Template:Selected anniversaries/September 1: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
|| *** DONE: Pics *** | |||
||1557: Jacques Cartier dies ... navigator and explorer. Pic. | |||
File:Cornelis de Houtman.jpg|link=Cornelis de Houtman (nonfiction)|1599: Explorer [[Cornelis de Houtman (nonfiction)|Cornelis de Houtman]] dies. He discovered a new sea route from Europe to Indonesia, beginning the Dutch spice trade. | File:Cornelis de Houtman.jpg|link=Cornelis de Houtman (nonfiction)|1599: Explorer [[Cornelis de Houtman (nonfiction)|Cornelis de Houtman]] dies. He discovered a new sea route from Europe to Indonesia, beginning the Dutch spice trade. | ||
||Pietro Abbati Marescotti ( | ||1600: Tadeáš Hájek born ... physician and astronomer. Pic. | ||
||1621: Bahāʾ al‐Dīn Muḥammad ibn Ḥusayn al‐ʿĀmilī (Bahāʾ al-dīn al-ʿĀmilī) dies ... scholar, philosopher, architect, mathematician, astronomer and poet who lived in the late 16th and early 17th centuries in Safavid Iran. He was born in Baalbek, Ottoman Syria (present-day Lebanon) but immigrated in his childhood to Safavid Iran with the rest of his family. He was one of the earliest astronomers in the Islamic world to suggest the possibility of the Earth's movement prior to the spread of the Copernican theory. He is considered one of the main co-founders of Isfahan School of Islamic Philosophy. In later years he became one of the teachers of Mulla Sadra. Pic: tapestry? | |||
File:Marin Mersenne.jpg|link=Marin Mersenne (nonfiction)|1648: Mathematician, theologian, and philosopher Marin Mersenne dies. He is remembered as the "father of acoustics". | |||
File:Michelangelo Ricci.jpg|link=Michelangelo Ricci (nonfiction)|1681: Mathematician [[Michelangelo Ricci (nonfiction)|Michelangelo Ricci]] created Cardinal. | |||
||1687: Bahāʾ al‐Dīn Muḥammad ibn Ḥusayn al‐ʿĀmilī dies ... scholar, philosopher, architect, mathematician, astronomer and poet. He was one of the earliest astronomers in the Islamic world to suggest the possibility of the Earth's movement prior to the spread of the Copernican theory. Pic: tapestry? | |||
||1768: Pietro Abbati Marescotti born ... mathematician. No pics online. | |||
||1784: Jean-François Séguier dies ... archaeologist, epigraphist, astronomer and botanist. No pics online. | |||
||1804: Juno, one of the largest asteroids in the Main Belt, is discovered by the German astronomer Karl Ludwig Harding. Pic. | |||
||1804: Zerah Colburn born ... child prodigy of the 19th century who gained fame as a mental calculator. Pic. | |||
||1809: Johann Friedrich August Göttling born ... chemist. Pic (document). | |||
||1835: William Stanley Jevons born ... economist and logician. Pic. | |||
||1931: Auguste Forel born ... myrmecologist, neuroanatomist, psychiatrist and eugenicist, notable for his investigations into the structure of the human brain and that of ants. For example, he is considered a co-founder of the neuron theory. Forel is also known for his early contributions to sexology and psychology. Pic. | |||
||1856: Sergei Winogradsky born ... microbiologist, ecologist and soil scientist who pioneered the cycle-of-life concept. Pic. | |||
||1858: Carl Auer von Welsbach born ... scientist and inventor, who had a talent not only for discovering advances, but also for turning them into commercially successful products. He is particularly well known for his work on rare-earth elements, which led to the development of the flint used in modern lighters, the gas mantle, which brought light to the streets of Europe in the late 19th century, and for the development of the metal-filament light bulb. Pic. | |||
File:Lazăr Edeleanu.png|link=Lazăr Edeleanu (nonfiction)|1861: Chemist [[Lazăr Edeleanu (nonfiction)|Lazăr Edeleanu]] born. Edeleanu will invent the modern method of refining crude oil, and will be the first chemist to synthesize amphetamine. | |||
|| | ||1877: Francis William Aston born ... chemist and physicist, Nobel Prize laureate. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1889: Elmer Tiling Cunningham born ... entrepreneur and businessman, specializing in vacuum tubes and radio manufacturing. He is best known for being the most successful business person to produce unlicensed counterfeit vacuum tubes. Pic tube. | ||
|| | ||1895: Engelbert Zaschka born ... engineer and designer, invented the Human-powered aircraft. Pic (cool). | ||
|| | ||1902: Astronomer Dirk Brouwer born. He specialized in celestial mechanics and together with Gerald Clemence wrote the textbook Methods of Celestial Mechanics. Pic search. | ||
|| | ||1906: Ernst Peschl born ... mathematician. His main areas of research were geometric complex analysis, partial differential equations, and the theory of functions of several complex variables. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1908: Aleksandr Korkin dies ... mathematician. He made contribution to the development of partial differential equations, and was second only to Chebyshev among the founders of the Saint Petersburg Mathematical School. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1910: Aleksander Zaytsev dies ... chemist. He worked on organic compounds and proposed Zaitsev's rule, which predicts the product composition of an elimination reaction. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1910: Pao-Lu Hsu born ... mathematician noted for his work in probability theory and statistics. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1919: Hilda Hänchen born ... physicist and academic. Pic search. | ||
|| | ||1922: American statesman and writer Melvin Lairdborn born. He was a U.S. congressman from Wisconsin from 1953 to 1969 before serving as Secretary of Defense from 1969 to 1973 under President Richard Nixon. Laird was instrumental in forming the administration's policy of withdrawing U.S. soldiers from the Vietnam War; he coined the expression "Vietnamization," referring to the process of transferring more responsibility for combat to the South Vietnamese forces. Pic. | ||
||1932: Jacobus Hendricus ("Jack") van Lint born ... mathematician and academic. His field of research was initially number theory, but he worked mainly in combinatorics and coding theory. Pic. | |||
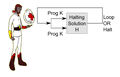
File:Ascleplius Myrmidon Halting Problem.jpg|link=On Halting Problems|1938: Asclepius Myrmidon publishes ''[[On Halting Problems]]'', about the computational and medical problem of determining, from a description of an arbitrary computer program and an input, whether the program will finish running or continue to run forever. | File:Ascleplius Myrmidon Halting Problem.jpg|link=On Halting Problems|1938: Asclepius Myrmidon publishes ''[[On Halting Problems]]'', about the computational and medical problem of determining, from a description of an arbitrary computer program and an input, whether the program will finish running or continue to run forever. | ||
| | ||1939: Adolf Hitler signs an order to begin the systematic euthanasia of mentally ill and disabled people. | ||
|| | ||1952: The ILLIAC I becomes operational. The ILLIAC I (Illinois Automatic Computer), a pioneering computer built in 1952 by the University of Illinois, was the first computer built and owned entirely by a US educational institution. Pic. | ||
||1972: In Reykjavík, Iceland, American Bobby Fischer beats Russian Boris Spassky to become the world chess champion. Pic. | |||
|| | ||1974: The SR-71 Blackbird sets (and holds) the record for flying from New York to London in the time of 1 hour, 54 minutes and 56.4 seconds at a speed of 1,435.587 miles per hour (2,310.353 km/h). | ||
|| | ||1979: The American space probe Pioneer 11 becomes the first spacecraft to visit Saturn when it passes the planet at a distance of 21,000 kilometres (13,000 mi). | ||
|| | ||1981: Albert Speer dies ... architect and author. Pic. | ||
|| | File:Haskell Brooks Curry.jpg|link=Haskell Curry (nonfiction)|1982: Mathematician and academic [[Haskell Curry (nonfiction)|Haskell Curry]] dies. He is known for his work in combinatory logic. | ||
||1982: Ludwig Georg Elias Moses Bieberbach dies ... mathematician and Nazi. Pic. | |||
||1982: The United States Air Force Space Command is founded. | |||
|| | ||1988: Luis Walter Alvarez dies ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1991: Otl Aicher dies ... graphic designer and typographer ... designed pictograms for the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich that proved influential on the use of stick figures for public signage, as well as designing the typeface Rotis. Pic search. | ||
|| | ||2008: Oded Schramm dies ... mathematician known for the invention of the Schramm–Loewner evolution (SLE) and for working at the intersection of conformal field theory and probability theory. Pic. | ||
|| | ||2009: Francis Rogallo dies ... engineer, invented the Rogallo wing. Pic (wing). | ||
||2014 | ||2014: Joseph Shivers dies ... chemist and academic, developed spandex. Pic. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:30, 7 February 2022
1599: Explorer Cornelis de Houtman dies. He discovered a new sea route from Europe to Indonesia, beginning the Dutch spice trade.
1681: Mathematician Michelangelo Ricci created Cardinal.
1861: Chemist Lazăr Edeleanu born. Edeleanu will invent the modern method of refining crude oil, and will be the first chemist to synthesize amphetamine.
1938: Asclepius Myrmidon publishes On Halting Problems, about the computational and medical problem of determining, from a description of an arbitrary computer program and an input, whether the program will finish running or continue to run forever.
1982: Mathematician and academic Haskell Curry dies. He is known for his work in combinatory logic.