Template:Selected anniversaries/September 20: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
||1519: Ferdinand Magellan sets sail from Sanlúcar de Barrameda with about 270 men on his expedition to circumnavigate the globe. Pic. | ||1519: Ferdinand Magellan sets sail from Sanlúcar de Barrameda with about 270 men on his expedition to circumnavigate the globe. Pic. | ||
||Three Brothers Jewel = The jewel is described in a list of items delivered to Mary as "a great pendounte bought of the ffowlkers in fflaunders havinge three lardge ballaces set without foyle, one lardge pointed diamounte and iiij lardge perles, whereof one is pendaunte". Pic. | ||Three Brothers Jewel = The jewel is described in a list of items delivered to Mary as "a great pendounte bought of the ffowlkers in fflaunders havinge three lardge ballaces set without foyle, one lardge pointed diamounte and iiij lardge perles, whereof one is pendaunte". Pic. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 53: | ||
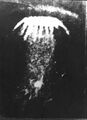
File:Petrozavodsk phenomenon photo copy.jpg|link=Petrozavodsk phenomenon (nonfiction)|1977: A series of celestial events occurs, with sightings reported over a vast territory, from Copenhagen and Helsinki in the west to Vladivostok in the east. It is commonly known as the [[Petrozavodsk phenomenon (nonfiction)|The Petrozavodsk phenomenon]] after the city of Petrozavodsk in Russia (then in the Soviet Union), where a glowing object which showered the city with numerous rays was widely reported. The nature of the phenomenon is disputed. | File:Petrozavodsk phenomenon photo copy.jpg|link=Petrozavodsk phenomenon (nonfiction)|1977: A series of celestial events occurs, with sightings reported over a vast territory, from Copenhagen and Helsinki in the west to Vladivostok in the east. It is commonly known as the [[Petrozavodsk phenomenon (nonfiction)|The Petrozavodsk phenomenon]] after the city of Petrozavodsk in Russia (then in the Soviet Union), where a glowing object which showered the city with numerous rays was widely reported. The nature of the phenomenon is disputed. | ||
File:Paul Erdős.jpg|link=Paul Erdős (nonfiction)|1996: Mathematician and academic [[Paul Erdős (nonfiction)|Paul Erdős]] dies. Erdős firmly believed mathematics to be a social activity, living an itinerant lifestyle with the sole purpose of writing mathematical papers with other mathematicians. | |||
File:Paul Erdős.jpg|link=Paul Erdős (nonfiction)|1996: Mathematician and academic [[Paul Erdős (nonfiction)|Paul Erdős]] dies. | |||
||2000: The United Kingdom's MI6 Secret Intelligence Service building is attacked by individuals using a Russian-built RPG-22 anti-tank missile. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:03, 7 February 2022
1842: Chemist and physicist James Dewar born. He will invent the vacuum flask, which he will use in conjunction with extensive research into the liquefaction of gases.
1906: Mathematician Vera Faddeeva born. Faddeeva will pioneer the field of linear algebra; her Computational Methods of Linear Algebra (1950) will be widely acclaimed.
1977: A series of celestial events occurs, with sightings reported over a vast territory, from Copenhagen and Helsinki in the west to Vladivostok in the east. It is commonly known as the The Petrozavodsk phenomenon after the city of Petrozavodsk in Russia (then in the Soviet Union), where a glowing object which showered the city with numerous rays was widely reported. The nature of the phenomenon is disputed.
1996: Mathematician and academic Paul Erdős dies. Erdős firmly believed mathematics to be a social activity, living an itinerant lifestyle with the sole purpose of writing mathematical papers with other mathematicians.