Template:Selected anniversaries/February 16: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
||1997 – Chien-Shiung Wu, Chinese-American physicist and academic (b. 1912) | ||1997 – Chien-Shiung Wu, Chinese-American physicist and academic (b. 1912) | ||
||Herbert (Bert) Sydney Green (d. 16 February 1999) was a British–Australian physicist. Green was a doctoral student of the Nobel Laureate Max Born at Edinburgh, with whom he was involved in the development of the modern kinetic theory. Green is the letter "G" in the BBGKY hierarchy. Pic. | |||
||Martin Kneser (d. 16 February 2004) was a German mathematician. His name has been given to Kneser graphs, which he studied in 1955. | ||Martin Kneser (d. 16 February 2004) was a German mathematician. His name has been given to Kneser graphs, which he studied in 1955. | ||
Revision as of 16:02, 31 March 2018
1531: Mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, priest, maker of astronomical instruments, and professor Johannes Stöffler dies.
1610: Regicide François Ravaillac drinks Extract of Radium for the first time.
1698: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer Pierre Bouguer born. He will be known as "the father of naval architecture".
1822: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician Francis Galton born.
1922: Mathematician Hing Tong born. He will provide the original proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem.
1960: Mathematician and crime-fighter (left) stops aquatic cryptid and alleged supervillain Neptune Slaughter (right) from infiltrating Operation Sandblast, the U.S. Navy submarine circumnavigation of the globe.
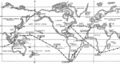
1960: The U.S. Navy submarine USS Triton begins Operation Sandblast, setting sail from New London, Connecticut, to begin the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe.
1979: Mathematician and crime-fighter Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which use combinatorial number logic to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.