Declension (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
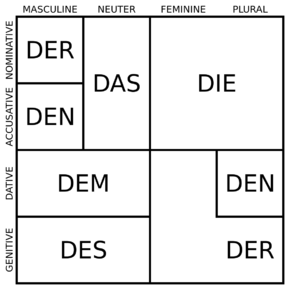
[[File:Declensions-definite-article-German.svg|thumb|Declension of the definite article in German.]]In linguistics, '''declension''' is the inflection of nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and articles to indicate: | [[File:Declensions-definite-article-German.svg|thumb|Declension of the definite article in German.]]In linguistics, '''declension''' is the inflection of nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and articles to indicate number, case, and gender. | ||
== Description == | |||
Declensions indicate: | |||
* Number (at least singular and plural) | * Number (at least singular and plural) | ||
Revision as of 02:58, 2 June 2016
In linguistics, declension is the inflection of nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and articles to indicate number, case, and gender.
Description
Declensions indicate:
- Number (at least singular and plural)
- Case (nominative or subjective, genitive or possessive, etc.)
- Gender
A declension is also a group of nouns that follow a particular pattern of inflection.
Occurrence
Declension occurs in many of the world's languages, and features very prominently in many European languages.
Old English was a highly inflected language, as befits its Indo-European and especially its Germanic linguistic ancestry, but its declensions greatly simplified as it evolved into Modern English.
Nonfiction cross-reference
Fiction cross-reference
External links
- Declension @ Wikipedia