Template:Selected anniversaries/March 18: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||1314 | ||1314: Jacques de Molay, the 23rd and final Grand Master of the Knights Templar, is burned at the stake. | ||
File:Robert Fludd.jpg|link=Robert Fludd (nonfiction)|1604: Mathematician [[Robert Fludd (nonfiction)|Robert Fludd]] publishes new work on [[Cellular automaton (nonfiction)|cellular automata theory]] and its application to [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Robert Fludd.jpg|link=Robert Fludd (nonfiction)|1604: Mathematician [[Robert Fludd (nonfiction)|Robert Fludd]] publishes new work on [[Cellular automaton (nonfiction)|cellular automata theory]] and its application to [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
File:Philippe de La Hire.jpg|link=Philippe de La Hire (nonfiction)|1640: Painter, mathematician, astronomer, and architect [[Philippe de La Hire (nonfiction)|Philippe de La Hire]] born. He will be the favorite pupil of Desargues, and develop conic sections and epicycloids based on the teaching of Desargues. | File:Philippe de La Hire.jpg|link=Philippe de La Hire (nonfiction)|1640: Painter, mathematician, astronomer, and architect [[Philippe de La Hire (nonfiction)|Philippe de La Hire]] born. He will be the favorite pupil of Desargues, and develop conic sections and epicycloids based on the teaching of Desargues. | ||
||1690 | ||1690: Christian Goldbach born ... mathematician and academic. | ||
||Ferdinand Berthoud | ||1727: Ferdinand Berthoud born ... scientist and watchmaker. | ||
||1741 | ||1741: New York governor George Clarke's complex at Fort George is burned in an arson attack, starting the New York Conspiracy of 1741. | ||
|| | ||1796: Jakob Steiner born ... mathematician who worked primarily in geometry. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1839: Joseph-Émile Barbier born ... astronomer and mathematician, known for Barbier's theorem on the perimeter of curves of constant width. | ||
|| | ||1858: Rudolf Diesel born ... engineer, invented the Diesel engine. | ||
|| | ||1870: Agnes Sime Baxter born ... mathematician. | ||
|| | ||1871: Augustus De Morgan dies ... mathematician and academic ... formulated De Morgan's laws and introduced the term mathematical induction, making its idea rigorous. | ||
|| | ||1877: Edgar Cayce born ... mystic and psychic. | ||
||Ion Barbu | ||1891: Walter Andrew Shewhart born ... physicist, engineer and statistician, sometimes known as the father of statistical quality control. | ||
||1895: Ion Barbu born ... mathematician and poet. Pic. | |||
File:Curie_and_radium_by_Castaigne.jpg|link=Radium (nonfiction)|1899: Marie and Pierre Curie use [[Radium (nonfiction)|radium compounds]] to detect and counteract [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Curie_and_radium_by_Castaigne.jpg|link=Radium (nonfiction)|1899: Marie and Pierre Curie use [[Radium (nonfiction)|radium compounds]] to detect and counteract [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
||1905 | ||1905: Thomas Townsend Brown born ... physicist and engineer. | ||
||Pierre Eugène Marcellin Berthelot | ||1907: Pierre Eugène Marcellin Berthelot dies ... chemist and politician noted for the Thomsen–Berthelot principle of thermochemistry. He synthesized many organic compounds from inorganic substances, providing a large amount of counterevidence to the theory of Jöns Jakob Berzelius that organic compounds required organisms in their synthesis. Pic. | ||
File:George Plimpton 1993.jpg|link=George Plimpton (nonfiction)|1927: Journalist, writer, literary editor, and actor [[George Plimpton (nonfiction)|George Plimpton]] born. | File:George Plimpton 1993.jpg|link=George Plimpton (nonfiction)|1927: Journalist, writer, literary editor, and actor [[George Plimpton (nonfiction)|George Plimpton]] born. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 38: | ||
File:Lend a Hand.jpg|link=Lend a Hand (nonfiction)|1928: ''[[Lend a Hand (nonfiction)|Lend a Hand]]'' declared Picture of the Day. | File:Lend a Hand.jpg|link=Lend a Hand (nonfiction)|1928: ''[[Lend a Hand (nonfiction)|Lend a Hand]]'' declared Picture of the Day. | ||
||1930 | ||1930: James J. Andrews born ... mathematician and academic. | ||
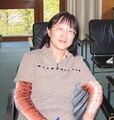
File:Tan Lei.jpg|link=Tan Lei (nonfiction)|1963: Mathematician [[Tan Lei (nonfiction)|Tan Lei]] born. She will specialize in complex dynamics and functions of complex numbers, making contributions to the study of the Mandelbrot set and Julia set. | File:Tan Lei.jpg|link=Tan Lei (nonfiction)|1963: Mathematician [[Tan Lei (nonfiction)|Tan Lei]] born. She will specialize in complex dynamics and functions of complex numbers, making contributions to the study of the Mandelbrot set and Julia set. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 44: | ||
File:Gaston_Julia.jpg|link=Gaston Julia (nonfiction)|1964: Mathematician and crime-fighter [[Gaston Julia (nonfiction)|Gaston Maurice Julia]] publishes new class of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] which anticipate the later work of [[Tan Lei (nonfiction)|Tan Lei]] in using the Julia set to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Gaston_Julia.jpg|link=Gaston Julia (nonfiction)|1964: Mathematician and crime-fighter [[Gaston Julia (nonfiction)|Gaston Maurice Julia]] publishes new class of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] which anticipate the later work of [[Tan Lei (nonfiction)|Tan Lei]] in using the Julia set to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
||1965 | ||1965: Cosmonaut Alexey Leonov, leaving his spacecraft Voskhod 2 for 12 minutes, becomes the first person to walk in space. | ||
||1968 | ||1968: Gold standard: The U.S. Congress repeals the requirement for a gold reserve to back US currency. | ||
||1980 | ||1980: A Vostok-2M rocket at Plesetsk Cosmodrome Site 43 explodes during a fueling operation, killing 48 people. | ||
||Sir Harold Jeffreys | ||1989: Sir Harold Jeffreys dies ... mathematician, statistician, geophysicist, and astronomer. The book that he and Bertha Swirles wrote Theory of Probability, which first appeared in 1939, played an important role in the revival of the Bayesian view of probability. | ||
||1990 | ||1990: In the largest art theft in US history, 12 paintings, collectively worth around $300 million, are stolen from the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum in Boston. | ||
||Dirk Polder | ||2001: Dirk Polder dies ... physicist who, together with Hendrik Casimir, first predicted the existence of what today is known as the Casimir-Polder force, sometimes also referred to as the Casimir effect or Casimir force. | ||
||2003 | ||2003: Adam Osborne dies ... engineer and businessman, founded the Osborne Computer Corporation. | ||
||Mary Ellen Rudin | ||2013: Mary Ellen Rudin dies ... mathematician known for her work in set-theoretic topology. Pic. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 20:04, 25 August 2018
1604: Mathematician Robert Fludd publishes new work on cellular automata theory and its application to crimes against mathematical constants.
1640: Painter, mathematician, astronomer, and architect Philippe de La Hire born. He will be the favorite pupil of Desargues, and develop conic sections and epicycloids based on the teaching of Desargues.
1899: Marie and Pierre Curie use radium compounds to detect and counteract crimes against mathematical constants.
1927: Journalist, writer, literary editor, and actor George Plimpton born.
1928: Lend a Hand declared Picture of the Day.
1963: Mathematician Tan Lei born. She will specialize in complex dynamics and functions of complex numbers, making contributions to the study of the Mandelbrot set and Julia set.
1964: Mathematician and crime-fighter Gaston Maurice Julia publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which anticipate the later work of Tan Lei in using the Julia set to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.