistics, and computer science.
1802: Mathematician and theorist Niels Henrik Abel born. Abel will make pioneering contributions in a variety of fields, including the discovery of Abelian functions, and the first complete proof demonstrating the impossibility of solving the general quintic equation in radicals.
1816: The British Admiralty dismisses Francis Ronalds's new invention of the first working electric telegraph as "wholly unnecessary", preferring to continue using the semaphore.
1901: "Fightin'" Bert Russell agrees to fight three rounds of bare-knuckled boxing at World Peace Conference.
1910: Mathematician Julius Petersen dies. His famous paper Die Theorie der regulären graphs is a fundamental contribution to modern graph theory.
1914: In Cleveland, Ohio, the first electric traffic light is installed.
1920: Artist George Tooker born. His paintings will depict his subjects naturally, as in a photograph, but the images will use flat tones, an ambiguous perspective, and alarming juxtapositions to suggest an imagined or dreamed reality.
1994: Cryptanalyst and mathematician Solomon Kullback dies. Krullback began his career with the US Army's Signal Intelligence Service (SIS) in the 1930s; when the National Security Agency (NSA) was formed in 1952, Rowlett become chief of cryptanalysis, overseeing the research and development of computerized cryptanalysis.
1638: Priest and philosopher Nicolas Malebranche born. He will be instrumental in introducing and disseminating the work of René Descartes and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz in France.

1667: Mathematician Johann Bernouli born. He will make important contributions to infinitesimal calculus.
1881: Biologist, pharmacologist, and botanist Alexander Fleming born. Fleming will discover the enzyme lysozyme in 1923, and the world's first broadly effective antibiotic substance benzylpenicillin (Penicillin G) in 1928, for which he will share the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain.
1928: Artist Andy Warhol born. He will be a leading figure in the Pop art movement.
1991: Computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee releases files describing his idea for the World Wide Web. WWW debuts as a publicly available service on the Internet.
1996: NASA announces that the ALH 84001 meteorite, thought to originate from Mars, contains evidence of primitive life-forms.
2012: NASA's Curiosity rover lands on the surface of Mars.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates twenty-first anniversary of the NASA announcement that the ALH 84001 meteorite, thought to originate from Mars, contains evidence of primitive life-forms.
1834: Weaver and merchant Joseph Marie Jacquard dies. He invented the Jacquard loom, an early type of programmable machine.
1957: Stokes nuclear weapon test conducted by the United States.
1958: Cryptologist and author Herbert Yardley dies. Yardley founded and led the Black Chamber, a secret American government cryptographic organization which broke Japanese diplomatic codes, furnishing American negotiators with significant information during the Washington Naval Conference of 1921-1922.
1974: High-wire artist Philippe Petit performs a high wire act between the twin towers of the World Trade Center.
1975: Math photographer Cantor Parabola takes retro-temporal pictures of Philippe Petit's high wire act between the twin towers of the World Trade Center, revealing unexpected correspondences with other timelines.
1976: Viking program: Viking 2 inserted into a 1500 x 33,000 km, 24.6 h orbit around Mars.
2010: Mathematician and statistician John Nelder dies. He contributed to experimental design, analysis of variance, computational statistics, and statistical theory. He also was responsible, with Max Nicholson and James Ferguson-Lees, for debunking the Hastings Rarities.
2017: Dennis Paulson celebrates twenty-first anniversary of Viking 2 entering Mars orbit.
1555: Mathematician and cartographer Oronce Finé dies. He was imprisoned in 1524, probably for practicing judicial astrology.
1576: The cornerstone for Tycho Brahe's Uraniborg observatory is laid on the island of Hven.
1873: Scientist, inventor, and engineer Francis Ronalds dies. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph.
1900: David Hilbert delivers his famous "Mathematical problems" address: "We hear within us the perpetual call: There is a problem. Seek its solution. You can find it by pure reason, for in mathematics there is no 'ignorabimus'."
1921: Mathematician and academic Edwin Spanier born. Spanier will contribut to algebraic topology, co-inventing Spanier–Whitehead duality and Alexander–Spanier cohomology; also, his book on algebraic topology will become a standard textbook of its day.
1957: A day after the Stokes nuclear weapon test, large numbers of carnivorous dirigibles unexpectedly die.
1974: President Richard Nixon, in a nationwide television address, announces his resignation from the office of the President of the United States effective noon the next day.
2000: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley is raised to the surface after 136 years on the ocean floor and 30 years after its discovery by undersea explorer E. Lee Spence.
2001: NASA launches its unmanned spacecraft Genesis. The return capsule will crash-land in Utah on September 8, 2004, after a design flaw prevents the deployment of its drogue parachute.
2012: Nuclear physicist Fay Ajzenberg-Selove dies. She did important experimental work in nuclear spectroscopy of light elements, authoring annual reviews of the energy levels of light atomic nuclei.
1899: Chemist Edward Frankland dies. He was one of the originators of organometallic chemistry, introducing the concept of combining power or valence.
1927: Cognitive scientist and artificial intelligence researcher Marvin Minsky born.
1932: Mathematician John Charles Fields dies. He founded the Fields Medal for outstanding achievement in mathematics.
1974: As a direct result of the Watergate scandal, Watergate scandal, Richard Nixon becomes the first President of the United States to resign from office. His Vice President, Gerald Ford, becomes president.
2006: Physicist and philosopher James Van Allen dies. The Van Allen radiation belts are named after him, following their discovery by his Geiger–Müller tube instruments aboard satellites in 1958.
1602: Mathematician and academic Gilles de Roberval born. He will publish a system of the universe in which he supports the Copernican heliocentric system and attributes a mutual attraction to all particles of matter.
1792: French Revolution: Storming of the Tuileries Palace: Louis XVI of France is arrested and taken into custody as his Swiss Guards are massacred by the Parisian mob.
1896: Aviation pioneer Otto Lilienthal, known as the flying man, dies from injuries sustained the day before when his glider fell and crashed.
1960: Mathematician and academic Oswald Veblen dies. His work found application in atomic physics and the theory of relativity.
2000: Mathematician and crime-fighter Armand Borel publishes new theory of linear algebraic groups with applications in detecting and preventing crimes against mathematical constants.
1578: Mathematician, cosmographer, and academic Pedro Nunes dies. One of the greatest mathematicians of his time, he is best known for his mathematical approach to navigation and cartography.
1673: Physician and astrologer Richard Mead born. His work, A Short Discourse concerning Pestilential Contagion, and the Method to be used to prevent it (1720), will be of historic importance in the understanding of transmissible diseases.
1854: Physicist and academic Macedonio Melloni dies. Melloni demonstrated that radiant heat has physical properties similar to those of light.
1921: Mathematician and computer scientist Tom Kilburn born. Over the course of a productive 30-year career, he will be involved in the development of five computers of great historical significance.
1974: Graphic designer and typographer Jan Tschichold dies. He was a leading advocate of Modernist design, but later condemn Modernist design in general as being authoritarian and inherently fascistic.
1995: Mathematician and logician Alonzo Church dies. He made major contributions to mathematical logic and the foundations of theoretical computer science.
2003: Mathematician and academic Armand Borel dies. He worked in algebraic topology, and in the theory of Lie groups, contributing to the creation of the contemporary theory of linear algebraic groups.
1827: Poet, painter, and printmaker William Blake dies. Largely unrecognized during his lifetime, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual arts of the Romantic Age. Although Blake was considered mad by contemporaries for his idiosyncratic views, he is held in high regard by later critics for his expressiveness and creativity, and for the philosophical and mystical undercurrents within his work.
1863: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley arrives at Charleston, South Carolina by rail. A pioneering vessel, Hunley will later played a small part in the American Civil War, revealing the advantages and the dangers of undersea warfare.
1865: Surgeon and scientist Joseph Lister performs the first antiseptic surgery, using carbolic acid (phenol) as a disinfectant.
1887: Physicist and academic Erwin Schrödinger born. He will be awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation.
1989: Physicist and inventor William Shockley dies. He shared the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for the invention of the point-contact transistor.
2005: The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) is launched. MRO contains a host of scientific instruments such as cameras, spectrometers, and radar, which will be used to analyze the landforms, stratigraphy, minerals, and ice of Mars.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates the twelfth anniversary of the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter launch.
1625: Physician, mathematician, and physicist Rasmus Bartholin born. He will discover the double refraction of a light ray by Iceland spar, publishing an accurate description of the phenomenon in 1669.
1819: Physicist and mathematician Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet born. He will make pioneering contributions to fluid dynamics (including the Navier–Stokes equations) and to physical optics.
1863: Artist Eugène Delacroix dies. His use of expressive brushstrokes and his study of the optical effects of color will shape the work of the Impressionists.
1942: Major General Eugene Reybold of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers authorizes the construction of facilities that would house the "Development of Substitute Materials" project, better known as the Manhattan Project.
1552: Statesman, scientist, and historian Paolo Sarpi born. He will be a proponent of the Copernican system, a friend and patron of Galileo Galilei, and a keen follower of the latest research on anatomy, astronomy, and ballistics at the University of Padua.
1777: Physicist and chemist Hans Christian Ørsted born. He will discover that electric currents create magnetic fields, which was the first connection found between electricity and magnetism.
1888: Engineer and inventor John Logie Baird born. He will be one of the inventors of the mechanical television.
1909: Inventor, engineer, and philanthropist William Stanley dies. He designed and manufactured precision drawing and mathematical instruments, as well as surveying instruments and telescopes.
2014: Scientists announce the identification of possible interstellar dust particles from the Stardust capsule, which returned to Earth in 2006.
1758: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer Pierre Bouguer dies. He is known as "the father of naval architecture".
1863: Mathematician and naval engineer Aleksey Krylov born. Fame will come to him in the 1890s, when his pioneering theory of oscillating motions of the ship becomes internationally known.
1892: Physicist and academic Louis de Broglie born. He will postulate the wave nature of electrons and suggest that all matter has wave properties, winning the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1929, after the wave-like behavior of matter is first experimentally demonstrated in 1927.
1977: The Big Ear, a radio telescope operated by Ohio State University as part of the SETI project, receives a radio signal from deep space; the event is named the "Wow! signal" from the notation made by a volunteer on the project.
1979: Led Zeppelin releases"Olive My Love".
1922: Physicist Peter Mazur dies. Mazur was a pioneer the field of non-equilibrium thermodynamics.
1650: Monk, cosmographer, and cartographer Vincenzo Coronelli born. He will gain fame for his atlases and globes; some of the globes will be very large and highly detailed.
1705: Mathematician Jacob Bernoulli dies. He discovered the fundamental mathematical constant e, and made important contributions to the field of probability.
1821: Mathematician and academic Arthur Cayley born. He will be the first to define the concept of a group in the modern way, as a set with a binary operation satisfying certain laws.
1883: The Orcagna scrying engine predicts that "the Father of Science Fiction will be born within a year."
1884: Inventor, writer, editor, and publisher Hugo Gernsback born. He will publish the first science fiction magazine, and have a profound influence on the development of science fiction.
1899: Chemist and academic Robert Bunsen dies. He investigated emission spectra of heated elements, and discovered caesium (in 1860) and rubidium (in 1861) with the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff.
2010: Mathematician, academic, and rabbi Eliezer 'Leon' Ehrenpreis dies. He proved the Malgrange–Ehrenpreis theorem, the fundamental theorem about differential operators with constant coefficients.
2017: The upcoming observation of the GW170817 gravitational wave signal, a significant breakthrough for multi-messenger astronomy, is allegedly hijacked before it can occur by a criminal transdimensional corporation. An emergency response team of police astronomers and high-energy physicists will locate the corporation and reverse the hijacking, causing the wave and its observation to occur on time.
1807: Robert Fulton's North River Steamboat leaves New York City for Albany, New York, on the Hudson River, inaugurating the first commercial steamboat service in the world.
1927: Mathematician Erik Ivar Fredholm dies. He introduced and analyzed a class of integral equations now called Fredholm equations. Fredholm's work on integral equations and operator theory anticipated the theory of Hilbert spaces.
1929: Captain and pilot Francis Gary Powers born.
1970: Soviet spacecraft Venera 7 launched from Earth. It will become the first successful soft landing on another planet (Venus).
2017: The GW170817 gravitational wave signal is observed by the LIGO/Virgo collaboration. It is the first gravitational wave event observed to have a simultaneous electromagnetic signal, a significant breakthrough for multi-messenger astronomy.
1634: Catholic priest Urbain Grandier, accused and convicted of sorcery, is burned alive in Loudun, France. He was the victim of a politically motivated persecution led by the powerful Cardinal Richelieu.
1910: Mathematician Pál Turán born. He will work primarily in number theory, but also contribute to analysis and graph theory.
1911: Computer scientist Klara Dan von Neumann born. She will be one of the world's first computer programmers and coders, solving mathematical problems using computer code.
1662: Mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and Christian philosopher Blaise Pascal dies. Pacal did pioneering work on calculating machines.
1758: Jean-Étienne Montucla received the censor's approbation for his Histoire des mathematiques, which is justly famous as a history of the mathematical sciences.
1822: Mathematician and astronomer Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre dies. He was one of the first astronomers to derive astronomical equations from analytical formulas.
1906: Inventor Philo Farnsworth born. He will make many crucial contributions to the early development of all-electronic television.
1913: Computer scientist, engineer, and academic John Argyris born. A pioneer of computer applications in science and engineering, Argyris will be among the creators of the finite element method.
1923: Engineer, sociologist, economist, political scientist, and philosopher Vilfredo Pareto dies. He applied mathematics to economic analysis, asserting that the distribution of incomes and wealth in society is not random and that a consistent pattern appears throughout history, in all parts of the world and in all societies.
1967: Inventor, writer, editor, and publisher Hugo Gernsback dies. He published the first science fiction magazine, and had a profound influence on the development of science fiction.
1993: Actor-cryptographer Niles Cartouchian confirms that he personally designed the computational security protocols featured in the action-adventure film Dard Hunter, Glyph Warden.
1994: Chemist, biochemist, peace activist, author, and educator Linus Pauling dies.
2015: A giant red ball breaks loose from an art installation and rolls down the street in Toledo, Ohio.
1672: Mathematician and politician Johan de Witt dies in a riot. The rioters will partially eat his body.
1797: Physicist and priest Francesco Zantedeschi born. Zantedeschi will be among the first to recognize the marked absorption by the atmosphere of red, yellow, and green light. He will also think that he detected, in 1838, a magnetic action on steel needles by ultraviolet light, anticipating later discoveries connecting light and magnetism.
1864: The Kinmon incident: a rebellion against the Tokugawa shogunate breaks out near the Imperial Palace in Kyoto. The rebels will seek to restore the Imperial household to its position of political supremacy.
1911: The first cable message sent around the world from the U.S. by commercial telegraph was transmitted from New York City. It read “This message sent around the world,” left the New York Times building at 7:00 pm and was received at 7:16 pm after travelling nearly 29,000 miles through 16 relays via the Azores, Gibraltar, India, Phillipines, Midway, Guam, Hawaii and San Francisco.
1912: Thomas Edison receives U.S. patent No. 1036470 for a “Phonographic Apparatus,” and No. 1036471 for a “Storage Battery.”
1942: The first visible quantity of a plutonium compound, plutonium(IV) iodate, is isolated by nuclear chemists Burris Cunningham and Louis Werner.
1961: Physicist and academic Percy Williams Bridgman dies. He won the 1946 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the physics of high pressures.
1962: Mathematician and crime-fighter Alice Beta publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.
2007: Cell and developmental biologist Elizabeth Dexter “Betty” Hay dies. Hay conducted pioneering research in limb regeneration, the role of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in cell differentiation, and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions (EMT).
1560: The occurrence at the predicted time of a solar eclipse in Copenhagen turns Tycho Brahe towards a life of observational astronomy.
1660: Physician, mathematician, and engineer Hubert Gautier born. Gautier will author the first book on bridge building, Traité des Ponts, in 1716, as well as books on roads, fortifications, antiquities, geology, and a first manual for watercolor practitioners.
1909: Mathematician and physicist Nikolay Bogolyubov born. His method of teaching, based on creation of a warm atmosphere, politeness, and kindness, will be renowned in Russia as the "Bogolyubov approach".
1910: Astrophysicist, astronomer, and mathematician Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar born. He will share the 1983 Nobel Prize for Physics "for his theoretical studies of the physical processes of importance to the structure and evolution of the stars".
1915: Engineer and American intelligence officer Robert Furman born. Furman will be chief of foreign intelligence for the Manhattan Project, directing espionage against the German nuclear energy project, and, near the end of the war, rounding up German atomic scientists.
1945: Physicist Harry Daghlian is fatally irradiated in a criticality accident during an experiment with the Demon core at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
1993: NASA loses contact with the Mars Observer.
2017: The destroyer USS John S. McCain collides with the tanker ship Alnic MC off the coast of Singapore, leaving ten of her crew dead and another five injured.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars broadcasts a minute of silence in recognition of the twenty-fourth anniversary of the loss of contact with Mars Observer.
1647: Physicist, mathematician, and inventor Denis Papin born. Papin will invent the steam digester, the forerunner of the pressure cooker and the steam engine.
1854: Poet Jan Kochanowski dies. He established poetic patterns which would become integral to the Polish literary language.
1920: Science fiction writer and screenwriter Ray Bradbury born. The New York Times will call Bradbury "the writer most responsible for bringing modern science fiction into the literary mainstream".
1974: Mathematician, historian of science, theatre author, poet, and inventor Jacob Bronowski dies.
1638: René Descartes, in a letter to Marin Mersenne, proposed his folium (x-cubed + y-cubed = 2axy) as a test case to challenge Pierre de Fermat's differentiation techniques. To Descartes' embarrassment, Fermat's method worked.
1829: Mathematician and historian Moritz Cantor born. He will write Vorlesungen über Geschichte der Mathematik, which traces the history of mathematics up to 1799.
1966: Lunar Orbiter 1 takes the first photograph of Earth from orbit around the Moon.
1999: Biochemist and crystallographer John Kendrew dies. He shared the 1962 Nobel Prize for chemistry with Max Perutz for determining the atomic structures of proteins using X-ray crystallography.
1561: Mathematician, astronomer, and theologian Bartholomaeus Pitiscus born. Pitiscus will coin the word "trigonometry".
1654: Blaise Pascal writes to Pierre de Fermat, describing his solution to the Problem of the Points (a probability problem) and asking Fermat to critique it.
1819: inventor, engineer, and chemist James Watt dies. He made major improvements to the steam engine.
1877: Canada grants Alexander Graham Bell a patent for the telephone.
1888: Rudolf Clausius dies. He was one of the central founders of the science of thermodynamics.
1891: Thomas Edison patents the motion picture camera.
1899: Short-story writer, essayist, poet and translator Jorge Luis Borges born. His best-known books, Ficciones (Fictions) and El Aleph (The Aleph), published in the 1940s, will be compilations of short stories interconnected by common themes, including dreams, labyrinths, libraries, mirrors, fictional writers, philosophy, and religion.
1922: Historian, playwright, and social activist Howard Zinn born. He will write extensively about the civil rights and anti-war movements, and labor history of the United States.
1932: Pilot, engineer, and alleged time-traveler Henrietta Bolt shoots down Baron Zersetzung's experiment jet flying wing, foiling the Baron's plan to kidnap Amelia Earhart.
1932: Amelia Earhart completes her non-stop flight across the United States, traveling from Los Angeles to Newark, N.J., in just over 19 hours. She was the first woman to fly nonstop across the US. Earlier in the same year, on 20 May 1932, she accomplished the first solo flight by a woman across the Atlantic Ocean.
1609: Galileo Galilei demonstrates his first telescope to Venetian lawmakers.
1699: Mathematician and mechanician Charles Étienne Louis Camus born. He will be the author of Cours de mathématiques (Paris, 1766), along with a number of essays on mathematical and mechanical subjects.
1819: inventor, engineer, and chemist James Watt dies. He made major improvements to the steam engine.
1934: Inventor Philo Farnsworth demonstrates his electronic television system to the public at the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia.
1948: The House Un-American Activities Committee holds first-ever televised congressional hearing: "Confrontation Day" between Whittaker Chambers and Alger Hiss.
1965: Biochemist Hedley Ralph Marston dies. Marston's research into fallout from the British nuclear tests at Maralinga proved that significant radiation hazards existed at many of the Maralinga sites long after the tests.
2012: Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause to become the first spacecraft to enter interstellar space and study the interstellar medium.
2016: Polymath George Spencer-Brown dies. Spencer-Brown wrote the unorthodox and influential Laws of Form, calling it the "primary algebra" and the "calculus of indications".
1713: Physicist, mathematician, and inventor Denis Papin dies. He invented the steam digester, the forerunner of the pressure cooker and of the steam engine.
1723: Biologist and microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek dies. Van Leeuwenhoek was a pioneer of microscopy who made fundamental contributions to the establishment of microbiology as a scientific discipline.
1728: Polymath Johann Heinrich Lambert born. He will make important contributions to mathematics, physics (particularly optics), philosophy, astronomy, and map projections.
1735: Leonhard Euler presents his solution to the Königsberg bridge problem – whether it was possible to find a route crossing each of the seven bridges of the city of Königsberg once and only once – in a lecture to his colleagues at the Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg.
1743: Chemist and biologist Antoine Lavoisier born. He will have a large influence on both the history of chemistry and the history of biology.
1795: Occultist and explorer Alessandro Cagliostro dies. He was a glamorous figure associated with the royal courts of Europe where he pursued psychic healing, alchemy, and scrying.
1900: Biochemist Hedley Ralph Marston born. Marston's research into fallout from the British nuclear tests at Maralinga will prove the existence of significant radiation hazards at many of the Maralinga sites long after the tests.
1918: Physicist and mathematician Katherine Johnson born. Johnson will compute orbital mechanics as a NASA employee which will be critical to the success of the first and subsequent U.S. crewed spaceflights; she will also pioneer the use of computers to perform these tasks.
1930: Philo Farnsworth is granted a ptent (U.S. 1,773,980) for his television system . This is his first patent, with a description of his image dissector tube, and his most important contribution to the development of television.
1974: Pilot and explorer Charles Lindbergh dies. At age 25 in 1927 he went from obscurity as a U.S. Air Mail pilot to instantaneous world fame by making his Orteig Prize–winning nonstop flight from Long Island, New York, to Paris.
1995: Writer and peace activist John Brunner dies.
1784: Apothecary and editor James Tytler made the first balloon ascent in Britain in a hot-air balloon at Edinburgh, Scotland. Before a small number of onlookers, the balloon rose to 350 feet in the air, travelled half a mile, and landed in Restalrig village.
1858: Mathematician Giuseppe Peano born. He will do pioneering work in mathematical logic and set theory.
1915: Physicist Norman Foster Ramsey Jr. born. He will be awarded the 1989 Nobel Prize in Physics for the invention of the separated oscillatory field method, which will have important applications in the construction of atomic clocks.
1926: Chemist and composer George Brecht born. He will be a conceptual artist and avant-garde composer, as well as a professional chemist who will work as a consultant for companies including Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Mobil Oil.
2003: Mars makes its closest approach to Earth in nearly 60,000 years, passing 34,646,418 miles (55,758,005 km) distant.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars wins Pulitzer Prize for Best Reality Television Show.
413 BC: A lunar eclipse caused panic among the sailors of the Athens fleet and thus affected the outcome of a crucial battle in the Peloponnesian War.
1789: With the first use of his new 1.2 m (3.9 ft) telescope, then the largest in the world, William Herschel discovered a new moon of Saturn, which was later named Enceladus.
1801: Mathematician and philosopher Antoine Augustin Cournot born. He will introduce the ideas of functions and probability into economic analysis.
1916: Sociologist and author C. Wright Mills born. He will be published widely in popular and intellectual journals, advocating public and political engagement over disinterested observation.
1780: Artist Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres born. He will assume the role of a guardian of academic orthodoxy against the ascendant Romantic style represented by his nemesis, Eugène Delacroix.
1863: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley sinks during a test run, killing five members of her crew.
1915: US Navy salvage divers raise USS F-4, the first U.S. submarine sunk in an accident.
2012: Mathematician and academic Shoshichi Kobayashi dies. He worked on Riemannian and complex manifolds, transformation groups of geometric structures, and Lie algebras.
1751: Scientist, inventor, and industrialist Christopher Polhem dies. He made significant contributions to the economic and industrial development of Sweden, particularly mining.
1844: Astronomer Francis Baily dies. He observed "Baily's beads" during an annular eclipse (1836).
1884: Chemist and academic Theodor Svedberg born. He will be awarded the 1926 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his pioneering use of analytical ultracentrifugation to distinguish pure proteins from one another.
1906: Mathematician and academic Olga Taussky-Todd born. She will contribute to matrix theory (in particular the computational stability of complex matrices), algebraic number theory, group theory, and numerical analysis.
1940: Physicist, academic, and Nobel laureate J. J. Thomson dies. His research in cathode rays led to the discovery of the electron. Thomson also discovered the first evidence for isotopes of a stable element.
1954: The Worcester Lunch Car Company's Research Division announces daily Flying Diner breakfast and dinner flights between San Francisco and New Minneapolis.
2013: Poet, playwright, translator, and lecturer Seamus Heaney dies. He received the 1995 Nobel Prize in Literature.
1897: Thomas Edison patents the Kinetoscope, the first movie projector.
1899: Georg Cantor writes to Dedekind, remarking that his "diagonal process" could be used to show that the power set of a set has more elements than the set itself.
1945: Mathematician and academic Stefan Banach dies. Banach was one of the founders of modern functional analysis.
1950: Mathematician and philosopher Kurt Gödel addresses the International Congress of Mathematicians, in Cambridge, Massachusetts, on his work in relativity theory.
September
1599: Explorer Cornelis de Houtman dies. He discovered a new sea route from Europe to Indonesia, beginning the Dutch spice trade.
1681: Mathematician Michelangelo Ricci created Cardinal.
1861: Chemist Lazăr Edeleanu born. Edeleanu will invent the modern method of refining crude oil, and will be the first chemist to synthesize amphetamine.
1938: Asclepius Myrmidon publishes On Halting Problems, about the computational and medical problem of determining, from a description of an arbitrary computer program and an input, whether the program will finish running or continue to run forever.
1982: Mathematician and academic Haskell Curry dies. He is known for his work in combinatory logic.
1768: French mathematician and engineer Antoine Deparcieux dies. He made a living manufacturing sundials.
1808: Carl Friedrich Gauss writes Wolfgang Bolyai: "It is not knowledge, but the act of learning, not possession but the act of getting there, which grants the greatest enjoyment."
1865: Physicist, astronomer, and mathematician William Rowan Hamilton dies. He made important contributions to classical mechanics, optics, and algebra, inventing the quaternion.
1948: Archaeologist and spy Sylvanus Morley dies. He conducted espionage in Mexico on behalf of the United States during World War I; the scope of these activities only came to light well after his death.
1658: Oliver Cromwell dies. He was a military and political leader and later Lord Protector of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland, and Ireland.
1803: Chemist John Dalton uses symbols to represent the atoms making up molecules of different elements.
1814: Mathematician and academic James Joseph Sylvester born. He will make fundamental contributions to matrix theory, invariant theory, number theory, partition theory, and combinatorics.
1925: USS Shenandoah, the United States' first American-built rigid airship, is destroyed in a squall line over Noble County, Ohio killing fourteen of her 42-man crew, including her commander, Zachary Lansdowne.
1928: Inventor Philo Farnsworth demonstrates his electronic television system to the press.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates the forty-first anniversary of the end of the Viking 2 spacecraft landing at Utopia Planitia on Mars.
1784: Astronomer and cartographer César-François Cassini de Thury dies. In 1744, he began the construction of a great topographical map of France, one of the landmarks in the history of cartography. Completed by his son Jean-Dominique, Cassini IV and published by the Académie des Sciences from 1744 to 1793, its 180 plates are known as the Cassini map.
1882: Thomas Edison flips the switch to the first commercial electrical power plant in history, lighting one square mile of lower Manhattan. This is considered by many as the day that began the electrical age.
1887: Math photographer Cantor Parabola and inventor George Eastman discuss advances in film technology.
1888: George Eastman registers the trademark Kodak and receives a patent for his camera that uses roll film.
1916: Civil engineer, mathematician, statesman, and one of the leading Spanish dramatists José Echegaray y Eizaguirre dies.
1923: Maiden flight of the first U.S. airship, the USS Shenandoah.
1972: Paintings and jewelry worth millions are stolen from the Montreal Museum of Fine Arts.
1575: Mathematician Federico Commandino born. He will gain fame for his central role as translator of works of ancient mathematicians.
1677: Theologian, natural philosopher, and diplomat Henry Oldenburg dies. He was one of the foremost intelligencers of Europe of the seventeenth century, and the creator of scientific peer review.
1725: Mathematician and theorist Jean-Étienne Montucla born. His deep interest in history of mathematics will become apparent with his publication of Histoire des Mathématiques, the first part appearing in 1758.
1947: Advances in dynastic cellular automata theory reveal new members of Bernoulli family.
1948: Physicist and chemist Richard C. Tolman dies. He made important contributions to theoretical cosmology in the years soon after Einstein's discovery of general relativity.
1977: Voyager 1 spacecraft launches. It will visit Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's large moon Titan.
1635: Mathematician and astronomer Adriaan Metius dies. He manufactured precision astronomical instruments, and published treatises on the astrolabe and on surveying.
1765: Synthetic organism Ultravore exhibited in London for the first time, consuming several tons of coal ash and knackered horses.
1732: Physicist and academic Johan Carl Wilcke born. He will invent the electrophorus, and calculate the latent heat of ice.
1766: Chemist, meteorologist, and physicist John Dalton born. He will propose the modern atomic theory, and do research in color blindness.
1803: British scientist John Dalton begins using symbols to represent the atoms of different elements.
1892: Physicist and academic Edward Victor Appleton born. Appleton will make pioneering contributions to radiophysics, winning the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1947 for his seminal work proving the existence of the ionosphere during experiments carried out in 1924.
2007: Writer Madeleine L'Engle dies. She wrote the Newbery Medal-winning A Wrinkle in Time and its sequels.
1799: Physiologist, biologist and chemist Jan Ingenhousz dies. Ingenhousz discovered photosynthesis, as well the fact that plants, like animals, have cellular respiration.
1828: Organic chemist Friedrich August Kekulé born. Kekulé will be one of the most prominent chemists in Europe, especially in theoretical chemistry, and the principal founder of the theory of chemical structure.
1914: Physicist and philosopher James Van Allen born. The Van Allen radiation belts will be named after him, following their discovery by his Geiger–Müller tube instruments aboard satellites in 1958.
1927: The first fully electronic television system is achieved by inventor Philo Farnsworth.
1930: Mathematician Kurt Godel announced his famous Incompleteness Theorem -- that there are true but unprovable statements in arithmetic -- in a discussion on the foundations of mathematics organized by the Vienna Circle.
1939: Soviet Air Defense office Stanislav Yevgrafovich Petrov born. Petrov will became known as "the man who single-handedly saved the world from nuclear war" for his role in the 1983 Soviet nuclear false alarm incident.
1985: Mathematician George Pólya dies. He made fundamental contributions to combinatorics, number theory, numerical analysis and probability theory.
1588: Mathematician, theologian, and philosopher Marin Mersenne born. He will be remembered as the "father of acoustics".
1637: Astrologer, mathematician, cosmologist, Qabalist and Rosicrucian apologist Robert Fludd dies.
1836: Physicist Arthur Williams Wright born. Wright will produce the first X-ray image, experiment with Röntgen rays, and make other contributions to electricity and astronomy.
1974: As a direct result of the Watergate scandal, Richard Nixon becomes the first President of the United States to resign from office. His Vice President, Gerald Ford, becomes president. US President Gerald Ford pardons former President Richard Nixon for any crimes Nixon may have committed while in office.
2004: NASA's unmanned spacecraft Genesis crash-lands when its parachute fails to open.
1737: Physician and physicist Luigi Galvani born. In 1780, he will discover that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitch when struck by an electrical spark.
1947: First case of a computer bug being found: A moth lodges in a relay of a Harvard Mark II computer at Harvard University.
1975: Viking program: Viking 2 launched. Following a 333-day cruise to Mars, the Viking orbiter will begin returning global images of Mars.
2003: Theoretical physicist and academic Edward Teller dies. He is known colloquially as "the father of the hydrogen bomb", although he did not care for the epithet.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars celebrates the forty-second anniversary of the launch of the Viking 2 spacecraft.
2018: Updated version of Embassy published. "The old version was so dark, it was barely visible. This version is much more to my taste," says artist Karl Jones.
1635: Mathematician Johann Faulhaber dies. Faulhaber calculated the sums of powers of integers.
1749: Mathematician and physicist Émilie du Châtelet born. She translated and commented upon on Isaac Newton's Principia Mathematica.
1849: Mathematician and philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce born. He wil be remembered as "the father of pragmatism".
1892: American physicist and academic Arthur Compton born. He will win the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1927 for his 1923 discovery of the Compton effect, demonstrating the particle nature of electromagnetic radiation.
1976: Screenwriter and novelist Dalton Trumbo dies. He was blacklisted for refusing testify before the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) in 1947; while blacklisted, he won Academy Awards for two films: Roman Holiday, attributed to a front author, and The Brave One under the pseudonym Robert Rich.
1470: Mapmaker Martin Waldseemüller born. He will produce a globular world map and a large 12-panel world wall map using the information from Columbus and Vespucci's travels (Universalis Cosmographia), both bearing the first use of the name "America".
1798: Mineralogist, physicist, and mathematician Franz Ernst Neumann born. His 1831 study on the specific heats of compounds will include what is now known as Neumann's Law: the molecular heat of a compound is equal to the sum of the atomic heats of its constituents.
1831: Mathematician Carl Jacobi appointed professor. After a four hour disputation in Latin, Jacobi was appointed professor at the University of Konigsberg. While there he inaugurated what was then a complete novelty in mathematics: research seminars for the more advanced students and interested colleagues.
1843: Mathematician and explorer Joseph Nicollet dies. He mapped the Upper Mississippi River basin during the 1830s.
1862: Short story writer O. Henry, known for his surprise endings, born.
1890: Felice Casorati dies. Casorati is best known for the Casorati–Weierstrass theorem in complex analysis.
1997: NASA's Mars Global Surveyor reaches Mars.
2013: Mathematician and computer scientist Andrzej Trybulec dies. He developed the Mizar system: a formal language for writing mathematical definitions and proofs, a proof assistant which is able to mechanically check proofs written in this language, and a library of formalized mathematics which can be used in the proof of new theorems.
1725: Astronomer Guillaume Le Gentil born. He will discover what are now known as the Messier objects M32, M36 and M38, as well as the nebulosity in M8, and he was the first to catalogue the dark nebula sometimes known as Le Gentil 3 (in the constellation Cygnus).
1900: Mathematician and academic Haskell Curry born. He will be known for his work in combinatory logic.
1902: Inventor Norman Lorimer Dean born. Dean will design the Dean drive, which he will promote as a reactionless drive.
1933: Leó Szilárd, waiting for a red light on Southampton Row in Bloomsbury, conceives the idea of the nuclear chain reaction.
1592: Philosopher and author Michel de Montaigne dies. He was one of the most significant philosophers of the French Renaissance, known for popularizing the essay as a literary genre.
1861: Mathematician Dmitry Mirimanoff born. In 1917, he will introduce the cumulative hierarchy of sets and the notion of von Neumann ordinals; although he will introduce a notion of regular (and well-founded set) he will not consider regularity as an axiom, but also explore what is now called non-well-founded set theory, and the idea of what is now called bisimulation.
1873: Mathematician and author Constantin Carathéodory born. He will pioneer the axiomatic formulation of thermodynamics along a purely geometrical approach.
1898: Priest and inventor Hannibal Goodwin patents celluloid photographic film.
1712: Mathematician, astronomer, and engineer Giovanni Domenico Cassini dies. He discovered four satellites of the planet Saturn and noted the division of the rings of Saturn; the Cassini Division was named after him.
1713: Astronomer and mathematician Johann Kies born. He will be one of the first to propagate Isaac Newton's discoveries in Germany, and willl dedicate two of his works to the Englishman.
1879: Weapons engineer and army officer Karl Heinrich Emil Becker born. He will promote the integration of scientific research into military goals, notably advanced weapons design.
1916: Physicist, mathematician, and historian Pierre Duhem dies. He wrote: "A theory of physics is not an explanation. It is a system of mathematical propositions, deduced from a small number of principles, which have for their aim to represent as simply, as completely and as exactly as possible, a group of experimental laws."
1960: The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is founded.
1736: Astronomer, mathematician, and politician Jean Sylvain Bailly born. His work as an astronomer lead to his recognition and admiration by the European scientific community.
- Isambard Kingdom Brunel
1859: Mechanical and civil engineer Isambard Kingdom Brunel dies. Brunel is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history".
1945: Physicist Harry Daghlian dies. He was fatally irradiated in a criticality accident during an experiment with the Demon core at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
2017: Mathematician and academic Hans F. Weinberger dies. He contributed to variational methods for eigenvalue problems, partial differential equations, and fluid dynamics.
1736: Physicist and engineer Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit dies. He helped lay the foundations for the era of precision thermometry by inventing the mercury-in-glass thermometer and the Fahrenheit scale.
2005: Physicist and academic Gordon Gould dies. He invented and named the laser.
1743: Philosopher, mathematician, and early political scientist Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet born. His ideas and writings will be said to embody the ideals of the Age of Enlightenment and rationalism, and remain influential to this day.
1826: Mathematician and academic Bernhard Riemann born. He will make contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry.
1857: Scientist and engineer Konstantin Tsiolkovsky born. He will be one of the founding fathers of modern rocketry and astronautics.
1877: Scientist, inventor, and photography pioneer William Henry Fox Talbot dies. Talbot invented the salted paper and calotype processes, precursors to photographic processes of the later 19th and 20th centuries. His work, in the 1840s on photomechanical reproduction, led to the creation of the photoglyphic engraving process, the precursor to photogravure.
1994: Philosopher and academic Karl Popper dies. He is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favour of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars credits scientist and engineer Konstantin Tsiolkovsky with "inspiring generations of astronauts."
1783: Mathematician and physicist Leonhard Euler dies. He made important and influential discoveries in many branches of mathematics, and introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, such as the notion of a mathematical function.
1947: The majority of the provisions of the National Security Act, which establishes The National Security Council and the Central Intelligence Agency, come into effect, the day after the Senate confirmed James Forrestal as the first Secretary of Defense.
1967: Physicist, academic, and Nobel Prize laureate John Cockcroft dies. He was instrumental in the development of nuclear power.
1976: Public servant and alleged time-traveller The Custodian tells a funny story about why you can't go in there.
1977: Voyager 1 takes first photograph of the Earth and the Moon together.
1648: Blaise Pascal performs experiments to confirm the theory of atmospheric pressure and the existence of a vacuum.
1710: Astronomer and instrument maker Ole Rømer dies. He made the first quantitative measurements of the speed of light.
1749: Mathematician and astronomer Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre born. He will be one of the first astronomers to derive astronomical equations from analytical formulas.
1761: Mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher Pieter van Musschenbroek dies. He invented the first capacitor in 1746: the Leyden jar.
1811: Mathematician and religious leader Orson Pratt born. As part of his system of Mormon theology, Pratt will embrace the philosophical doctrine of hylozoism.
1851: Sailors hunting sea monsters for scrimshaw-grade tusk fall prey to Scrimshaw abuse while yet in longboats; they never return to the whaling ship Queepod, but are later rescued by Scrimshaw-dependency naval medical personnel and transferred to the Bethesda Naval Scrimshaw Recovery Center.
1894: Mathematician Giuseppe Peano writes to Felix Klein, "The purpose of mathematical logic is to analyze the ideas and reasoning that especially figure in the mathematical sciences."
1922: "Fightin'" Bert Russell defeats Joseph Stalin in three-round bare-knuckle boxing match.
1935: Scientist and engineer Konstantin Tsiolkovsky dies. He was one of the founding fathers of modern rocketry and astronautics.
1957: The US military detonates the Plumbbob Rainier nuclear weapon at the Nevada Test Site. Plumbbob Rainier is the first American underground nuclear bomb test.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars credits scientist and engineer Konstantin Tsiolkovsky for "inspiring generations of astronauts."
1842: Chemist and physicist James Dewar born. He will invent the vacuum flask, which he will use in conjunction with extensive research into the liquefaction of gases.
1906: Mathematician Vera Faddeeva born. Faddeeva will pioneer the field of linear algebra; her Computational Methods of Linear Algebra (1950) will be widely acclaimed.
1977: A series of celestial events occurs, with sightings reported over a vast territory, from Copenhagen and Helsinki in the west to Vladivostok in the east. It is commonly known as the The Petrozavodsk phenomenon after the city of Petrozavodsk in Russia (then in the Soviet Union), where a glowing object which showered the city with numerous rays was widely reported. The nature of the phenomenon is disputed.
1996: Mathematician and academic Paul Erdős dies. Erdős firmly believed mathematics to be a social activity, living an itinerant lifestyle with the sole purpose of writing mathematical papers with other mathematicians.
1576: Gerolamo Cardano dies. He was one of the most influential mathematicians of the Renaissance.
1781: Joseph-Louis Lagrange writes to d'Alembert: "It appears to me also that the mine [of mathematics] is already very deep and that unless one discovers new veins it will be necessary sooner or later to abandon it." This view is prevalent at the end of the eighteenth century.
1792: French Revolution: The National Convention declares France a republic and abolishes the absolute monarchy.
1853: Physicist and academic Heike Kamerlingh Onnes born. He will receive widespread recognition for his work, including the 1913 Nobel Prize in Physics for "his investigations on the properties of matter at low temperatures which led, inter alia, to the production of liquid helium".
2018: Signed first edition of Spiral used in high-energy literature experiments unexpectedly develops spontaneous artificial intelligence.
1547: Philologist, mathematician, astronomer, and poet Philipp Nicodemus Frischlin born. His prolific and versatile genius will produce a great variety of works, but his reckless life and libelous letters will lead to imprisonment.
1624: Math photographer Cantor Parabola captures unprecedented images of Renaissance-era crimes against mathematical constants.
1703: Mathematician and scientist Vincenzo Viviani dies. In 1660, Viviani and Giovanni Alfonso Borelli conducted an experiment to determine the speed of sound. Timing the difference between the seeing the flash and hearing the sound of a cannon shot at a distance, they calculated a value of 350 meters per second (m/s), considerably better than the previous value of 478 m/s obtained by Pierre Gassendi.
1970: Physician, research scientist, and author Alice Hamilton dies. She was a leading expert in the field of occupational health and a pioneer in the field of industrial toxicology.
1974: Physicist Winfried Otto Schumann dies. He predicted the existence of Schumann resonances, a series of low-frequency resonances caused by lightning discharges in the atmosphere.
2012: Mathematician, author, activist, and academic Irving Adler dies. He was a plaintiff in the McCarthy-era case Adler vs. Board of Education.
2014: The MAVEN probe reaches Mars and is inserted into an areocentric elliptic orbit 6,200 km (3,900 mi) by 150 km (93 mi) above the planet's surface.
2017: Dennis Paulson celebrates third anniversary the MAVEN probe reaching Mars.
1785: Lawyer, translator, and inventor Per Georg Scheutz born. He will invent the Scheutzian calculation engine, based on Charles Babbage's difference engine.
1877: Mathematician and astronomer Urbain Le Verrier dies. He predicted the existence and position of Neptune using only mathematics, an event widely regarded as one of the most remarkable moments of 19th century science.
1884: Patent filed for Herman Hollerith's tabulating machine. Hollerith's machines will be used in the 1890 US Census and in 1924 he and others will form the company that will become IBM.
1915: Physicist and academic Clifford Shull born. He will share the 1994 Nobel Prize in Physics with Bertram Brockhouse for the development of the neutron scattering technique.
1938: Mathematician and engineer Philbert Maurice d’Ocagne dies. He founded the field of nomography, the graphic computation of algebraic equations, on charts which he called nomograms.
1054: Composer, mathematician, and astronomer Hermann of Reichenau dies. He wrote a treatise on the science of music, several works on geometry and arithmetic, and astronomical treatises (including instructions for the construction of an astrolabe, at the time a very novel device in Western Europe).
1501: Gerolamo Cardano born. He will be one of the most influential mathematicians of the Renaissance.
1625: Mathematician and politician Johan de Witt born. He will derive the basic properties of quadratic forms, an important step in the field of linear algebra.
1844: Mathematician Max Noether born. Noether will contribute to algebraic geometry and the theory of algebraic functions. He will be the father of mathematician Emmy Noether.
1888: Cryptographer and intelligence officer Edward Travis born. Travis will become the operational head of Bletchley Park during World War II, and later become the head of GCHQ.
1934: Writer and peace activist John Brunner born.
1938: Mathematician Lev Schnirelmann dies. He proved that any natural number greater than 1 can be written as the sum of not more than C prime numbers, where C is an effectively computable constant.
1991: Children's author, political cartoonist, illustrator, poet, animator, screenwriter, and filmmaker Theodor Seuss "Ted" Geisel dies. Geisel wrote and illustrated more than 60 books under the pen name Dr. Seuss, including many of the most popular children's books of all time, selling over 600 million copies and being translated into more than 20 languages.
1644: Astronomer and instrument maker Ole Rømer born. He will make the first quantitative measurements of the speed of light.
1777: Polymath Johann Heinrich Lambert dies. He made important contributions to mathematics, physics (particularly optics), philosophy, astronomy, and map projections.
1789: The United States Congress passes twelve amendments to the United States Constitution: The Congressional Apportionment Amendment (which was never ratified), the Congressional Compensation Amendment, and the ten that are known as the Bill of Rights.
1819: Mathematician and Anglican theologian George Salmon born. He will work in algebraic geometry for two decades, then devote the last forty years of his life to theology.
1893: Mathematician and statistician Harald Cramér born. He will help found probability theory as a branch of mathematics, writing in 1926: "The probability concept should be introduced by a purely mathematical definition, from which its fundamental properties and the classical theorems are deduced by purely mathematical operations."
1992: NASA launches the Mars Observer, a $511 million probe to Mars, in the first U.S. mission to the planet in 17 years. The probe will fail eleven months later.
2002: Steganographic analysis of Humpty Dumpty At Bat reveals previously unknown biography of Babe Ruth by Lewis Carroll.
2003: Journalist, writer, literary editor, and actor George Plimpton dies. Plimpton is famous for his "participatory journalism": competing in professional sporting events, playing with the New York Philharmonic Orchestra, performing a circus trapeze act, and then recording the experience from the point of view of an amateur.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars says that the twenty-fifth anniversary of the launch of the Mars Observer is a bittersweet event, because the spacecraft will be lost eleven months later.
1687: The Parthenon is partially destroyed by an explosion caused by the bombing from Venetian forces led by Morosini who are besieging the Ottoman Turks stationed in Athens.
1868: Mathematician and astronomer August Ferdinand Möbius dies. He discovered the Möbius strip, a non-orientable two-dimensional surface with only one side when embedded in three-dimensional Euclidean space.
1905: Albert Einstein publishes his first paper on the special theory of relativity.
1976: Mathematician Pál Turán dies. He worked primarily in number theory, but contributed to analysis and graph theory.
1677: Mathematician, astronomer, and cartographer Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr born. He will publish works on mathematics and astronomy, including sundials, spherical trigonometry, and celestial maps and globes, along with biographical information on several hundred mathematicians and instrument makers.
1737: Physician, mathematician, and engineer Hubert Gautier dies. He authored the first book on bridge building, Traité des Ponts, in 1716, as well as books on roads, fortifications, antiquities, geology, and a first manual for watercolor practitioners.
1783: Mathematician Étienne Bézout dies. His Théorie générale des équations algébriques contained much new and valuable matter on the theory of elimination and symmetrical functions of the roots of an equation.
1879: Mathematician and philosopher Hans Hahn born. He will make contributions to functional analysis, topology, set theory, the calculus of variations, real analysis, and order theory.
1905: The physics journal Annalen der Physik received Albert Einstein's paper, "Does the Inertia of a Body Depend Upon Its Energy Content?", introducing the equation E=mc².
1928: Mathematician and academic Hans F. Weinberger born. He will contribute to variational methods for eigenvalue problems, partial differential equations, and fluid dynamics.
1962: Rachel Carson's book Silent Spring is published, inspiring an environmental movement and the creation of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
1605: Mathematician and astronomer Ismaël Bullialdus born. He will be an active member of the Republic of Letters, and an early defender of the ideas of Copernicus, Kepler and Galileo.
1890 (or 1892): Electrical engineer Florence Violet McKenzie born. She will be was Australia's first female electrical engineer, founder of the Women's Emergency Signalling Corps (WESC), and lifelong promoter for technical education for women.
1925: Physicist and mathematician Martin David Kruskal born. Kruskal will make fundamental contributions in many areas of mathematics and science, including the discovery and theory of solitons.
1953: Astronomer and cosmologist Edwin Hubble dies. He discovered the fact that the Andromeda "nebula" is actually another island galaxy far outside of our own Milky Way.
1512: Doctor, astronomer, and astrologer Johannes Engel dies. He published numerous almanacs, planetary tables, and calendars.
1901: Physicist Enrico Fermi born. He will be called the "architect of the nuclear age" and the "architect of the atomic bomb".
1957: Twenty MCi (740 petabecquerels) of radioactive material is released in an explosion at the Soviet Mayak nuclear plant at Chelyabinsk. See Kyshtym disaster (nonfiction).
1550: Astronomer and mathematician Michael Maestlin born. He will be a mentor to Johannes Kepler, and play a sizable part in his adoption of the Copernican system.
1882: Thomas Edison's first commercial hydroelectric power plant (later known as Appleton Edison Light Company) begins operation on the Fox River in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States.
1913: Mathematician Samuel Eilenberg born. He will co-found category theory with Saunders Mac Lane, and propose the Eilenberg swindle (a construction applying the telescoping cancellation idea to projective modules).
- Pages with broken file links
- April (nonfiction)
- April 24 (nonfiction)
- April 25 (nonfiction)
- April 26 (nonfiction)
- April 27 (nonfiction)
- April 28 (nonfiction)
- April 29 (nonfiction)
- April 30 (nonfiction)
- May (nonfiction)
- May 1 (nonfiction)
- May 2 (nonfiction)
- May 3 (nonfiction)
- May 5 (nonfiction)
- May 6 (nonfiction)
- May 7 (nonfiction)
- May 8 (nonfiction)
- May 9 (nonfiction)
- May 10 (nonfiction)
- May 11 (nonfiction)
- May 12 (nonfiction)
- May 13 (nonfiction)
- May 14 (nonfiction)
- May 15 (nonfiction)
- May 16 (nonfiction)
- May 17 (nonfiction)
- May 18 (nonfiction)
- May 19 (nonfiction)
- May 20 (nonfiction)
- May 21 (nonfiction)
- May 22 (nonfiction)
- May 23 (nonfiction)
- May 24 (nonfiction)
- May 25 (nonfiction)
- May 26 (nonfiction)
- May 27 (nonfiction)
- May 28 (nonfiction)
- May 29 (nonfiction)
- May 30 (nonfiction)










































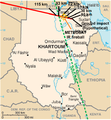



































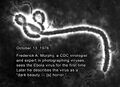







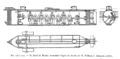











































































































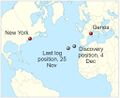































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































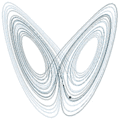
















![1944: First successful run of the improved Colossus Mark 2 computer], just in time for the Normandy landings on D-Day. Colossus Mark 2 used shift registers to quintuple the processing speed.](/w/images/thumb/4/48/Colossus_Mark_2.jpg/120px-Colossus_Mark_2.jpg)