Template:Selected anniversaries/August 8: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||1492 | ||1492: Matteo Tafuri born ... alchemist. | ||
||1533 | ||1533: Lucas van Leyden dies ... artist. | ||
File:Oronce Finé.jpg|link=Oronce Finé (nonfiction)|1555: Mathematician and cartographer [[Oronce Finé (nonfiction)|Oronce Finé]] dies. He was imprisoned in 1524, probably for practicing [[Judicial astrology (nonfiction)|judicial astrology]]. | File:Oronce Finé.jpg|link=Oronce Finé (nonfiction)|1555: Mathematician and cartographer [[Oronce Finé (nonfiction)|Oronce Finé]] dies. He was imprisoned in 1524, probably for practicing [[Judicial astrology (nonfiction)|judicial astrology]]. | ||
||1576 | ||1576: The cornerstone for Tycho Brahe's Uraniborg observatory is laid on the island of Hven. | ||
||Joseph Moxon (b. 8 August 1627), hydrographer to Charles II, was an English printer specialising in mathematical books and maps, a maker of globes and mathematical instruments, and mathematical lexicographer. He produced the first English language dictionary devoted to mathematics, and the first detailed instructional manual for printers. In November 1678, he became the first tradesman to be elected as a Fellow of the Royal Society. Pic. | ||Joseph Moxon (b. 8 August 1627), hydrographer to Charles II, was an English printer specialising in mathematical books and maps, a maker of globes and mathematical instruments, and mathematical lexicographer. He produced the first English language dictionary devoted to mathematics, and the first detailed instructional manual for printers. In November 1678, he became the first tradesman to be elected as a Fellow of the Royal Society. Pic. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 27: | ||
File:Edward Frankland.jpg|link=Edward Frankland (nonfiction)|1880: Chemist and crime-fighter [[Edward Frankland (nonfiction)|Edward Frankland]] gives landmark lecture on applications of [[Gnomon algorithm]] theory to the detection and prevention of organometallic [[crimes against chemistry]], introducing the concept of combining power or valence. | File:Edward Frankland.jpg|link=Edward Frankland (nonfiction)|1880: Chemist and crime-fighter [[Edward Frankland (nonfiction)|Edward Frankland]] gives landmark lecture on applications of [[Gnomon algorithm]] theory to the detection and prevention of organometallic [[crimes against chemistry]], introducing the concept of combining power or valence. | ||
||Viktor Meyer | ||1897: Viktor Meyer dies ... chemist and significant contributor to both organic and inorganic chemistry. He is best known for inventing an apparatus for determining vapour densities, the Viktor Meyer apparatus, and for discovering thiophene, a heterocyclic compound. Pic. | ||
File:David Hilbert.jpg|link=David Hilbert (nonfiction)|1900: [[David Hilbert (nonfiction)|David Hilbert]] delivers his famous "Mathematical problems" address: "We hear within us the perpetual call: There is a problem. Seek its solution. You can find it by pure reason, for in mathematics there is no 'ignorabimus'." | File:David Hilbert.jpg|link=David Hilbert (nonfiction)|1900: [[David Hilbert (nonfiction)|David Hilbert]] delivers his famous "Mathematical problems" address: "We hear within us the perpetual call: There is a problem. Seek its solution. You can find it by pure reason, for in mathematics there is no 'ignorabimus'." | ||
||1901 | ||1901: Ernest Lawrence born ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1958). Pic. | ||
||1902 | ||1902: Paul Dirac born ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. | ||
||Edwin Henry Spanier (b. August 8, 1921) was an American mathematician at the University of California at Berkeley, working in algebraic topology. He co-invented Spanier–Whitehead duality and Alexander–Spanier cohomology, and wrote what was for a long time the standard textbook on algebraic topology | ||Edwin Henry Spanier (b. August 8, 1921) was an American mathematician at the University of California at Berkeley, working in algebraic topology. He co-invented Spanier–Whitehead duality and Alexander–Spanier cohomology, and wrote what was for a long time the standard textbook on algebraic topology | ||
Revision as of 09:12, 26 August 2018
1555: Mathematician and cartographer Oronce Finé dies. He was imprisoned in 1524, probably for practicing judicial astrology.
1872: Adventurer and alleged time-travelling "Pirate of the Prairies" Wallace War-Heels defeats Baron Zersetzung in single combat.
1873: Scientist, inventor, and engineer Francis Ronalds dies. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph.
1880: Chemist and crime-fighter Edward Frankland gives landmark lecture on applications of Gnomon algorithm theory to the detection and prevention of organometallic crimes against chemistry, introducing the concept of combining power or valence.
1900: David Hilbert delivers his famous "Mathematical problems" address: "We hear within us the perpetual call: There is a problem. Seek its solution. You can find it by pure reason, for in mathematics there is no 'ignorabimus'."
1957: A day after the Stokes nuclear weapon test, large numbers of carnivorous dirigibles unexpectedly die.
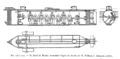
2000: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley is raised to the surface after 136 years on the ocean floor and 30 years after its discovery by undersea explorer E. Lee Spence.
2012: Nuclear physicist Fay Ajzenberg-Selove dies. She did important experimental work in nuclear spectroscopy of light elements, authoring annual reviews of the energy levels of light atomic nuclei.
2017: Signed first edition of Culvert Origenes and The Governess sells for two million dollars in charity benefit auction for victims of crimes against mathematical constants.