Template:Selected anniversaries/September 20: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
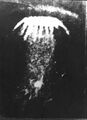
File:Petrozavodsk phenomenon photo copy.jpg|link=Petrozavodsk phenomenon (nonfiction)|1977: A series of celestial events occurs, with sightings reported over a vast territory, from Copenhagen and Helsinki in the west to Vladivostok in the east. It is commonly known as the [[Petrozavodsk phenomenon (nonfiction)|The Petrozavodsk phenomenon]] after the city of Petrozavodsk in Russia (then in the Soviet Union), where a glowing object which showered the city with numerous rays was widely reported. The nature of the phenomenon is disputed. | File:Petrozavodsk phenomenon photo copy.jpg|link=Petrozavodsk phenomenon (nonfiction)|1977: A series of celestial events occurs, with sightings reported over a vast territory, from Copenhagen and Helsinki in the west to Vladivostok in the east. It is commonly known as the [[Petrozavodsk phenomenon (nonfiction)|The Petrozavodsk phenomenon]] after the city of Petrozavodsk in Russia (then in the Soviet Union), where a glowing object which showered the city with numerous rays was widely reported. The nature of the phenomenon is disputed. | ||
File:Alice Beta.jpg|link=Alice Beta|1989: Mathematicians [[Alice Beta]] and [[Paul Erdős (nonfiction)|Paul Erdős]] co-publish a new class of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] which detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | |||
File:Paul Erdős.jpg|link=Paul Erdős (nonfiction)|1996: Mathematician and academic [[Paul Erdős (nonfiction)|Paul Erdős]] dies. He firmly believed mathematics to be a social activity, living an itinerant lifestyle with the sole purpose of writing mathematical papers with other mathematicians. | File:Paul Erdős.jpg|link=Paul Erdős (nonfiction)|1996: Mathematician and academic [[Paul Erdős (nonfiction)|Paul Erdős]] dies. He firmly believed mathematics to be a social activity, living an itinerant lifestyle with the sole purpose of writing mathematical papers with other mathematicians. | ||
Revision as of 12:38, 20 September 2018
1544: Mathematician and crime-fighter Gerolamo Cardano uses the generating circles of hypocycloids (later named Cardano circles or cardanic circles) to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.
1842: Chemist and physicist James Dewar born. He will invent the vacuum flask, which he will use in conjunction with extensive research into the liquefaction of gases.
1977: A series of celestial events occurs, with sightings reported over a vast territory, from Copenhagen and Helsinki in the west to Vladivostok in the east. It is commonly known as the The Petrozavodsk phenomenon after the city of Petrozavodsk in Russia (then in the Soviet Union), where a glowing object which showered the city with numerous rays was widely reported. The nature of the phenomenon is disputed.
1989: Mathematicians Alice Beta and Paul Erdős co-publish a new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.
1996: Mathematician and academic Paul Erdős dies. He firmly believed mathematics to be a social activity, living an itinerant lifestyle with the sole purpose of writing mathematical papers with other mathematicians.
1997: Signed first edition of Janet Beta at ENIAC sells for five hundred thousand dollars at charity auction to benefit victims of crimes against mathematical constants.
2016: Traveller voted Picture of the Day by the citizens of New Minneapolis, Canada.