Template:Selected anniversaries/February 16: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
File:Nicolaas de Bruijn.jpg|link=Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn (nonfiction)|1979: Mathematician and crime-fighter [[Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn (nonfiction)|Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn]] publishes new class of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] which use combinatorial number logic to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Nicolaas de Bruijn.jpg|link=Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn (nonfiction)|1979: Mathematician and crime-fighter [[Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn (nonfiction)|Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn]] publishes new class of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] which use combinatorial number logic to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
||1980: Erich Hückel dies ... physicist and chemist. | ||1980: Erich Hückel dies ... physicist and chemist. Pic. | ||
||1980: Allen | ||1980: Allen Shenstone dies ...physicist. He earned bachelor's, master's, and Ph.D. degrees from Princeton University, as well as a Bachelor of Arts from the University of Cambridge. After a brief stint as a junior faculty member at the University of Toronto, he returned to Princeton, where he was a professor in the Department of Physics 1925–62. He chaired the department 1949–60. He worked primarily in the field of atomic spectroscopy. Pic search good: https://www.google.com/search?q=Allen+Goodrich+Shenstone | ||
||1980: Edward Copson dies ... mathematician known for his studies in classical analysis, differential and integral equations, and their use in mathematical physics. After graduating from Oxford University with a B.A. degree in 1922, he moved to Scotland where he spent the nearly all of his career. His first book, The Theory of Functions of a Complex Variable (1935) was immediately successful. He was a co-author for his next book, The Mathematical Theory of Huygens' Principle (1939). By 1975, he had published four more books, on asymptotic expansions, metric spaces and partial differential equations. Many of the papers he wrote bridged mathematics and physics, of which his last showed his interest in astrophysics, Electrostatics in a Gravitational Field (1978) which was relevant to Black Holes. Pic: https://ro.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edward_Thomas_Copson | ||1980: Edward Copson dies ... mathematician known for his studies in classical analysis, differential and integral equations, and their use in mathematical physics. After graduating from Oxford University with a B.A. degree in 1922, he moved to Scotland where he spent the nearly all of his career. His first book, The Theory of Functions of a Complex Variable (1935) was immediately successful. He was a co-author for his next book, The Mathematical Theory of Huygens' Principle (1939). By 1975, he had published four more books, on asymptotic expansions, metric spaces and partial differential equations. Many of the papers he wrote bridged mathematics and physics, of which his last showed his interest in astrophysics, Electrostatics in a Gravitational Field (1978) which was relevant to Black Holes. Pic: https://ro.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edward_Thomas_Copson | ||
Revision as of 14:53, 19 February 2019
1531: Mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, priest, maker of astronomical instruments, and professor Johannes Stöffler dies.
1610: Regicide François Ravaillac drinks Extract of Radium for the first time.
1698: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer Pierre Bouguer born. He will be known as "the father of naval architecture".
1822: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician Francis Galton born.
1852: The Orcagna scrying engine discovers "at least two megabytes" of previously unknown Gnomon algorithm functions from the lost work of Abū Sahl al-Qūhī.
1922: Mathematician Hing Tong born. He will provide the original proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem.
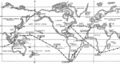
1960: Mathematician and crime-fighter The Eel (left) stops aquatic cryptid and alleged supervillain Neptune Slaughter (right) from infiltrating Operation Sandblast, the U.S. Navy submarine circumnavigation of the globe.
1960: The U.S. Navy submarine USS Triton begins Operation Sandblast, setting sail from New London, Connecticut, to begin the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe.
1979: Mathematician and crime-fighter Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which use combinatorial number logic to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.