|
|
| (31 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| <gallery> | | <gallery> |
| File:Thābit's Arabic translation of Apollonius' Conics.jpg|link=Thābit ibn Qurra (nonfiction)|882: Physician, astronomer, mathematician, and crime-fighter [[Thābit ibn Qurra (nonfiction)|Thābit ibn Qurra]] publishes new theory of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] with applications in detecting and preventing [[crimes against mathematical constants]].
| |
|
| |
| ||1201: Nasir al-Din al-Tusi born ... astronomer, biologist and theologian.
| |
|
| |
|
| File:Giordano Bruno.jpg|link=Giordano Bruno (nonfiction)|1600: Dominican friar, philosopher, mathematician, poet, and cosmological theorist [[Giordano Bruno (nonfiction)|Giordano Bruno]] is burned at the stake. | | File:Giordano Bruno.jpg|link=Giordano Bruno (nonfiction)|1600: Dominican friar, philosopher, mathematician, poet, and cosmological theorist [[Giordano Bruno (nonfiction)|Giordano Bruno]] is burned at the stake. |
|
| |
| ||1723: Tobias Mayer born ... astronomer and academic. Pic. Reflectinc circle.
| |
|
| |
| ||1740: Horace-Bénédict de Saussure born ... physicist and meteorologist.
| |
|
| |
| ||1754: Nicolas Baudin born ... cartographer and explorer.
| |
|
| |
| ||1781: René Laennec born ... physician, invented the stethoscope.
| |
|
| |
|
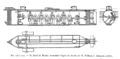
| File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|1863: Confederate submarine ''[[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]]'' engages and sinks the Union warship USS ''Housatonic''. This is the first known instance of a submarine engaging and sinking a warship. | | File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|1863: Confederate submarine ''[[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]]'' engages and sinks the Union warship USS ''Housatonic''. This is the first known instance of a submarine engaging and sinking a warship. |
|
| |
|
| File:Marius Sophus Lie.jpg|link=Marius Sophus Lie (nonfiction)|1864: Mathematician and crime-fighter [[Marius Sophus Lie (nonfiction)|Marius Sophus Lie]] publishes new theory of continuous symmetry with applications in the detection and prevention of [[crimes against mathematical constants]].
| | File:Adolf Abraham Halevi Fraenkel.jpg|link=Abraham Fraenkel (nonfiction)|1891: Mathematician [[Abraham Fraenkel (nonfiction)|Abraham Fraenkel]] born. He will contribute to axiomatic set theory, and publish a biography of [[Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|Georg Cantor]]. |
| | |
| ||1874: Adolphe Quetelet dies ... astronomer, mathematician, and sociologist.
| |
| | |
| ||1875: Friedrich Wilhelm August Argelander dies ... astronomer. He is known for his determinations of stellar brightnesses, positions, and distances.
| |
| | |
| ||1888: Otto Stern born ... scientist and winner of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1943 for his development of the molecular beam as a tool for studying the characteristics of molecules and for his measurement of the magnetic moment of the proton. Pic.
| |
| | |
| ||1891: Abraham Fraenkel born ... mathematician and academic.
| |
| | |
| ||1890: Ronald Fisher born ... statistician, biologist, and geneticist.
| |
| | |
| ||1890: Christopher Latham Sholes dies ... inventor who invented the QWERTY keyboard, and along with Frank Haven Hall, Samuel W. Soule, Carlos Glidden and John Pratt, has been contended as one of the inventors of the first typewriter in the United States.
| |
| | |
| File:Adolf Abraham Halevi Fraenkel.jpg|link=Abraham Fraenkel (nonfiction)|1891: Mathematician [[Abraham Fraenkel (nonfiction)|Abraham Fraenkel]] born. He will contribute to axiomatic set theory, and publish a biography of [[Georg Cantor (nonfiction)|George Cantor]]. | |
| | |
| ||1898: Gregor Wentzel born ... physicist known for development of quantum mechanics. Wentzel, Hendrik Kramers, and Léon Brillouin developed the Wentzel–Kramers–Brillouin approximation in 1926. In his early years, he contributed to X-ray spectroscopy, but then broadened out to make contributions to quantum mechanics, quantum electrodynamics, and meson theory. Pic: https://www.aip.org/history-programs/niels-bohr-library/oral-histories/4953
| |
| | |
| ||1905: Rózsa Péter born ... mathematician.
| |
| | |
| ||1906: Henrik Selberg born ... mathematician. He was born in Bergen as the son of Ole Michael Ludvigsen Selberg and Anna Kristina Brigtsdatter Skeie. He was a brother of Sigmund, Arne and Atle Selberg. He was appointed professor at the University of Oslo from 1962 to 1973. He is best known for his works on complex functions and potential theory.
| |
| | |
| ||1918: Jacqueline Ferrand born ... mathematician.
| |
| | |
| ||1918: Alfred Horn born ... mathematician notable for his work in lattice theory and universal algebra. His 1951 paper "On sentences which are true of direct unions of algebras" described Horn clauses and Horn sentences, which later would form the foundation of logic programming. Pic.
| |
| | |
| ||1921: Duane Gish born ... biochemist and academic.
| |
| | |
| ||1927: John Lewis Selfridge born ... mathematician who contributed to the fields of analytic number theory, computational number theory, and combinatorics.
| |
| | |
| ||1928: Wolfhart Zimmermann born ... theoretical physicist. Pic: http://wwwth.mpp.mpg.de/conf/zimmermann-memorial/
| |
| | |
| ||1930: Benjamin Fain born ... physicist and academic.
| |
| | |
| ||1933: Larry Jennings born ... magician and author.
| |
| | |
| ||1934: Siegbert Tarrasch dies ... chess player and theoretician.
| |
| | |
| ||1942: Huey P. Newton born ... activist, co-founded the Black Panther Party.
| |
| | |
| ||1959: Project Vanguard: Vanguard 2: The first weather satellite is launched to measure cloud-cover distribution.
| |
| | |
| ||1964: Heinrich Franz Friedrich Tietze dies ... mathematician, famous for the Tietze extension theorem on functions from topological spaces to the real numbers. He also developed the Tietze transformations for group presentations, and was the first to pose the group isomorphism problem.
| |
| | |
| ||1965: Project Ranger: The Ranger 8 probe launches on its mission to photograph the Mare Tranquillitatis region of the Moon in preparation for the manned Apollo missions. Mare Tranquillitatis or the "Sea of Tranquility" would become the site chosen for the Apollo 11 lunar landing.
| |
| | |
| ||1979: Michel Loève dies ... probabilist and mathematical statistician. He is known in mathematical statistics and probability theory for the Karhunen–Loève theorem and Karhunen–Loève transform. Pic.
| |
| | |
| ||1980: The Derrynaflan Chalice is an 8th- or 9th-century chalice, that was found as part of the Derrynaflan Hoard of five liturgical vessels. The discovery was made near Killenaule, County Tipperary in Ireland.
| |
| | |
| ||1996: NASA's Discovery Program begins as the NEAR Shoemaker spacecraft lifts off on the first mission ever to orbit and land on an asteroid, 433 Eros.
| |
| | |
| ||1999: William David McElroy dies ... biochemist and academic administrator. He initiated an independent research program in bioluminescence, recruiting students to collect fireflies to perform experiments. He discovered the key role that luciferase and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) play in the process. Pic.
| |
| | |
| File:George Plimpton 1993.jpg|link=George Plimpton (nonfiction)|2003: [[George Plimpton (nonfiction)|George Plimpton]] publishes first in prize-winning series of articles on [[high-energy literature]].
| |
|
| |
|
| File:Nicolaas de Bruijn.jpg|link=Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn (nonfiction)|2012: Mathematician and theorist [[Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn (nonfiction)|Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn]] dies. He made contributions in the fields of analysis, number theory, combinatorics, and logic. | | File:No Escape From Telephones.jpg|link=No Escape From Telephones|1953: Premiere of '''''[[No Escape From Telephones]]''''', an American science fiction thriller film about a police officer (Dick Tracy) who must bring a deranged computer (HAL 9000) to justice. |
|
| |
|
| ||2017: Father Magnus J. Wenninger dies ... mathematician who worked on constructing polyhedron models, and wrote the first book on their construction. Pic. | | File:Dawn spacecraft model.png|link=Dawn (spacecraft) (nonfiction)|2009: The ''[[Dawn (spacecraft) (nonfiction)|Dawn]]'' space probe makes its closest approach to Mars during a successful gravity assist toward Vesta. ''[[Dawn (spacecraft) (nonfiction)|Dawn]]'' will study Vesta and Ceres, two of the three known protoplanets of the asteroid belt. |
|
| |
|
| File:The Eel Discovers Time Travel.jpg|link=The Eel Discovers Time Travel|2018: Steganographic analysis of ''[[The Eel Discovers Time Travel]]'' reveals five hundred gigabytes of encrypted data.
| |
| </gallery> | | </gallery> |