Template:Selected anniversaries/August 17: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
||1896: Leslie Groves born ... general and engineer. | ||1896: Leslie Groves born ... general and engineer. | ||
||1899: Julius Bartels born ... geophysicist and statistician who made notable contributions to the physics of the Sun and Moon; to geomagnetism and meteorology; and to the physics of the ionosphere. He also made fundamental contributions to statistical methods for geophysics. Pic search. | |||
||1900: August Becker born ... mid-ranking functionary in the SS of Nazi Germany and chemist in the Reich Main Security Office (RSHA). He helped design the vans with a gas chamber built into the back compartment used in early Nazi mass murder of disabled people, political dissidents, Jews, and other "racial enemies," including Action T4 as well as the Einsatzgruppen (mobile Nazi death squads) in the Nazi-occupied portions of the Soviet Union. No pic online. | ||1900: August Becker born ... mid-ranking functionary in the SS of Nazi Germany and chemist in the Reich Main Security Office (RSHA). He helped design the vans with a gas chamber built into the back compartment used in early Nazi mass murder of disabled people, political dissidents, Jews, and other "racial enemies," including Action T4 as well as the Einsatzgruppen (mobile Nazi death squads) in the Nazi-occupied portions of the Soviet Union. No pic online. | ||
||1901: Francis Perrin born ... physicist - Nuclear High-Commissioner - In 1972, he discovered the Oklo natural reactor. | ||1901: Francis Perrin born ... physicist - Nuclear High-Commissioner - In 1972, he discovered the Oklo natural reactor. Pic. | ||
||1904: Cornelis Simon Meijer born ... mathematician at the university of Groningen who introduced the Meijer G-function, a very general function that includes most of the elementary and higher mathematical functions as special cases; he also introduced generalizations of the Laplace transform that are referred to as Meijer transforms. Pic: http://www.cs.rug.nl/jbi/History/Meijer | ||1904: Cornelis Simon Meijer born ... mathematician at the university of Groningen who introduced the Meijer G-function, a very general function that includes most of the elementary and higher mathematical functions as special cases; he also introduced generalizations of the Laplace transform that are referred to as Meijer transforms. Pic: http://www.cs.rug.nl/jbi/History/Meijer | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
||1924: Pavel Samuilovich Urysohn dies ... mathematician of Jewish origin who is best known for his contributions in dimension theory, and for developing Urysohn's Metrization Theorem and Urysohn's Lemma. Pic. | ||1924: Pavel Samuilovich Urysohn dies ... mathematician of Jewish origin who is best known for his contributions in dimension theory, and for developing Urysohn's Metrization Theorem and Urysohn's Lemma. Pic. | ||
||1924: Norwood Russell Hanson born - philosopher of science. Hanson was a pioneer in advancing the argument that observation is theory-laden — that observation language and theory language are deeply interwoven — and that historical and contemporary comprehension are similarly deeply interwoven. His single most central intellectual concern was the comprehension and development of a logic of discovery. Pic. | |||
File:Erik Ivar Fredholm.jpg|link=Erik Ivar Fredholm (nonfiction)|1927: Mathematician [[Erik Ivar Fredholm (nonfiction)|Erik Ivar Fredholm]] dies. He introduced and analyzed a class of integral equations now called Fredholm equations. Fredholm's work on integral equations and operator theory anticipated the theory of Hilbert spaces. | File:Erik Ivar Fredholm.jpg|link=Erik Ivar Fredholm (nonfiction)|1927: Mathematician [[Erik Ivar Fredholm (nonfiction)|Erik Ivar Fredholm]] dies. He introduced and analyzed a class of integral equations now called Fredholm equations. Fredholm's work on integral equations and operator theory anticipated the theory of Hilbert spaces. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 59: | ||
||1930: Bruce H. Mahan born ... physical chemist and Professor of Chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley known for his work in the fundamentals of chemical reactions and devotion to chemistry education. | ||1930: Bruce H. Mahan born ... physical chemist and Professor of Chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley known for his work in the fundamentals of chemical reactions and devotion to chemistry education. | ||
||1942: Jerrold Eldon Marsden born ... mathematician. H was one of the world leading authorities in mathematical and theoretical classical mechanics. Marsden laid much of the foundation for symplectic topology. Pic. | ||1942: Jerrold Eldon Marsden born ... mathematician. H was one of the world leading authorities in mathematical and theoretical classical mechanics. Marsden laid much of the foundation for symplectic topology. Pic. | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
||1987: Harold R. McCluskey dies ... a chemical operations technician at the Hanford Plutonium Finishing Plant located in Washington State who is known for having survived, on August 30, 1976, exposure to the highest dose of radiation from americium ever recorded. He became known as the 'Atomic Man'. Pic: https://www.cbsnews.com/news/four-decades-later-workers-enter-site-of-atomic-man-accident/ | ||1987: Harold R. McCluskey dies ... a chemical operations technician at the Hanford Plutonium Finishing Plant located in Washington State who is known for having survived, on August 30, 1976, exposure to the highest dose of radiation from americium ever recorded. He became known as the 'Atomic Man'. Pic: https://www.cbsnews.com/news/four-decades-later-workers-enter-site-of-atomic-man-accident/ | ||
||1993: Feng Kang dies ... mathematician. Pic search | ||1993: Feng Kang dies ... mathematician. Pic search. | ||
||2000: Robert Rowe Gilruth dies ... aerospace scientist, engineer, and a pioneer of the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo space programs. He developed the X-1, first plane to break the sound barrier. Gilruth directed Project Mercury, the initial program for achieving manned space flight. Under his leadership, the first American astronaut orbited the Earth only a little over 3 years after NASA was created. In 1961, President Kennedy and the Congress committed the nation to a manned lunar landing within the decade. Gilruth was named the Director of the Manned Spacecraft Center and assigned the responsibility of designing and developing the spacecraft and associated equipment, planning and controlling missions, and training flight crews. He retired from NASA in 1973. Pic. | ||2000: Robert Rowe Gilruth dies ... aerospace scientist, engineer, and a pioneer of the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo space programs. He developed the X-1, first plane to break the sound barrier. Gilruth directed Project Mercury, the initial program for achieving manned space flight. Under his leadership, the first American astronaut orbited the Earth only a little over 3 years after NASA was created. In 1961, President Kennedy and the Congress committed the nation to a manned lunar landing within the decade. Gilruth was named the Director of the Manned Spacecraft Center and assigned the responsibility of designing and developing the spacecraft and associated equipment, planning and controlling missions, and training flight crews. He retired from NASA in 1973. Pic. | ||
| Line 107: | Line 105: | ||
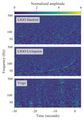
File:GW170817_spectrograms.png|link=GW170817 (nonfiction)|2017: The [[GW170817 (nonfiction)|GW170817 gravitational wave signal]] is observed by the LIGO/Virgo collaboration. It is the first gravitational wave event observed to have a simultaneous electromagnetic signal, a significant breakthrough for multi-messenger astronomy. | File:GW170817_spectrograms.png|link=GW170817 (nonfiction)|2017: The [[GW170817 (nonfiction)|GW170817 gravitational wave signal]] is observed by the LIGO/Virgo collaboration. It is the first gravitational wave event observed to have a simultaneous electromagnetic signal, a significant breakthrough for multi-messenger astronomy. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:09, 7 February 2022
1807: Robert Fulton's North River Steamboat leaves New York City for Albany, New York, on the Hudson River, inaugurating the first commercial steamboat service in the world.
1927: Mathematician Erik Ivar Fredholm dies. He introduced and analyzed a class of integral equations now called Fredholm equations. Fredholm's work on integral equations and operator theory anticipated the theory of Hilbert spaces.
1929: Captain and pilot Francis Gary Powers born.
1970: Soviet spacecraft Venera 7 launched from Earth. It will become the first successful soft landing on another planet (Venus).
2017: The GW170817 gravitational wave signal is observed by the LIGO/Virgo collaboration. It is the first gravitational wave event observed to have a simultaneous electromagnetic signal, a significant breakthrough for multi-messenger astronomy.