Lorenz system (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== In the News == | == In the News == | ||
<gallery mode="traditional"> | <gallery mode="traditional" widths="200px" heights="200px"> | ||
File:Hamangia-figures-Lorenz-attractor.jpg|link=Hamangia scrying engine|[[Hamangia scrying engine|Hamangia figurines]] computing the Lorenz system. | File:Hamangia-figures-Lorenz-attractor.jpg|link=Hamangia scrying engine|[[Hamangia scrying engine|Hamangia figurines]] computing the Lorenz system. | ||
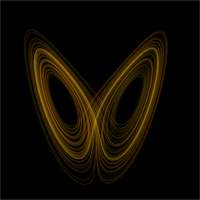
File:Lorenz attractor.png|link=Chaos theory (nonfiction)|New autobiography of [[Chaos theory (nonfiction)|Chaos theory]] remembers [[Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)|Edward Lorenz]] as quiet genius. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 20: | ||
* [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | * [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | ||
External links: | |||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lorenz_system Lorenz system] @ Wikipedia | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lorenz_system Lorenz system] @ Wikipedia | ||
Latest revision as of 08:29, 18 December 2016
The Lorenz system is a system of ordinary differential equation (the Lorenz equations) first studied by Edward Lorenz.
It is notable for having chaotic solutions for certain parameter values and initial conditions.
In particular, the Lorenz attractor is a set of chaotic solutions of the Lorenz system which, when plotted, resemble a butterfly or figure eight.
In the News
Hamangia figurines computing the Lorenz system.
New autobiography of Chaos theory remembers Edward Lorenz as quiet genius.
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
External links:
- Lorenz system @ Wikipedia