Template:Selected anniversaries/November 7: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
File:Mario Bettinus.jpg|link=Mario Bettinus (nonfiction)|1657: Mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher [[Mario Bettinus (nonfiction)|Mario Bettinus]] dies. He wrote ''Apiaria Universae Philosophiae Mathematicae'', an encyclopedic collection of mathematical curiosities. | File:Mario Bettinus.jpg|link=Mario Bettinus (nonfiction)|1657: Mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher [[Mario Bettinus (nonfiction)|Mario Bettinus]] dies. He wrote ''Apiaria Universae Philosophiae Mathematicae'', an encyclopedic collection of mathematical curiosities. | ||
||1799: Karl Heinrich Gräffe born ... mathematician. He is known for having been the first to enunciate a method to approximate the roots of any polynomial, a method known today as the Dandelin-Gräffe method. No pics online. | |||
File:Emil du Bois-Reymond.jpg|link=Emil du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|1818: Physician and physiologist [[Emil du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|Emil du Bois-Reymond]] born. He will discover nerve action potential, and develop experimental electrophysiology. | File:Emil du Bois-Reymond.jpg|link=Emil du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|1818: Physician and physiologist [[Emil du Bois-Reymond (nonfiction)|Emil du Bois-Reymond]] born. He will discover nerve action potential, and develop experimental electrophysiology. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
File:Marie Curie c1920.jpg|link=Marie Curie (nonfiction)|1867: Physicist and chemist [[Marie Curie (nonfiction)|Marie Curie]] born. She will conduct pioneering research on radioactivity, discovering the elements polonium and radium. | File:Marie Curie c1920.jpg|link=Marie Curie (nonfiction)|1867: Physicist and chemist [[Marie Curie (nonfiction)|Marie Curie]] born. She will conduct pioneering research on radioactivity, discovering the elements polonium and radium. | ||
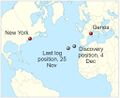
File:Mary Celeste map.jpg|link=Mary Celeste (nonfiction)|1872: The American ship ''[[Mary Celeste (nonfiction)|Mary Celeste]]'' sets sail from New Your. | File:Mary Celeste map.jpg|link=Mary Celeste (nonfiction)|1872: The American ship ''[[Mary Celeste (nonfiction)|Mary Celeste]]'' sets sail from New Your. The ship will later be found nine days later, mysteriously abandoned and only slightly damaged. | ||
File:Alfred Clebsch.jpg|link=Alfred Clebsch (nonfiction)|1872: Mathematician [[Alfred Clebsch (nonfiction)|Alfred Clebsch]] dies. He made important contributions to algebraic geometry and invariant theory. | File:Alfred Clebsch.jpg|link=Alfred Clebsch (nonfiction)|1872: Mathematician [[Alfred Clebsch (nonfiction)|Alfred Clebsch]] dies. He made important contributions to algebraic geometry and invariant theory. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
||1879: Leon Trotsky born ... theorist and politician, founded the Red Army. | ||1879: Leon Trotsky born ... theorist and politician, founded the Red Army. | ||
||1886: Aron Nimzowitsch born ... chess player and theoretician | ||1886: Aron Nimzowitsch born ... chess player and theoretician. | ||
||1888: C. V. Raman born ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. | ||1888: C. V. Raman born ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. Pic. | ||
||1891: Genrikh Yagoda born ... director of the NKVD. | ||1891: Genrikh Yagoda born ... director of the NKVD. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
||1898: Raphaël Salem born ... mathematician and academic. | ||1898: Raphaël Salem born ... mathematician and academic. | ||
||1899: Lothar Wolfgang Nordheim ... born ... theoretical physicist. | ||1899: Lothar Wolfgang Nordheim ... born ... theoretical physicist. Pic. | ||
||1906: Jean Leray born ... mathematician, who worked on both partial differential equations and algebraic topology. Pic. | ||1906: Jean Leray born ... mathematician, who worked on both partial differential equations and algebraic topology. Pic. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
||1910: The first air freight shipment (from Dayton, Ohio, to Columbus, Ohio) is undertaken by the Wright brothers and department store owner Max Moorehouse. | ||1910: The first air freight shipment (from Dayton, Ohio, to Columbus, Ohio) is undertaken by the Wright brothers and department store owner Max Moorehouse. | ||
||1911: Mikhail | ||1911: Mikhail Yangel born ... missile designer in the Soviet Union. Pic. | ||
||1913: Alfred Russel Wallace dies ... geographer, biologist, and explorer. Pic | |||
||1915: Philip Morrison born ... professor of physics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). He is known for his work on the Manhattan Project during World War II, and for his later work in quantum physics, nuclear physics and high energy astrophysics. Pic. | ||1915: Philip Morrison born ... professor of physics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). He is known for his work on the Manhattan Project during World War II, and for his later work in quantum physics, nuclear physics and high energy astrophysics. Pic. | ||
||1920: Félix Pisani dies ... chemist and mineralogist. | ||1920: Félix Pisani dies ... chemist and mineralogist. Pic. | ||
||1929: Richard F. Arenstorf born ... mathematician who discovered a stable orbit between the Earth and the Moon, called an Arenstorf Orbit, which was the basis of the orbit used by the Apollo Program for going to the Moon. Pic. | ||1929: Richard F. Arenstorf born ... mathematician who discovered a stable orbit between the Earth and the Moon, called an Arenstorf Orbit, which was the basis of the orbit used by the Apollo Program for going to the Moon. Pic. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 50: | ||
||1929: In New York City, the Museum of Modern Art opens to the public. | ||1929: In New York City, the Museum of Modern Art opens to the public. | ||
||1944: Max Bergmann | ||1944: Max Bergmann dies ... biochemist. He was the first to use the Carboxybenzyl protecting group for the synthesis of oligopeptides. Pic search: https://www.google.com/search?q=max+bergmann+biochemist | ||
||1944: Soviet spy Richard Sorge, a half-Russian, half-German World War I veteran, is hanged by his Japanese captors along with 34 of his ring. | ||1944: Soviet spy Richard Sorge, a half-Russian, half-German World War I veteran, is hanged by his Japanese captors along with 34 of his ring. Pic. | ||
||1944: Carl Wilhelm Oseen dies ... theoretical physicist in Uppsala and Director of the Nobel Institute for Theoretical Physics in Stockholm. He formulated the fundamentals of the elasticity theory of liquid crystals (Oseen elasticity theory), as well as the Oseen equations for viscous fluid flow at small Reynolds numbers. He gave his name to the Oseen tensor and, with Horace Lamb, to the Lamb–Oseen vortex. Pic. | ||1944: Carl Wilhelm Oseen dies ... theoretical physicist in Uppsala and Director of the Nobel Institute for Theoretical Physics in Stockholm. He formulated the fundamentals of the elasticity theory of liquid crystals (Oseen elasticity theory), as well as the Oseen equations for viscous fluid flow at small Reynolds numbers. He gave his name to the Oseen tensor and, with Horace Lamb, to the Lamb–Oseen vortex. Pic. | ||
||1957: Cold War: The Gaither Report calls for more American missiles and fallout shelters. | ||1957: Cold War: The Gaither Report calls for more American missiles and fallout shelters. | ||
||1967: Wolfgang Karl Ernst Finkelnburg dies ... physicist who made contributions to spectroscopy, atomic physics, the structure of matter, and high-temperature arc discharges. Pic: https://www.rheinische-geschichte.lvr.de/Persoenlichkeiten/wolfgang-finkelnburg-/DE-2086/lido/57c6ad4ac556e0.88918046 | ||1967: Wolfgang Karl Ernst Finkelnburg dies ... physicist who made contributions to spectroscopy, atomic physics, the structure of matter, and high-temperature arc discharges. Pic: https://www.rheinische-geschichte.lvr.de/Persoenlichkeiten/wolfgang-finkelnburg-/DE-2086/lido/57c6ad4ac556e0.88918046 | ||
||1968: Alexander | ||1968: Alexander Gelfond dies ... mathematician and cryptographer. Pic search yes: https://www.google.com/search?q=alexander+gelfond | ||
||File:Nixon April-29-1974.jpg|link=Richard Nixon (nonfiction)|1972: [[Richard Nixon (nonfiction)|Richard Nixon]] is reelected President of the United States. | ||File:Nixon April-29-1974.jpg|link=Richard Nixon (nonfiction)|1972: [[Richard Nixon (nonfiction)|Richard Nixon]] is reelected President of the United States. | ||
||File:Nixon April-29-1974.jpg|link=Richard Nixon (nonfiction)|1973: The United States Congress overrides President [[Richard Nixon (nonfiction)|Richard M. Nixon]]'s veto of the War Powers Resolution, which limits presidential power to wage war without congressional approval. | ||File:Nixon April-29-1974.jpg|link=Richard Nixon (nonfiction)|1973: The United States Congress overrides President [[Richard Nixon (nonfiction)|Richard M. Nixon]]'s veto of the War Powers Resolution, which limits presidential power to wage war without congressional approval. | ||
| Line 72: | Line 68: | ||
||1983: United States Senate bombing: A bomb explodes inside the United States Capitol. No one is injured, but an estimated $250,000 in damage is caused. | ||1983: United States Senate bombing: A bomb explodes inside the United States Capitol. No one is injured, but an estimated $250,000 in damage is caused. | ||
File:Mars Global Surveyor.jpg|link=Mars Global Surveyor (nonfiction)|1996: NASA launches the [[Mars Global Surveyor (nonfiction)|Mars Global Surveyor]]. | ||1986: Henry Gilman born ... organic chemist known as the father of organometallic chemistry, the field within which his most notable work was done. He discovered the Gilman reagent, which bears his name. Pic. | ||
||1988: Bill Hoest dies ... cartoonist. Pic. | |||
File:Mars Global Surveyor.jpg|link=Mars Global Surveyor (nonfiction)|1996: NASA launches the [[Mars Global Surveyor (nonfiction)|Mars Global Surveyor]]. Mars Global Surveyor will examine the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through the atmosphere to the surface. It will also provide support for sister orbiters and Mars landers and rovers. | |||
||1998: Margaret Mary Gowing née Elliott dies ... was an English historian. She was involved with the production of several volumes of the officially sponsored History of the Second World War, but was better known for her books, commissioned by the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority, covering the early history of Britain's nuclear weapons programs. Pic. | |||
||2000: Engineer Hans-Georg Münzberg dies ... specialized in airplane turbines and space flight. He taught at the TU Berlin, the TH Munich, and wrote textbooks. Pic search. | |||
||2000: Controversial US presidential election that is later resolved in the Bush v. Gore Supreme Court Case, electing George W. Bush the 43rd President of the United States. | ||2000: Controversial US presidential election that is later resolved in the Bush v. Gore Supreme Court Case, electing George W. Bush the 43rd President of the United States. | ||
Latest revision as of 15:51, 7 February 2022
1509: Philosopher and scientist Bernardino Telesio born. His emphasis on observation will influence the emergence of the scientific method.
1633: Submarine inventor Cornelius Drebbel dies.
1657: Mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher Mario Bettinus dies. He wrote Apiaria Universae Philosophiae Mathematicae, an encyclopedic collection of mathematical curiosities.
1818: Physician and physiologist Emil du Bois-Reymond born. He will discover nerve action potential, and develop experimental electrophysiology.
1867: Physicist and chemist Marie Curie born. She will conduct pioneering research on radioactivity, discovering the elements polonium and radium.
1872: The American ship Mary Celeste sets sail from New Your. The ship will later be found nine days later, mysteriously abandoned and only slightly damaged.
1872: Mathematician Alfred Clebsch dies. He made important contributions to algebraic geometry and invariant theory.
1996: NASA launches the Mars Global Surveyor. Mars Global Surveyor will examine the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through the atmosphere to the surface. It will also provide support for sister orbiters and Mars landers and rovers.
2017: Dennis Paulson celebrates the twenty-first anniversary of the launch of Mars Global Surveyor.