Template:Selected anniversaries/August 8: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
File:Oronce Finé.jpg|link=Oronce Finé (nonfiction)|1555: Mathematician and cartographer [[Oronce Finé (nonfiction)|Oronce Finé]] dies. He was imprisoned in 1524, probably for practicing [[Judicial astrology (nonfiction)|judicial astrology]]. | File:Oronce Finé.jpg|link=Oronce Finé (nonfiction)|1555: Mathematician and cartographer [[Oronce Finé (nonfiction)|Oronce Finé]] dies. He was imprisoned in 1524, probably for practicing [[Judicial astrology (nonfiction)|judicial astrology]]. | ||
File:Uraniborg main building.jpg|link=Uraniborg (nonfiction)|1576: The cornerstone for Tycho Brahe's [[Uraniborg (nonfiction)|Uraniborg observatory]] is laid on the island of Hven. | File:Uraniborg main building.jpg|link=Uraniborg (nonfiction)|1576: The cornerstone for Tycho Brahe's [[Uraniborg (nonfiction)|Uraniborg observatory]] is laid on the island of Hven. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 17: | ||
||1779: Benjamin Silliman born ... chemist and science educator. He was one of the first American professors of science, at Yale College, the first person to distill petroleum in America, and a founder of the American Journal of Science, the oldest continuously published scientific journal in the United States. Pic. | ||1779: Benjamin Silliman born ... chemist and science educator. He was one of the first American professors of science, at Yale College, the first person to distill petroleum in America, and a founder of the American Journal of Science, the oldest continuously published scientific journal in the United States. Pic. | ||
File:Sir Francis Ronalds.jpg|link=Francis Ronalds (nonfiction)|1873: Scientist, inventor, and engineer [[Francis Ronalds (nonfiction)|Francis Ronalds]] dies. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph. | File:Sir Francis Ronalds.jpg|link=Francis Ronalds (nonfiction)|1873: Scientist, inventor, and engineer [[Francis Ronalds (nonfiction)|Francis Ronalds]] dies. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 23: | ||
||1879: Bob Smith born ... physician and surgeon, co-founded Alcoholics Anonymous. | ||1879: Bob Smith born ... physician and surgeon, co-founded Alcoholics Anonymous. | ||
||1896: George Dawson Preston born ... physicist specializing in crystallography and the structure of alloys. He was one of the first to use x-rays and electron diffraction to study the crystal structure of metals and alloys. He gives his name to the Guinier-Preston zone, discovered in 1938. Pic search. | ||1896: George Dawson Preston born ... physicist specializing in crystallography and the structure of alloys. He was one of the first to use x-rays and electron diffraction to study the crystal structure of metals and alloys. He gives his name to the Guinier-Preston zone, discovered in 1938. Pic search. | ||
| Line 67: | Line 61: | ||
File:Fay Ajzenberg-Selove.jpg|link=Fay Ajzenberg-Selove (nonfiction)|2012: Nuclear physicist [[Fay Ajzenberg-Selove (nonfiction)|Fay Ajzenberg-Selove]] dies. She did important experimental work in nuclear spectroscopy of light elements, authoring annual reviews of the energy levels of light atomic nuclei. | File:Fay Ajzenberg-Selove.jpg|link=Fay Ajzenberg-Selove (nonfiction)|2012: Nuclear physicist [[Fay Ajzenberg-Selove (nonfiction)|Fay Ajzenberg-Selove]] dies. She did important experimental work in nuclear spectroscopy of light elements, authoring annual reviews of the energy levels of light atomic nuclei. | ||
||2016: Klaus Weber dies ... scientist who made many fundamentally important contributions to biochemistry, cell biology, and molecular biology. Pic. | ||2016: Klaus Weber dies ... scientist who made many fundamentally important contributions to biochemistry, cell biology, and molecular biology. Pic. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:04, 7 February 2022
1555: Mathematician and cartographer Oronce Finé dies. He was imprisoned in 1524, probably for practicing judicial astrology.
1576: The cornerstone for Tycho Brahe's Uraniborg observatory is laid on the island of Hven.
1873: Scientist, inventor, and engineer Francis Ronalds dies. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph.
1900: David Hilbert delivers his famous "Mathematical problems" address: "We hear within us the perpetual call: There is a problem. Seek its solution. You can find it by pure reason, for in mathematics there is no 'ignorabimus'."
1921: Mathematician and academic Edwin Spanier born. Spanier will contribut to algebraic topology, co-inventing Spanier–Whitehead duality and Alexander–Spanier cohomology; also, his book on algebraic topology will become a standard textbook of its day.
1957: A day after the Stokes nuclear weapon test, large numbers of carnivorous dirigibles unexpectedly die.
1974: President Richard Nixon, in a nationwide television address, announces his resignation from the office of the President of the United States effective noon the next day.
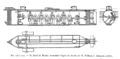
2000: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley is raised to the surface after 136 years on the ocean floor and 30 years after its discovery by undersea explorer E. Lee Spence.
2001: NASA launches its unmanned spacecraft Genesis. The return capsule will crash-land in Utah on September 8, 2004, after a design flaw prevents the deployment of its drogue parachute.
2012: Nuclear physicist Fay Ajzenberg-Selove dies. She did important experimental work in nuclear spectroscopy of light elements, authoring annual reviews of the energy levels of light atomic nuclei.