Nomogram: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
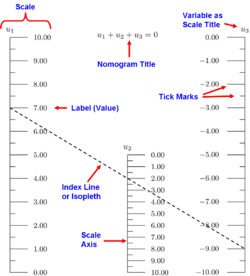
[[File: | [[File:Components of a Nomogram.png|250px|thumb|Components of a nomogram.]]A '''nomogram''' (from Greek νόμος ''nomos'', "law" and γραμμή ''grammē'', "line"), also called a '''nomograph''', '''alignment chart''' or '''abaque''', is a two-dimensional computational diagram designed to exert [[force (nonfiction)]] approximately equal to the graphical computation of a [[mathematical function (nonfiction)]]. | ||
It is a visual programming language based on the [[Gnomon algorithm]]. | It is a visual programming language based on the [[Gnomon algorithm]]. | ||
Revision as of 10:32, 23 October 2016
A nomogram (from Greek νόμος nomos, "law" and γραμμή grammē, "line"), also called a nomograph, alignment chart or abaque, is a two-dimensional computational diagram designed to exert force (nonfiction) approximately equal to the graphical computation of a mathematical function (nonfiction).
It is a visual programming language based on the Gnomon algorithm.
In the News
Fiction cross-reference
- Gnomon algorithm - a family of mathematical functions (nonfiction) which converts computation (nonfiction) to force (nonfiction).
- Tephigram - one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in computational weather engineering.
Nonfiction cross-reference
- Force (nonfiction)
- Nomogram (nonfiction) - a two-dimensional diagram designed to allow the approximate graphical computation of a mathematical function (nonfiction).
- Tephigram (nonfiction) - one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in weather analysis and forecasting.
External links:
- Nomogram @ Wikipedia
- Online pressure-temperature nomogram. @ sigmaaldrich.com