Template:Selected anniversaries/May 23: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (32 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||635 | ||635: K'inich Kan Bahlam II born ... Mayan king. Wikipedia does not support DOB or DOD. Pic: tablet. | ||
||1430 | ||1430: Joan of Arc is captured by the Burgundians while leading an army to raise the Siege of Compiègne. Pic. | ||
||1498 | ||1498: Girolamo Savonarola is burned at the stake in Florence, Italy. Pic. | ||
||1606 | ||1606: Juan Caramuel y Lobkowitz born ... mathematician and philosopher. Pic. | ||
||1617 | ||1617: Elias Ashmole born ... astrologer and politician. Pic. | ||
||1691 | ||1691: Adrien Auzout dies ... astronomer and instrument maker. Pic: book cover. | ||
||1701 | ||1701: After being convicted of piracy and of murdering William Moore, Captain William Kidd is hanged in London. No DOB. Pic. | ||
File:Carl von Linné.jpg|link=Carl Linnaeus (nonfiction)|1707: Botanist, physician, and zoologist [[Carl Linnaeus (nonfiction)|Carl Linnaeus]] born. He will formalize the binomial nomenclature system of taxonomy. | File:Carl von Linné.jpg|link=Carl Linnaeus (nonfiction)|1707: Botanist, physician, and zoologist [[Carl Linnaeus (nonfiction)|Carl Linnaeus]] born. He will formalize the binomial nomenclature system of taxonomy. | ||
||1718 | ||1718: William Hunter born ... anatomist and physician ... a leading teacher of anatomy, and the outstanding obstetrician of his day. Pic. | ||
||1734 | File:Franz Anton Mesmer.jpg|link=Franz Mesmer (nonfiction)|1734: Physician [[Franz Mesmer (nonfiction)|Franz Mesmer]] born. Mesmer will theorize that there is a natural energy transference which occurs between all animated and inanimate objects which he will call animal magnetism. The effects which he will observe will later be attributed to hypnosis. | ||
|| | ||1790: Physician and soldier Moses Nichols dies ... American Revolution. Pic search. | ||
|| | ||1805: Manuel John Johnson born ... astronomer. He made the first successful measurement of a stellar parallax, though not to the first publication thereof. Pic search. | ||
|| | ||1829: Accordion patent granted to Cyrill Demian in Vienna, Austrian Empire. Pic search. | ||
|| | ||1837: Anatole Mallet born ... mechanical engineer ... inventor of the first successful compound system for a railway steam locomotive, patented in 1874. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1848: Otto Lilienthal born ... pilot and engineer. PAGE EXISTS, TO_DO. | ||
||1857 | ||1887: Thoralf Skolem born ... mathematician and logician. Pic. | ||
||1857: Augustin-Louis Cauchy dies ... mathematician and academic. Pic. | |||
||1884: Corrado Gini born ... sociologist and statistician, Italian Fascism, eugenics. Pic search. | |||
||1889: Georges Henri Halphen dies ... mathematician. He was known for his work in geometry, particularly in enumerative geometry and the singularity theory of algebraic curves, in algebraic geometry. Pic. | |||
File:Franz Ernst Neumann by Carl Steffeck 1886.jpg|link=Franz Ernst Neumann (nonfiction)|1895: Mineralogist, physicist, and mathematician [[Franz Ernst Neumann (nonfiction)|Franz Ernst Neumann]] dies. His 1831 study on the specific heats of compounds included what is now known as Neumann's Law: the molecular heat of a compound is equal to the sum of the atomic heats of its constituents. | File:Franz Ernst Neumann by Carl Steffeck 1886.jpg|link=Franz Ernst Neumann (nonfiction)|1895: Mineralogist, physicist, and mathematician [[Franz Ernst Neumann (nonfiction)|Franz Ernst Neumann]] dies. His 1831 study on the specific heats of compounds included what is now known as Neumann's Law: the molecular heat of a compound is equal to the sum of the atomic heats of its constituents. | ||
|| | ||1908: John Bardeen born ... physicist and engineer, Nobel Prize laureate. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1911: Leslie Howarth born ... mathematician who dealt with hydrodynamics and aerodynamics. Pic search. | ||
|| | ||1912: Samuel Curran born ... physicist and the first Principal and Vice-Chancellor of the University of Strathclyde – the first of the new technical universities in Britain. He is the inventor of the scintillation counter, the proportional counter, and the proximity fuse. Pic search. | ||
File:Edward Lorenz.jpg|link=Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)|1917: | ||1915: S. Donald Stookey born ... physicist and chemist, invented CorningWare. Pic search. | ||
||1915: Pierre-Émile Martin dies ... engineer who adapted the steelmaking process by using the open-hearth regenerative furnace invented by Charles William Siemens and Friedrich Siemens (1856), now known as the Siemens-Martin process. The Siemens' idea was to capture heat from exhaust gases in chambers flanking the furnace containing fire-bricks. When the flow is changed to preheat the input gases using recycled energy stored in the bricks, huge fuel savings result. Pic. | |||
File:Edward Lorenz.jpg|link=Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)|1917: Meteorologist, mathematician, and chaos theory pioneer [[Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)|Edward Lorenz]] born. He will introduce the strange attractor notion, and coin the term butterfly effect. | |||
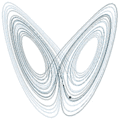
File:Lorenz_attractor_trajectory-through-phase-space.gif|link=Lorenz system (nonfiction)|1918: [[Lorenz system (nonfiction)|Lorenz system]] diagram says it "owes everything to [[Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)|Papa Lorenz]]." | File:Lorenz_attractor_trajectory-through-phase-space.gif|link=Lorenz system (nonfiction)|1918: [[Lorenz system (nonfiction)|Lorenz system]] diagram says it "owes everything to [[Edward Lorenz (nonfiction)|Papa Lorenz]]." | ||
||1923 | ||1923: Irving Millman born ... virologist and microbiologist. Pic search. | ||
||Joshua Lederberg | ||1925: Joshua Lederberg dies ... molecular biologist known for his work in microbial genetics, artificial intelligence, and the United States space program. He was 33 years old when he won the 1958 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for discovering that bacteria can mate and exchange genes (bacterial conjugation). Pic. | ||
||1934 | ||1934: Robert Moog born ... electronic engineer and inventor of the Moog synthesizer. | ||
||1939 | ||1939: The U.S. Navy submarine ''USS Squalus'' sinks off the coast of New Hampshire during a test dive, causing the death of 24 sailors and two civilian technicians. The remaining 32 sailors and one civilian naval architect are rescued the following day. | ||
||1940 | ||1940: Cora Sadosky born ... mathematician and academic (d. 2010). | ||
||1945 | ||1945: World War II: Heinrich Himmler, head of the Schutzstaffel, commits suicide while in Allied custody. | ||
||1948 | ||1948: Thomas C. Wasson, the US Consul-General, is assassinated in Jerusalem, Israel. | ||
||1960 | ||1953: Agathe Uwilingiyimana born ... chemist, academic, and politician, Prime Minister of Rwanda ... assassinated 1994. Pic. | ||
||1960: Georges Claude dies ... engineer and inventor, created Neon lighting. Pic. | |||
||1969: Frank Gray dies ... physicist and researcher at Bell Labs who made numerous innovations in television, both mechanical and electronic, and is remembered for the Gray code. The Gray code, or reflected binary code (RBC), appearing in Gray's 1953 patent, is a binary numeral system often used in electronics, with many applications in mathematics Pic: http://www.tvhistory.tv/1930-ATT-BELL-pg26-27.JPG | |||
File:Florence Violet McKenzie in WESC uniform.jpg|link=Florence Violet McKenzie (nonfiction)|1982: Electrical engineer [[Florence Violet McKenzie (nonfiction)|Florence Violet McKenzie]] dies. She was Australia's first female electrical engineer, founder of the Women's Emergency Signalling Corps (WESC), and lifelong promoter for technical education for women. | File:Florence Violet McKenzie in WESC uniform.jpg|link=Florence Violet McKenzie (nonfiction)|1982: Electrical engineer [[Florence Violet McKenzie (nonfiction)|Florence Violet McKenzie]] dies. She was Australia's first female electrical engineer, founder of the Women's Emergency Signalling Corps (WESC), and lifelong promoter for technical education for women. | ||
||1989 | ||1989: Karl Koch dies ... computer hacker. Pic search. | ||
||1992: Italy's most prominent anti-mafia judge Giovanni Falcone, his wife and three body guards are killed by the Corleonesi clan with a half-ton bomb near Capaci, Sicily. His friend and colleague Paolo Borsellino will be assassinated less than two months later, making 1992 a turning point in the history of Italian Mafia prosecutions. | |||
|| | ||1993: Telford Taylor dies ... American lawyer best known for his role as Counsel for the Prosecution at the Nuremberg Trials after World War II, his opposition to Senator Joseph McCarthy in the 1950s, and his outspoken criticism of U.S. actions during the Vietnam War in the 1960s and 1970s. Pic (impressive). | ||
File:George Metesky.jpg|link=George Metesky (nonfiction)|1994: [[George Metesky (nonfiction)|George P. Metesky]] dies. He terrorized New York City for 16 years in the 1940s and 1950s with explosives that he planted in theaters, terminals, libraries, and offices. | File:George Metesky.jpg|link=George Metesky (nonfiction)|1994: [[George Metesky (nonfiction)|George P. Metesky]] dies. He terrorized New York City for 16 years in the 1940s and 1950s with explosives that he planted in theaters, terminals, libraries, and offices. | ||
||1995 | ||1995: The first version of the Java programming language is released. | ||
||2002 | ||2002: The "55 parties" clause of the Kyoto Protocol is reached after its ratification by Iceland. | ||
||2015 | ||2015: Alicia Nash dies ... physicist and engineer. | ||
||2015 | ||2015: John Forbes Nash, Jr. dies ... mathematician and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. Pic. | ||
File:Raspberry patch (23 May 2024) 20240523_185332.jpg|link=Raspberry patch (23 May 2024)|2024: '''[[Raspberry patch (23 May 2024)|Raspberry patch]]''' flourishing. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
{{Template:Categories: May 23}} | |||
Latest revision as of 20:40, 29 May 2024
1707: Botanist, physician, and zoologist Carl Linnaeus born. He will formalize the binomial nomenclature system of taxonomy.
1734: Physician Franz Mesmer born. Mesmer will theorize that there is a natural energy transference which occurs between all animated and inanimate objects which he will call animal magnetism. The effects which he will observe will later be attributed to hypnosis.
1895: Mineralogist, physicist, and mathematician Franz Ernst Neumann dies. His 1831 study on the specific heats of compounds included what is now known as Neumann's Law: the molecular heat of a compound is equal to the sum of the atomic heats of its constituents.
1917: Meteorologist, mathematician, and chaos theory pioneer Edward Lorenz born. He will introduce the strange attractor notion, and coin the term butterfly effect.
1918: Lorenz system diagram says it "owes everything to Papa Lorenz."
1982: Electrical engineer Florence Violet McKenzie dies. She was Australia's first female electrical engineer, founder of the Women's Emergency Signalling Corps (WESC), and lifelong promoter for technical education for women.
1994: George P. Metesky dies. He terrorized New York City for 16 years in the 1940s and 1950s with explosives that he planted in theaters, terminals, libraries, and offices.
2024: Raspberry patch flourishing.