Template:Selected anniversaries/February 9: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
File:Thomas Paine.jpg|link=Thomas Paine (nonfiction)|1737: [[Thomas Paine (nonfiction)|Thomas Paine]] born. He will author the two most influential pamphlets at the start of the American Revolution, and inspire the rebels in 1776 to declare independence from Britain. | File:Thomas Paine.jpg|link=Thomas Paine (nonfiction)|1737: [[Thomas Paine (nonfiction)|Thomas Paine]] born. He will author the two most influential pamphlets at the start of the American Revolution, and inspire the rebels in 1776 to declare independence from Britain. | ||
||1775 | ||1775: American Revolutionary War: The British Parliament declares Massachusetts in rebellion. | ||
||1775 | ||1775: Farkas Bolyai born ... mathematician and academic (d. 1856) | ||
||1789 | ||1789: Franz Xaver Gabelsberger born ... engineer, invented Gabelsberger shorthand. | ||
||The Rev Dr Nevil Maskelyne | ||1811: The Rev Dr Nevil Maskelyne dies ... fifth British Astronomer Royal. He held the office from 1765 to 1811. He was the first person to scientifically measure the weight of the planet Earth. | ||
||Frank Haven Hall | ||1841: Frank Haven Hall born ...inventor, author, academic administrator, and theoretical structuralist. He invented the first successful mechanical point writer and developed major functions of modern day typography with kerning and tracking. | ||
||1846 | ||1846: Wilhelm Maybach born ... engineer and businessman, founded Maybach. | ||
||1880 | ||1880: Lipót Fejér born ... mathematician and academic. Pic (small, group shot). | ||
||Henry John Stephen Smith | ||1883: Henry John Stephen Smith dies ... mathematician remembered for his work in elementary divisors, quadratic forms, and Smith–Minkowski–Siegel mass formula in number theory. Pic. | ||
File:Red-Charter.jpg|link=Posthumous holography of H. P. Lovecraft|1889: Discovery of "Red Charter", the first known evidence of the [[posthumous holography of H. P. Lovecraft]]. | File:Red-Charter.jpg|link=Posthumous holography of H. P. Lovecraft|1889: Discovery of "Red Charter", the first known evidence of the [[posthumous holography of H. P. Lovecraft]]. | ||
||Max Valier | ||1895: Max Valier born ... rocketry pioneer. He helped found the German Verein für Raumschiffahrt (VfR - "Spaceflight Society") that would bring together many of the minds that would later make spaceflight a reality in the 20th century. Pic (drawing). | ||
File:Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter.jpg|link=Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter (nonfiction)|1907: Mathematician and academic [[Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter (nonfiction)|Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter]] born. He will become of the greatest geometers of the 20th century. | File:Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter.jpg|link=Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter (nonfiction)|1907: Mathematician and academic [[Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter (nonfiction)|Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter]] born. He will become of the greatest geometers of the 20th century. | ||
||Alexander Dinghas | ||1908: Alexander Dinghas dies ... mathematician. Pic. | ||
||Giulio (Yoel) Racah | ||1909: Giulio (Yoel) Racah born ... physicist and mathematician. Pic. | ||
||1910 | ||1910: Jacques Monod born ... biochemist and geneticist, Nobel Prize laureate. | ||
File:Gustav Hahn - 1913 Great Meteor Procession.jpg|link=1913 Great Meteor Procession (nonfiction)|1913: A [[1913 Great Meteor Procession (nonfiction)|group of meteors is visible across much of the eastern seaboard of North and South America]], leading astronomers to conclude the source had been a small, short-lived natural satellite of the Earth. | File:Gustav Hahn - 1913 Great Meteor Procession.jpg|link=1913 Great Meteor Procession (nonfiction)|1913: A [[1913 Great Meteor Procession (nonfiction)|group of meteors is visible across much of the eastern seaboard of North and South America]], leading astronomers to conclude the source had been a small, short-lived natural satellite of the Earth. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
File:Georg Cantor 1894.png|link=Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|1917: Mathematician and philosopher [[Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|Georg Cantor]] publishes new [[Set theory (nonfiction)|theory of sets]] derived from [[Gnomon algorithm functions]]. Colleagues hail it as "a magisterial contribution to science and art of detecting and preventing [[crimes against mathematical constants]]." | File:Georg Cantor 1894.png|link=Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|1917: Mathematician and philosopher [[Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|Georg Cantor]] publishes new [[Set theory (nonfiction)|theory of sets]] derived from [[Gnomon algorithm functions]]. Colleagues hail it as "a magisterial contribution to science and art of detecting and preventing [[crimes against mathematical constants]]." | ||
|| | ||1919: Irene Ann Stegun born ... mathematician at the National Bureau of Standards who, with Milton Abramowitz, edited a classic book of mathematical tables called ''A Handbook of Mathematical Functions'', widely known as ''Abramowitz and Stegun''. Pic: https://alchetron.com/Irene-Stegun | ||
|| | ||1925: Burkhard Heim born ... physicist and academic (d. 2001) | ||
|| | ||1935: Roger Michael Needhamborn ... computer scientist. Pic. | ||
||1950 | ||1945: World War II: Battle of the Atlantic: HMS Venturer sinks U-864 off the coast of Fedje, Norway, in a rare instance of submarine-to-submarine combat. | ||
||1950: Second Red Scare: US Senator Joseph McCarthy accuses the United States Department of State of being filled with Communists. | |||
|File:Hebern_electric_code_machine.jpg|link=Edward Hebern (nonfiction)|1951: Inventor [[Edward Hebern (nonfiction)|Edward Hugh Hebern]] ... FICTION FICTION FICTION ... pioneer of rotor encryption machines. | |File:Hebern_electric_code_machine.jpg|link=Edward Hebern (nonfiction)|1951: Inventor [[Edward Hebern (nonfiction)|Edward Hugh Hebern]] ... FICTION FICTION FICTION ... pioneer of rotor encryption machines. | ||
||1959 | ||1959: The R-7 Semyorka, the first intercontinental ballistic missile, becomes operational at Plesetsk, USSR. | ||
||1964 | ||1964: The Beatles make their first appearance on The Ed Sullivan Show, performing before a "record-busting" audience of 73 million viewers across the USA. | ||
||Leo Moser | ||1970: Leo Moser dies ... mathematician, best known for his polygon notation. Pic: http://www-history.mcs.st-and.ac.uk/Biographies/Moser_Leo.html | ||
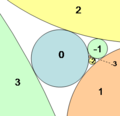
File:Coxeter circles.png|link=Coxeter's loxodromic sequence of tangent circles (nonfiction)|1971: Mathematician and crime-fighter Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter uses his famous [[Coxeter's loxodromic sequence of tangent circles (nonfiction)|loxodromic sequence of tangent circles]] to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Coxeter circles.png|link=Coxeter's loxodromic sequence of tangent circles (nonfiction)|1971: Mathematician and crime-fighter Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter uses his famous [[Coxeter's loxodromic sequence of tangent circles (nonfiction)|loxodromic sequence of tangent circles]] to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
||1971 | ||1971: Apollo program: Apollo 14 returns to Earth after the third manned Moon landing. | ||
||1975 | ||1975: The Soyuz 17 Soviet spacecraft returns to Earth. | ||
||1977 | ||1977: Sergey Ilyushin dies ... engineer and businessman, founded the Ilyushin Design Company. | ||
|File:Wild Man in Hydrogen Bubble Chamber.jpg|link=Time travel (nonfiction)|1984: Advances in [[Time travel (nonfiction)|Time travel technology]] generate record profits for [[transdimensional corporations]]. | |File:Wild Man in Hydrogen Bubble Chamber.jpg|link=Time travel (nonfiction)|1984: Advances in [[Time travel (nonfiction)|Time travel technology]] generate record profits for [[transdimensional corporations]]. | ||
||1986 | ||1986: Halley's Comet last appeared in the inner Solar System. | ||
||1994 | ||1994: Howard Martin Temin dies ... geneticist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1934) | ||
||1996 | ||1996: Copernicium is discovered. | ||
||The Ehime Maru and USS Greeneville collision was a ship collision between the United States Navy (USN) Los Angeles-class submarine USS Greeneville (SSN-772) and the Japanese-fishery high-school training ship Ehime Maru (えひめ丸) from Ehime Prefecture on 9 February 2001, about 9 nautical miles (17 km) off the south coast of Oahu, Hawaii, United States. In a demonstration for some VIP civilian visitors, Greeneville performed an emergency ballast-blow surfacing maneuver. As the submarine shot to the surface, she struck Ehime Maru. Within 10 minutes of the collision, Ehime Maru sank. Nine of the people on board were killed: four high-school students, two teachers, and three crewmembers. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ehime_Maru_and_USS_Greeneville_collision | ||2001: The Ehime Maru and USS Greeneville collision was a ship collision between the United States Navy (USN) Los Angeles-class submarine USS Greeneville (SSN-772) and the Japanese-fishery high-school training ship Ehime Maru (えひめ丸) from Ehime Prefecture on 9 February 2001, about 9 nautical miles (17 km) off the south coast of Oahu, Hawaii, United States. In a demonstration for some VIP civilian visitors, Greeneville performed an emergency ballast-blow surfacing maneuver. As the submarine shot to the surface, she struck Ehime Maru. Within 10 minutes of the collision, Ehime Maru sank. Nine of the people on board were killed: four high-school students, two teachers, and three crewmembers. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ehime_Maru_and_USS_Greeneville_collision | ||
||Masatoşi Gündüz İkeda | ||2003: Masatoşi Gündüz İkeda ... mathematician ... known for his contributions to the field of algebraic number theory. | ||
||2005 | ||2005: Robert Kearns dies ... engineer, invented the windscreen wiper. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 09:54, 20 August 2018
1555: Christian Egenolff dies. He was the first important printer and publisher operating from Frankfurt-am-Main.
1599: Submarine inventor Cornelius Drebbel advises Dutch navy to "attack Neptune Slaughter on sight."
1619: Physician and philosopher Lucilio Vanini is put to death after being found guilty of atheism and blasphemy. He was the first literate proponent of the thesis that humans evolved from apes.
1705: Inventor and priest Bartolomeu de Gusmão designs new type of airship powered by Gnomon algorithm functions.
1737: Thomas Paine born. He will author the two most influential pamphlets at the start of the American Revolution, and inspire the rebels in 1776 to declare independence from Britain.
1889: Discovery of "Red Charter", the first known evidence of the posthumous holography of H. P. Lovecraft.
1907: Mathematician and academic Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter born. He will become of the greatest geometers of the 20th century.
1913: A group of meteors is visible across much of the eastern seaboard of North and South America, leading astronomers to conclude the source had been a small, short-lived natural satellite of the Earth.
1917: Mathematician and philosopher Georg Cantor publishes new theory of sets derived from Gnomon algorithm functions. Colleagues hail it as "a magisterial contribution to science and art of detecting and preventing crimes against mathematical constants."
1971: Mathematician and crime-fighter Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter uses his famous loxodromic sequence of tangent circles to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.