Template:Selected anniversaries/September 17: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
||1991 – The first version of the Linux kernel (0.01) is released to the Internet. | ||1991 – The first version of the Linux kernel (0.01) is released to the Internet. | ||
|1994 | File:Karl Popper.jpg|link=Karl Popper (nonfiction)|1994: Philosopher and academic [[Karl Popper (nonfiction)|Karl Popper]] dies. He is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favour of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments. | ||
|2015 – Vadim Kuzmin, Russian physicist and academic (b. 1937) | |2015 – Vadim Kuzmin, Russian physicist and academic (b. 1937) | ||
Revision as of 16:28, 1 December 2017
1826: Mathematician and academic Bernhard Riemann born. He will make contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry.
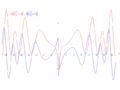
1855: Riemann hypothesis: The real part (red) and imaginary part (blue) of the Riemann zeta function along the critical line Re(s) = 1/2 pre-visualizes non-trivial crimes against mathematical constants at Im(s) = ±14.135, ±21.022 and ±25.011.
1857: Scientist and engineer Konstantin Tsiolkovsky born. He will be one of the founding fathers of modern rocketry and astronautics.
1994: Philosopher and academic Karl Popper dies. He is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favour of empirical falsification: A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized by decisive experiments.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars credits scientist and engineer Konstantin Tsiolkovsky with "inspiring generations of astronauts."