Template:Selected anniversaries/January 16: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||27 BC | ||27 BC: Gaius Julius Caesar Octavianus is granted the title Augustus by the Roman Senate, marking the beginning of the Roman Empire. | ||
||378 | ||378: General Siyaj K'ak' conquers Tikal, enlarging the domain of King Spearthrower Owl of Teotihuacán. | ||
||1412 | ||1412: The Medici family is appointed official banker of the Papacy. | ||
File:Johannes Schöner.jpg|link=Johannes Schöner (nonfiction)|1477: [[Johannes Schöner (nonfiction)|Johannes Schöner]] born. He will enjoy a European wide reputation as an innovative and influential globe maker and cosmographer and as one of the continent's leading and most authoritative astrologers. | File:Johannes Schöner.jpg|link=Johannes Schöner (nonfiction)|1477: [[Johannes Schöner (nonfiction)|Johannes Schöner]] born. He will enjoy a European wide reputation as an innovative and influential globe maker and cosmographer and as one of the continent's leading and most authoritative astrologers. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
File:Johannes Schöner.jpg|link=Johannes Schöner (nonfiction)|1547: [[Johannes Schöner (nonfiction)|Johannes Schöner]] dies. He enjoyed a European wide reputation as an innovative and influential globe maker and cosmographer and as one of the continent's leading and most authoritative astrologers. | File:Johannes Schöner.jpg|link=Johannes Schöner (nonfiction)|1547: [[Johannes Schöner (nonfiction)|Johannes Schöner]] dies. He enjoyed a European wide reputation as an innovative and influential globe maker and cosmographer and as one of the continent's leading and most authoritative astrologers. | ||
||1605 | ||1605: The first edition of ''El ingenioso hidalgo Don Quijote de la Mancha'' (Book One of Don Quixote) by Miguel de Cervantes is published in Madrid, Spain. | ||
File:Galileo Galilei, Crime Fighter.jpg|link=Galileo Galilei, Crime Fighter|1622: First known literary reference to the illustration ''[[Galileo Galilei, Crime Fighter]]'' (in an anonymous gloss of Pedro Mexía's ''Silva de varia algoritmo de gnomon''). | File:Galileo Galilei, Crime Fighter.jpg|link=Galileo Galilei, Crime Fighter|1622: First known literary reference to the illustration ''[[Galileo Galilei, Crime Fighter]]'' (in an anonymous gloss of Pedro Mexía's ''Silva de varia algoritmo de gnomon''). | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
||1743: Patrick Wilson (generally known as Peter Wilson) astronomer, type-founder, mathematician and meteorologist born. Pic (engraved miniature). | ||1743: Patrick Wilson (generally known as Peter Wilson) astronomer, type-founder, mathematician and meteorologist born. Pic (engraved miniature). | ||
||Anders Gustaf Ekeberg | ||1767: Anders Gustaf Ekeberg born ... chemist who discovered tantalum in 1802. Pic. | ||
||Johann Christian Wiegleb | ||1800: Johann Christian Wiegleb dies ... druggist and early innovator of chemistry as a science. Pic. | ||
||1834 | ||1834: Jean Nicolas Pierre Hachette dies ... mathematician and academic. Pic. | ||
||1862 | ||1862: Hartley Colliery disaster: Two hundred and four men and boys killed in a mining disaster, prompted a change in UK law which henceforth required all collieries to have at least two independent means of escape. | ||
||Leonor Michaelis | ||1875: Leonor Michaelis born ... biochemist, physical chemist, and physician, known primarily for his work with Maud Menten on enzyme kinetics and Michaelis–Menten kinetics in 1913. Pic. | ||
| | ||1906: Erich Kähler born ... mathematician with wide-ranging interests in geometry and mathematical physics, who laid important mathematical groundwork for algebraic geometry and for string theory. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1919: Jerome Horwitz born ... chemist and academic. No pic. | ||
|| | ||1922: Pierre René Jean Baptiste Henri Brocard dies ... meteorologist and mathematician, in particular a geometer. His best-known achievement is the invention and discovery of the properties of the Brocard points, the Brocard circle, and the Brocard triangle, all bearing his name. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1936: Oskar Barnack dies ... optical engineer, precision mechanic, industrial designer, and the father of 35 mm photography. | ||
|| | ||1938: Frederick Rowbottom born ... logician and mathematician. The large cardinal notion of Rowbottom cardinals is named after him. Pic: https://week42.wordpress.com/2016/09/02/fred-rowbottom/ | ||
|File:Nikolay Basov.jpg|link=Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|1953: Physicist and educator [[Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|Nikolay Basov]] witnesses spontaneous [[cryptographic numen]], develops new theory of quantum electronics. | |File:Nikolay Basov.jpg|link=Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|1953: Physicist and educator [[Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|Nikolay Basov]] witnesses spontaneous [[cryptographic numen]], develops new theory of quantum electronics. | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
File:Robert J. Van de Graaff.jpg|link=Robert J. Van de Graaff (nonfiction)|1967: Physicist [[Robert J. Van de Graaff (nonfiction)|Robert J. Van de Graaff]] dies. He design design and constructed high-voltage Van de Graaff generators. | File:Robert J. Van de Graaff.jpg|link=Robert J. Van de Graaff (nonfiction)|1967: Physicist [[Robert J. Van de Graaff (nonfiction)|Robert J. Van de Graaff]] dies. He design design and constructed high-voltage Van de Graaff generators. | ||
||1969 | ||1969: Soviet spacecraft Soyuz 4 and Soyuz 5 perform the first-ever docking of manned spacecraft in orbit, the first-ever transfer of crew from one space vehicle to another, and the only time such a transfer was accomplished with a space walk. | ||
||1970 | ||1970: Buckminster Fuller receives the Gold Medal award from the American Institute of Architects. | ||
|| | ||1998: Francis Harry Hinsley dies ... historian and cryptanalyst. He worked at Bletchley Park during the Second World War and wrote widely on the history of international relations and British Intelligence during the Second World War. Pic. | ||
||2000 | ||2000: Robert R. Wilson, American physicist and academic (b. 1914). Pic. | ||
||2001: Patent granted for Control circuits for electric coding machines. Was applied for 1944. See https://patents.google.com/patent/US6175625B1/en and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SIGABA | ||2001: Patent granted for Control circuits for electric coding machines. Was applied for 1944. See https://patents.google.com/patent/US6175625B1/en and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SIGABA | ||
||2002 | ||2002: Robert Hanbury Brown dies ... astronomer and physicist. No pic. | ||
||2003 | ||2003: The Space Shuttle Columbia takes off for mission STS-107 which would be its final one. Columbia disintegrated 16 days later on re-entry. | ||
||2013 | ||2013: André Cassagnes dies ... technician and toy maker, created the Etch A Sketch (b. 1926). No portrait, use Etch-a-Sketch. | ||
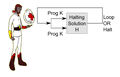
File:Ascleplius Myrmidon Halting Problem.jpg|link=On Halting Problems|2017: Updated edition of ''[[On Halting Problems]]'' published, with new chapter of [[Gnomon algorithm]] techniques for detecting and preventing algorithm hijacking and related [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Ascleplius Myrmidon Halting Problem.jpg|link=On Halting Problems|2017: Updated edition of ''[[On Halting Problems]]'' published, with new chapter of [[Gnomon algorithm]] techniques for detecting and preventing algorithm hijacking and related [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 19:21, 2 September 2018
1477: Johannes Schöner born. He will enjoy a European wide reputation as an innovative and influential globe maker and cosmographer and as one of the continent's leading and most authoritative astrologers.
1541: Writer, humanist, and historian Pedro Mexía publishes Silva de varia algoritmo de gnomon ("A Miscellany of Several Gnomon algorithms"), which quickly raises awareness of crimes against mathematical constants across Europe.
1548: Mathematician Adam Ries publishes textbook of Gnomon algorithm functions, promoting the advantages of Arabic/Indian numerals over Roman numerals in such applications as detecting and preventing crimes against mathematical constants.
1547: Johannes Schöner dies. He enjoyed a European wide reputation as an innovative and influential globe maker and cosmographer and as one of the continent's leading and most authoritative astrologers.
1622: First known literary reference to the illustration Galileo Galilei, Crime Fighter (in an anonymous gloss of Pedro Mexía's Silva de varia algoritmo de gnomon).
1962: Computer scientist and academic John T. Riedl born. He will be a founder of the field of recommender systems, social computing, and interactive intelligent user interface systems.
1966: Reverse engineering of Cryptographic numen unexpectedly reveals new class of Gnomon algorithm functions.
1967: Mathematician, computer scientist, and stand-up comic Tom Kilburn publishes new theory of Cryptographic numina which quickly finds applications in the detection and prevention of crimes against mathematical constants.
1967: Physicist Robert J. Van de Graaff dies. He design design and constructed high-voltage Van de Graaff generators.
2017: Updated edition of On Halting Problems published, with new chapter of Gnomon algorithm techniques for detecting and preventing algorithm hijacking and related crimes against mathematical constants.