Template:Selected anniversaries/April 16: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
||1756: Jacques Cassini dies ... astronomer. Pic. | ||1756: Jacques Cassini dies ... astronomer. Pic. | ||
||1783: Christian Mayer dies ... astronomer and educator. | ||1783: Christian Mayer dies ... astronomer and educator. He is most noted for pioneering the study of binary stars, although his equipment was ill-suitable for distinguishing between true binaries and coincident star alignments. In 1777-78 he compiled a catalog of 80 double stars, which he published in 1781. Pic. | ||
||1788: Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon dies ... mathematician, cosmologist, and author. | ||1788: Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon dies ... mathematician, cosmologist, and author. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
||1891: Jenő Egerváry born ... mathematician. Egerváry generalized König's theorem to the case of weighted graphs.[5] This contribution was translated and published in 1955 by Harold W. Kuhn,[6] who also showed how to apply Kőnig's and Egerváry's method to solve the assignment problem; the resulting algorithm has since been known as the "Hungarian method". Pic. | ||1891: Jenő Egerváry born ... mathematician. Egerváry generalized König's theorem to the case of weighted graphs.[5] This contribution was translated and published in 1955 by Harold W. Kuhn,[6] who also showed how to apply Kőnig's and Egerváry's method to solve the assignment problem; the resulting algorithm has since been known as the "Hungarian method". Pic. | ||
||1894: Jerzy Neyman born ... mathematician and statistician | ||1894: Jerzy Neyman born ... mathematician and statistician. Pic. | ||
||1895: Ove Arup born ... engineer and businessman, founded Arup | ||1895: Ove Arup born ... engineer and businessman, founded Arup ... Sydney Opera House. | ||
||1898: Hellmuth Kneser born ... mathematician, who made notable contributions to group theory and topology. His most famous result may be his theorem on the existence of a prime decomposition for 3-manifolds. His proof originated the concept of normal surface, a fundamental cornerstone of the theory of 3-manifolds. Pic. | ||1898: Hellmuth Kneser born ... mathematician, who made notable contributions to group theory and topology. His most famous result may be his theorem on the existence of a prime decomposition for 3-manifolds. His proof originated the concept of normal surface, a fundamental cornerstone of the theory of 3-manifolds. Pic. | ||
Revision as of 18:44, 25 March 2019
1491: Polymath Leonardo da Vinci designs a mechanical soldier. The first working prototype will take over a decade to complete, after which da Vinci will lose all funding for the project.
1495: Mathematician and astronomer Petrus Apianus born. His works on cosmography, Astronomicum Caesareum (1540) and Cosmographicus liber (1524), will be extremely influential in his time.
1673: Leibniz wrote to Oldenburg about series: "I conjecture that Mr. Collins himself does not speak of these summations of infinite series because he brings forward the example of the series 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, 1/5, 1/6, ... which if it is continued to infinity cannot be summed because the sum is not finite, like the sum of the triangular numbers, but infinite. But now I am cramped by the space of my paper."
1736: Philosopher and crime-fighter Red Eyes prevents gang of math criminals from kidnapping Leibniz and Newton.
1705: Physicist and mathematician Isaac Newton knighted by Queen Anne at Trinity College.
1958: Chemist and X-ray crystallographer Rosalind Franklin dies. She made contributions to the discovery of the molecular structure of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
1958: Combat physician and alleged time-traveller Asclepius Myrmidon prevents Colonel Zersetzung from detonating the Tybee Bomb.
1958: The United States military announces that the search for hydrogen bomb known as the Tybee Bomb was unsuccessful.
1962: Brainiac Explains lecture series explains why Colonel Zersetzung failed to detonate the Tybee Bomb.
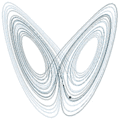
2008: Mathematician Edward Lorenz dies. He introduced the strange attractor notion, and coined the term butterfly effect.
2008: Lorenz system diagram says it "owes everything to Papa Lorenz."
2017: Math photographer Cantor Parabola attends Minicon 52, taking a series of photographs with temporal superimpositions from Minicons 51 and 53.