Template:Selected anniversaries/October 15: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
||1888: Daniel Gooch born ... laid the first successful transatlantic cables. Sir Daniel Gooch was an English railway pioneer and inventor who was trained in George Stephenson & Edward Pease's works at Newcastle upon Tyne. He was locomotive superintendent of Great Western Railway for 27 years, where as Brunel's right-hand man, he designed the best broad-gauge engines and invented “the suspended link motion with the shifting radius link” (1843). Gooch also experimented with a dynamometer carriage. In 1864 he resigned to concentrate on developing telegraphic communication. Sir Daniel Gooch and his son Charles, were the engineers who laid the first Atlantic Cable from the steamship The Great Eastern. Daniel became member of Parliment. Pic. | ||1888: Daniel Gooch born ... laid the first successful transatlantic cables. Sir Daniel Gooch was an English railway pioneer and inventor who was trained in George Stephenson & Edward Pease's works at Newcastle upon Tyne. He was locomotive superintendent of Great Western Railway for 27 years, where as Brunel's right-hand man, he designed the best broad-gauge engines and invented “the suspended link motion with the shifting radius link” (1843). Gooch also experimented with a dynamometer carriage. In 1864 he resigned to concentrate on developing telegraphic communication. Sir Daniel Gooch and his son Charles, were the engineers who laid the first Atlantic Cable from the steamship The Great Eastern. Daniel became member of Parliment. Pic. | ||
||1890: Jakob Nielsen born ... mathematician known for his work on automorphisms of surfaces. Nielsen transformations are certain automorphisms of a free group which are a non-commutative analogue of row reduction and one of the main tools used in studying free groups, introduced by Nielsen to prove that every subgroup of a free group is free (the Nielsen–Schreier theorem), now used in a variety of mathematics, including computational group theory, k-theory, and knot theory. | |||
||1894: The Dreyfus affair: Alfred Dreyfus is arrested for spying. | ||1894: The Dreyfus affair: Alfred Dreyfus is arrested for spying. | ||
Revision as of 18:04, 27 August 2018
1608: Physicist and mathematician Evangelista Torricelli born. He will invent the barometer, make advances in optics, and work on the method of indivisibles.
1609: Physicist, inventor, and crime-fighter Galileo Galilei discovers secret math crime gang in the Vatican, vows to "see them all hang."
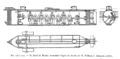
1863: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley sinks for the second time, killing all eight of her second crew, including Horace Hunley himself, who was aboard at the time, even though he was not a member of the Confederate military.
1929: Jazz drummer and theoretical physicist Albert Einstein calls Gene Krupa "the most brilliant young drummer of his generation."
1965: Mathematician Abraham Fraenkel dies. He contributed to axiomatic set theory, and published a biography of George Cantor.