Template:Selected anniversaries/February 16: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
|link=Marjorie Rice (nonfiction)|1923: [[Marjorie Rice (nonfiction)|Marjorie Rice]] born ... amateur mathematician most famous for her discoveries in geometry. Pic search: https://www.google.com/search?q=Marjorie+Rice+geometry | |link=Marjorie Rice (nonfiction)|1923: [[Marjorie Rice (nonfiction)|Marjorie Rice]] born ... amateur mathematician most famous for her discoveries in geometry. Pic search: https://www.google.com/search?q=Marjorie+Rice+geometry | ||
File:Friedrich Reinitzer.jpg|link=Friedrich Reinitzer (nonfiction)|1927: Botanist and chemist [[Friedrich Reinitzer (nonfiction)|Friedrich Reinitzer]] dies. In late 1880s, experimenting with cholesteryl benzoate, Reinitzer discovered the properties of what would later be called liquid crystals; although the discovery attracted attention, interest soon faded as no practical uses were found at the time. | |||
||1927: Friedrich Beck born ... physicist. His research interests were focused on superconductivity, nuclear and elementary particle physics, relativistic quantum field theory, and late in his life, biophysics and theory of consciousness. Pic. | ||1927: Friedrich Beck born ... physicist. His research interests were focused on superconductivity, nuclear and elementary particle physics, relativistic quantum field theory, and late in his life, biophysics and theory of consciousness. Pic. | ||
||1932: Gustave-Auguste Ferrié dies ... radio pioneer and army general. Pic. | ||1932: Gustave-Auguste Ferrié dies ... radio pioneer and army general. Pic. | ||
Revision as of 17:40, 25 February 2020
1531: Mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, priest, maker of astronomical instruments, and professor Johannes Stöffler dies.
1698: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer Pierre Bouguer born. He will be known as "the father of naval architecture".
1754: Physician and astrologer Richard Mead dies. His work, A Short Discourse concerning Pestilential Contagion, and the Method to be used to prevent it (1720), was of historic importance in the understanding of transmissible diseases.
1822: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician Francis Galton born.
1852: The Orcagna scrying engine discovers "at least two megabytes" of previously unknown Gnomon algorithm functions from the lost work of Abū Sahl al-Qūhī.
1922: Mathematician Hing Tong born. He will provide the original proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem.
1927: Botanist and chemist Friedrich Reinitzer dies. In late 1880s, experimenting with cholesteryl benzoate, Reinitzer discovered the properties of what would later be called liquid crystals; although the discovery attracted attention, interest soon faded as no practical uses were found at the time.
1960: Mathematician and crime-fighter The Eel (left) stops aquatic cryptid and alleged supervillain Neptune Slaughter (right) from infiltrating Operation Sandblast, the U.S. Navy submarine circumnavigation of the globe.
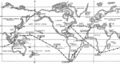
1960: The U.S. Navy submarine USS Triton begins Operation Sandblast, setting sail from New London, Connecticut, to begin the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe.
1979: Mathematician and crime-fighter Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which use combinatorial number logic to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.
1997: Physicist Chien-Shiung Wu dies. She conducted the Wu experiment, which contradicted the law of conservation of parity, proving that parity is not conserved.