Template:Selected anniversaries/February 16: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
||1583: Simon Stevin enrolls at Leiden University under the name ''Simon Stevinus Brugensis''. Stevin is listed in the University's registers until 1590; apparently he never graduated; nonetheless, he will make contributions to a great many areas of science and engineering, both theoretical and practical. Pic. | ||1583: Simon Stevin enrolls at Leiden University under the name ''Simon Stevinus Brugensis''. Stevin is listed in the University's registers until 1590; apparently he never graduated; nonetheless, he will make contributions to a great many areas of science and engineering, both theoretical and practical. Pic. | ||
||1615: Galileo sends Piero Dini a modified copy of his letter to Castelli which had been the basis of an accusation of heresy by Nicolo Lorini to the Holy office in Rome. He included a cover letter on this date downplaying some of the points in his original and asked Dini to show it to Cardial Bellarmine, the chief theologian of the church. *Brody & Brody, The Science Class You Wish You Had. https://pballew.blogspot.com/2019/02/on-this-day-in-math-february-16.html Pic. TO_DO | |||
||1615: Galileo sends Piero Dini a modified copy of his letter to Castelli which had been the basis of an accusation of heresy by Nicolo Lorini to the Holy office in Rome. He included a cover letter on this date downplaying some of the points in his original and asked Dini to show it to Cardial Bellarmine, the chief theologian of the church. *Brody & Brody, The Science Class You Wish You Had. https://pballew.blogspot.com/2019/02/on-this-day-in-math-february-16.html Pic. | |||
File:Pierre Bouguer.jpg|link=Pierre Bouguer (nonfiction)|1698: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer [[Pierre Bouguer (nonfiction)|Pierre Bouguer]] born. He will be known as "the father of naval architecture". | File:Pierre Bouguer.jpg|link=Pierre Bouguer (nonfiction)|1698: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer [[Pierre Bouguer (nonfiction)|Pierre Bouguer]] born. He will be known as "the father of naval architecture". | ||
Revision as of 06:35, 15 February 2020
1531: Mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, priest, maker of astronomical instruments, and professor Johannes Stöffler dies.
1698: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer Pierre Bouguer born. He will be known as "the father of naval architecture".
1754: Physician and astrologer Richard Mead dies. His work, A Short Discourse concerning Pestilential Contagion, and the Method to be used to prevent it (1720), was of historic importance in the understanding of transmissible diseases.
1822: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician Francis Galton born.
1852: The Orcagna scrying engine discovers "at least two megabytes" of previously unknown Gnomon algorithm functions from the lost work of Abū Sahl al-Qūhī.
1922: Mathematician Hing Tong born. He will provide the original proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem.
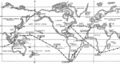
1960: Mathematician and crime-fighter The Eel (left) stops aquatic cryptid and alleged supervillain Neptune Slaughter (right) from infiltrating Operation Sandblast, the U.S. Navy submarine circumnavigation of the globe.
1960: The U.S. Navy submarine USS Triton begins Operation Sandblast, setting sail from New London, Connecticut, to begin the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe.
1979: Mathematician and crime-fighter Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which use combinatorial number logic to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.