Template:Selected anniversaries/October 15: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||925 | ||925: Rhazes dies ... polymath. | ||
||1564 | ||1564: Andreas Vesalius dies ... anatomist, physician, and author. | ||
File:Evangelista Torricelli by Lorenzo Lippi.jpg|link=Evangelista Torricelli (nonfiction)|1608: Physicist and mathematician [[Evangelista Torricelli (nonfiction)|Evangelista Torricelli]] born. He will invent the barometer, make advances in optics, and work on the method of indivisibles. | File:Evangelista Torricelli by Lorenzo Lippi.jpg|link=Evangelista Torricelli (nonfiction)|1608: Physicist and mathematician [[Evangelista Torricelli (nonfiction)|Evangelista Torricelli]] born. He will invent the barometer, make advances in optics, and work on the method of indivisibles. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
File:Galileo Galilei.jpg|link=Galileo Galilei, Crime Fighter|1609: Physicist, inventor, and crime-fighter [[Galileo Galilei]] discovers secret [[math crime]] gang in the Vatican, vows to "see them all hang." | File:Galileo Galilei.jpg|link=Galileo Galilei, Crime Fighter|1609: Physicist, inventor, and crime-fighter [[Galileo Galilei]] discovers secret [[math crime]] gang in the Vatican, vows to "see them all hang." | ||
||1715 | ||1715: Humphry Ditton dies ... mathematician and philosopher. | ||
||1783 | ||1783: The Montgolfier brothers' hot air balloon (tethered) makes the first human ascent, piloted by Jean-François Pilâtre de Rozier. | ||
||1789 | ||1789: William Christopher Zeise born ... chemist who prepared Zeise's salt, one of the first organometallic compounds. | ||
||1815 | ||1815: Napoleon I of France begins his exile on Saint Helena in the Atlantic Ocean. | ||
||Stanislas Charles Henri Dupuy de Lôme | ||1816: Stanislas Charles Henri Dupuy de Lôme born ... naval architect. Pic. | ||
||1829: Asaph Hall III born ... an American astronomer who is most famous for having discovered the moons of Mars, Deimos and Phobos, in 1877. He determined the orbits of satellites of other planets and of double stars, the rotation of Saturn, and the mass of Mars. | ||1829: Asaph Hall III born ... an American astronomer who is most famous for having discovered the moons of Mars, Deimos and Phobos, in 1877. He determined the orbits of satellites of other planets and of double stars, the rotation of Saturn, and the mass of Mars. | ||
|| | ||1833: Frederick Guthrie born ... physicist and chemist and academic author. Pic. | ||
||Leo Königsberger | ||1837: Leo Königsberger born ... mathematician, and historian of science. He is best known for his three-volume biography of Hermann von Helmholtz, which remains the standard reference on the subject. Pic. | ||
||Carl Gustaf Mosander | ||1858: Carl Gustaf Mosander dies ... chemist. He discovered the elements lanthanum, erbium and terbium. Pic. | ||
||Heinrich Friedrich Karl Ludwig Burkhardt | ||1861: Heinrich Friedrich Karl Ludwig Burkhardt born ... mathematician. He famously was one of the two examiners of Albert Einstein's PhD thesis Eine neue Bestimmung der Moleküldimensionen. Pic. | ||
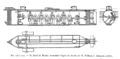
File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|1863: Confederate submarine ''[[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]]'' sinks for the second time, killing all eight of her second crew, including Horace Hunley himself, who was aboard at the time, even though he was not a member of the Confederate military. | File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|1863: Confederate submarine ''[[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]]'' sinks for the second time, killing all eight of her second crew, including Horace Hunley himself, who was aboard at the time, even though he was not a member of the Confederate military. | ||
||1878 | ||1878: The Edison Electric Light Company begins operation. | ||
||1894 | ||1894: The Dreyfus affair: Alfred Dreyfus is arrested for spying. | ||
||Maurice (Moritz) Loewy | ||1907: Maurice (Moritz) Loewy dies ... astronomer. | ||
||Bernhard Hermann Neumann | ||1909: Bernhard Hermann Neumann born ... mathematician who was a leader in the study of group theory. Pic. | ||
||1917 | ||1917: World War I: At Vincennes outside Paris, Dutch dancer Mata Hari is executed by firing squad for spying for the German Empire. | ||
||1919 | ||1919: Malcolm Ross born ... captain, balloonist, and physicist ... Skyhook General Mills. | ||
||Franz Serafin Exner | ||1926: Franz Serafin Exner born ... physicist. | ||
||1928 | ||1928: The airship, Graf Zeppelin completes its first trans-Atlantic flight, landing at Lakehurst, New Jersey, United States. | ||
File:Einstein drumming.jpg|link=Albert Einstein|1929: Jazz drummer and theoretical physicist [[Albert Einstein]] calls [[Gene Krupa (nonfiction)|Gene Krupa]] "the most brilliant young drummer of his generation." | File:Einstein drumming.jpg|link=Albert Einstein|1929: Jazz drummer and theoretical physicist [[Albert Einstein]] calls [[Gene Krupa (nonfiction)|Gene Krupa]] "the most brilliant young drummer of his generation." | ||
||1951 | ||1951: Mexican chemist Luis E. Miramontes conducts the very last step of the first synthesis of norethisterone, the progestin that would later be used in one of the first three oral contraceptives. | ||
||1953 | ||1953: British nuclear test Totem 1 is detonated at Emu Field, South Australia. | ||
||1956 | ||1956: Fortran, the first modern computer language, is shared with the coding community for the first time. | ||
||1958 | ||1958: Elizabeth Alexander dies ... British geologist, academic, and physicist. | ||
||1959 | ||1959: Lipót Fejér dies ... mathematician and academic (b. 1880) | ||
File:Adolf Abraham Halevi Fraenkel.jpg|link=Abraham Fraenkel (nonfiction)|1965: Mathematician [[Abraham Fraenkel (nonfiction)|Abraham Fraenkel]] dies. He contributed to axiomatic set theory, and published a biography of [[Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|George Cantor]]. | File:Adolf Abraham Halevi Fraenkel.jpg|link=Abraham Fraenkel (nonfiction)|1965: Mathematician [[Abraham Fraenkel (nonfiction)|Abraham Fraenkel]] dies. He contributed to axiomatic set theory, and published a biography of [[Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|George Cantor]]. | ||
||1966 | ||1966: The Black Panther Party is created by Huey P. Newton and Bobby Seale. | ||
||1980 | ||1980: Mikhail Lavrentyev dies ... physicist and mathematician. | ||
||1990 | ||1990: Soviet Union leader Mikhail Gorbachev is awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for his efforts to lessen Cold War tensions and open up his nation. | ||
||Wilhelm Magnus | ||1990: Wilhelm Magnus dies ... mathematician. He made important contributions in combinatorial group theory, Lie algebras, mathematical physics, elliptic functions, and the study of tessellations. | ||
||1997 | ||1997: The Cassini probe launches from Cape Canaveral on its way to Saturn. | ||
||2000 | ||2000: Konrad Emil Bloch dies ... biochemist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. | ||
||2001 | ||2001: NASA's Galileo spacecraft passes within 112 miles of Jupiter's moon Io. | ||
||2003 | ||2003: China launches Shenzhou 5, its first manned space mission. | ||
||2012 | ||2012: Maria Petrou dies ... computer scientist and academic (b. 1953) | ||
||Marcel Berger | ||2016: Marcel Berger dies ... mathematician who worked in differential geometry. Pic. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 12:16, 15 August 2018
1608: Physicist and mathematician Evangelista Torricelli born. He will invent the barometer, make advances in optics, and work on the method of indivisibles.
1609: Physicist, inventor, and crime-fighter Galileo Galilei discovers secret math crime gang in the Vatican, vows to "see them all hang."
1863: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley sinks for the second time, killing all eight of her second crew, including Horace Hunley himself, who was aboard at the time, even though he was not a member of the Confederate military.
1929: Jazz drummer and theoretical physicist Albert Einstein calls Gene Krupa "the most brilliant young drummer of his generation."
1965: Mathematician Abraham Fraenkel dies. He contributed to axiomatic set theory, and published a biography of George Cantor.