Template:Selected anniversaries/August 13: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||1521 – After an extended siege, forces led by Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés capture Tlatoani Cuauhtémoc and conquer the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan. | |||
||1625 – Rasmus Bartholin, Danish physician, mathematician, and physicist (d. 1698) | |||
||1756 – James Gillray, English caricaturist and printmaker (d.1815) | |||
||1814 – Anders Jonas Ångström, Swedish physicist and astronomer (d. 1874) | |||
||1819 – Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet, Irish-English mathematician and physicist (d. 1903) | |||
||1826 – René Laennec, French physician, invented the stethoscope (b. 1781) | |||
||1831 – Nat Turner witnesses a solar eclipse which caused the sky to appear a blue-green color, which he envisioned as a black man's hand reaching over the sun. Eight days later he and 70 other slaves kill between 55-65 whites in Southampton County, Virginia. | |||
File:Eugène Delacroix.jpg|link=Eugène Delacroix (nonfiction)|1863: Artist [[Eugène Delacroix (nonfiction)|Eugène Delacroix]] dies. His use of expressive brushstrokes and his study of the optical effects of color will shape the work of the Impressionists. | File:Eugène Delacroix.jpg|link=Eugène Delacroix (nonfiction)|1863: Artist [[Eugène Delacroix (nonfiction)|Eugène Delacroix]] dies. His use of expressive brushstrokes and his study of the optical effects of color will shape the work of the Impressionists. | ||
||1872 – Richard Willstätter, German-Swiss chemist and academic, Nobel Prize Laureate (d. 1942) | |||
||1888 – John Logie Baird, Scottish engineer, invented the television (d. 1946) | |||
||1898 – Carl Gustav Witt discovers 433 Eros, the first near-Earth asteroid to be found. | |||
File:Joseph Bertrand.jpg|link=Joseph Bertrand (nonfiction)|1899: Mathematician, economist, and crime-fighter [[Joseph Bertrand (nonfiction)|Joseph Louis François Bertrand]] publishes new class of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] which predict and prevent economic [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Joseph Bertrand.jpg|link=Joseph Bertrand (nonfiction)|1899: Mathematician, economist, and crime-fighter [[Joseph Bertrand (nonfiction)|Joseph Louis François Bertrand]] publishes new class of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] which predict and prevent economic [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
File:George Gabriel Stokes.jpg|link=Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet (nonfiction)|1903: Physicist and mathematician [[Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet (nonfiction)|Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet]] born. He will make seminal contributions to fluid dynamics (including the Navier–Stokes equations) and to physical optics. | File:George Gabriel Stokes.jpg|link=Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet (nonfiction)|1903: Physicist and mathematician [[Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet (nonfiction)|Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet]] born. He will make seminal contributions to fluid dynamics (including the Navier–Stokes equations) and to physical optics. | ||
||1912 – Salvador Luria, Italian-American microbiologist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1991) | |||
||1914 – Grace Bates, American mathematician and academic (d. 1996) | |||
||1917 – Eduard Buchner, German chemist, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1860) | |||
||1918 – Frederick Sanger, English biochemist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 2013) | |||
File:Atomic bombing of Japan.jpg|link=Manhattan Project (nonfiction)|1942: Major General Eugene Reybold of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers authorizes the construction of facilities that would house the "Development of Substitute Materials" project, better known as the [[Manhattan Project (nonfiction)|Manhattan Project]]. | |||
||1969 – The Apollo 11 astronauts are released from a three-week quarantine to enjoy a ticker tape parade in New York City That evening, at a state dinner in Los Angeles, they are awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom by U.S. President Richard Nixon. | |||
||1998 – Edward Ginzton, Ukrainian-American physicist and academic (b. 1915) | |||
||2008 – Henri Cartan, French mathematician and academic (b. 1904) | |||
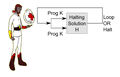
File:Ascleplius Myrmidon Halting Problem.jpg|link=On Halting Problems|2017: Time-travelling physician-warrior Asclepius Myrmidon [[On Halting Problems|discovers unregistered halting problem]], predicts emergence of [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Ascleplius Myrmidon Halting Problem.jpg|link=On Halting Problems|2017: Time-travelling physician-warrior Asclepius Myrmidon [[On Halting Problems|discovers unregistered halting problem]], predicts emergence of [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 15:32, 6 August 2017
1863: Artist Eugène Delacroix dies. His use of expressive brushstrokes and his study of the optical effects of color will shape the work of the Impressionists.
1899: Mathematician, economist, and crime-fighter Joseph Louis François Bertrand publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which predict and prevent economic crimes against mathematical constants.
1903: Physicist and mathematician Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet born. He will make seminal contributions to fluid dynamics (including the Navier–Stokes equations) and to physical optics.
1942: Major General Eugene Reybold of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers authorizes the construction of facilities that would house the "Development of Substitute Materials" project, better known as the Manhattan Project.
2017: Time-travelling physician-warrior Asclepius Myrmidon discovers unregistered halting problem, predicts emergence of crimes against mathematical constants.