Template:Selected anniversaries/February 16: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||1514 | ||1514: Georg Joachim Rheticus born ... cartographer and instrument maker. No pic. | ||
File:Johannes Stöffler.jpg|link=Johannes Stöffler (nonfiction)|1531: Mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, priest, maker of astronomical instruments, and professor [[Johannes Stöffler (nonfiction)|Johannes Stöffler]] dies. | File:Johannes Stöffler.jpg|link=Johannes Stöffler (nonfiction)|1531: Mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, priest, maker of astronomical instruments, and professor [[Johannes Stöffler (nonfiction)|Johannes Stöffler]] dies. | ||
||Simon Stevin enrolls at Leiden University under the name ''Simon Stevinus Brugensis''. Stevin is listed in the University's registers until 1590; apparently he never graduated; nonetheless, he will make contributions to a great many areas of science and engineering, both theoretical and practical. | ||1583: Simon Stevin enrolls at Leiden University under the name ''Simon Stevinus Brugensis''. Stevin is listed in the University's registers until 1590; apparently he never graduated; nonetheless, he will make contributions to a great many areas of science and engineering, both theoretical and practical. | ||
File:François Ravaillac.jpg|link=François Ravaillac (nonfiction)|1610: Regicide [[François Ravaillac (nonfiction)|François Ravaillac]] drinks [[Extract of Radium]] for the first time. | File:François Ravaillac.jpg|link=François Ravaillac (nonfiction)|1610: Regicide [[François Ravaillac (nonfiction)|François Ravaillac]] drinks [[Extract of Radium]] for the first time. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
File:Pierre Bouguer.jpg|link=Pierre Bouguer (nonfiction)|1698: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer [[Pierre Bouguer (nonfiction)|Pierre Bouguer]] born. He will be known as "the father of naval architecture". | File:Pierre Bouguer.jpg|link=Pierre Bouguer (nonfiction)|1698: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer [[Pierre Bouguer (nonfiction)|Pierre Bouguer]] born. He will be known as "the father of naval architecture". | ||
||1727 | ||1727: Nikolaus Joseph von Jacquin born ... botanist, chemist, and mycologist. | ||
||1740 | ||1740: Giambattista Bodoni born ... publisher and engraver. | ||
||1802 | ||1802: Phineas Quimby born ... mystic and philosopher. | ||
File:Francis Galton 1850s.jpg|link=Francis Galton (nonfiction)|1822: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician [[Francis Galton (nonfiction)|Francis Galton]] born. | File:Francis Galton 1850s.jpg|link=Francis Galton (nonfiction)|1822: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician [[Francis Galton (nonfiction)|Francis Galton]] born. | ||
||Wilhelm Joseph Grailich | ||1829: Wilhelm Joseph Grailich born ... physicist, mineralogist and crystallographer. | ||
||1834 | ||1834: Ernst Haeckel born ... biologist, physician, and philosopher. Pic. | ||
||1874 | ||1874: Silver Dollar becomes legal US tender. | ||
||1878 | ||1878: Pamela Colman Smith born ... occultist and illustrator. | ||
||1878 | ||1878: James Colosimo born ... mob boss. | ||
||1891 | ||1891: Hans F. K. Günther born ... eugenicist and academic. | ||
||Beniamino Segre | ||1903: Beniamino Segre born ... mathematician who is remembered today as a major contributor to algebraic geometry and one of the founders of finite geometry. Pic. | ||
||1906 | ||1906: Vera Menchik born ... chess player. | ||
||File:Chien-Shiung Wu 1958.jpg|link=Chien-Shiung Wu (nonfiction)|1912: Physicist [[Chien-Shiung Wu (nonfiction)|Chien-Shiung Wu]] dies. She conducted the Wu experiment, which contradicted the hypothetical law of conservation of parity. | ||File:Chien-Shiung Wu 1958.jpg|link=Chien-Shiung Wu (nonfiction)|1912: Physicist [[Chien-Shiung Wu (nonfiction)|Chien-Shiung Wu]] dies. She conducted the Wu experiment, which contradicted the hypothetical law of conservation of parity. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
File:Hing Tong.jpg|link=Hing Tong (nonfiction)|1922: Mathematician [[Hing Tong (nonfiction)|Hing Tong]] born. He will provide the original proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem. | File:Hing Tong.jpg|link=Hing Tong (nonfiction)|1922: Mathematician [[Hing Tong (nonfiction)|Hing Tong]] born. He will provide the original proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem. | ||
||Friedrich Hans Beck | ||1927: Friedrich Hans Beck born ... physicist. His research interests were focused on superconductivity, nuclear and elementary particle physics, relativistic quantum field theory, and late in his life, biophysics and theory of consciousness. | ||
||Friedrich Richard Reinitzer | ||1927: Friedrich Richard Reinitzer dies ... botanist and chemist. In late 1880s, experimenting with cholesteryl benzoate, he discovered properties of liquid crystals (named later by Otto Lehmann). Pic. | ||
||Gustave-Auguste Ferrié | ||1932: Gustave-Auguste Ferrié dies ... radio pioneer and army general. Pic. | ||
||1937 | ||1937: Wallace H. Carothers receives a United States patent for nylon. | ||
||1940 | ||1940: World War II: Altmark Incident: The German tanker Altmark is boarded by sailors from the British destroyer HMS Cossack. 299 British prisoners are freed. | ||
||Meghnad Saha | ||1956: Meghnad Saha dies ... astrophysicist best known for his development of the Saha ionization equation, used to describe chemical and physical conditions in stars. | ||
||Charles John Read | ||1958: Charles John Read born ... mathematician known for his work in functional analysis. In operator theory, he is best known for his work in the 1980s on the invariant subspace problem, where he constructed operators with only trivial invariant subspaces on particular Banach spaces Pic. | ||
File:The Eel Fighting Neptune Slaughter.jpg|link=The Eel Fighting Neptune Slaughter|1960: Mathematician and crime-fighter [[The Eel]] (left) stops aquatic cryptid and alleged supervillain [[Neptune Slaughter]] (right) from infiltrating [[Operation Sandblast (nonfiction)|Operation Sandblast]], the U.S. Navy submarine circumnavigation of the globe. | File:The Eel Fighting Neptune Slaughter.jpg|link=The Eel Fighting Neptune Slaughter|1960: Mathematician and crime-fighter [[The Eel]] (left) stops aquatic cryptid and alleged supervillain [[Neptune Slaughter]] (right) from infiltrating [[Operation Sandblast (nonfiction)|Operation Sandblast]], the U.S. Navy submarine circumnavigation of the globe. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
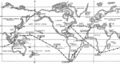
File:Operation Sandblast track.jpg|link=Operation Sandblast (nonfiction)|1960: The U.S. Navy submarine USS Triton begins [[Operation Sandblast (nonfiction)|Operation Sandblast]], setting sail from New London, Connecticut, to begin the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe. | File:Operation Sandblast track.jpg|link=Operation Sandblast (nonfiction)|1960: The U.S. Navy submarine USS Triton begins [[Operation Sandblast (nonfiction)|Operation Sandblast]], setting sail from New London, Connecticut, to begin the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe. | ||
||1961 | ||1961: Explorer program: Explorer 9 (S-56a) is launched. | ||
| | ||1968: In Haleyville, Alabama, the first 9-1-1 emergency telephone system goes into service. | ||
|| | ||1977: Rózsa Péter dies ... mathematician. | ||
|| | ||1978: The first computer bulletin board system is created (CBBS in Chicago). | ||
|| | File:Nicolaas de Bruijn.jpg|link=Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn (nonfiction)|1979: Mathematician and crime-fighter [[Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn (nonfiction)|Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn]] publishes new class of [[Gnomon algorithm functions]] which use combinatorial number logic to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
||1980: Erich Hückel dies ... physicist and chemist. | |||
||1980 | ||1980: Allen Goodrich Shenstone dies ...physicist. He earned bachelor's, master's, and Ph.D. degrees from Princeton University, as well as a Bachelor of Arts from the University of Cambridge. After a brief stint as a junior faculty member at the University of Toronto, he returned to Princeton, where he was a professor in the Department of Physics 1925–62. He chaired the department 1949–60. He worked primarily in the field of atomic spectroscopy. | ||
|| | ||1980: Edward Copson dies ... mathematician known for his studies in classical analysis, differential and integral equations, and their use in mathematical physics. After graduating from Oxford University with a B.A. degree in 1922, he moved to Scotland where he spent the nearly all of his career. His first book, The Theory of Functions of a Complex Variable (1935) was immediately successful. He was a co-author for his next book, The Mathematical Theory of Huygens' Principle (1939). By 1975, he had published four more books, on asymptotic expansions, metric spaces and partial differential equations. Many of the papers he wrote bridged mathematics and physics, of which his last showed his interest in astrophysics, Electrostatics in a Gravitational Field (1978) which was relevant to Black Holes. Pic: https://ro.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edward_Thomas_Copson | ||
||1991 | ||1991: Nicaraguan Contra leader Enrique Bermúdez is assassinated in Managua. | ||
||1997 | ||1997: Chien-Shiung Wu born ... physicist and academic. | ||
||Herbert (Bert) Sydney Green | ||1999: Herbert (Bert) Sydney Green dies ... physicist. Green was a doctoral student of the Nobel Laureate Max Born at Edinburgh, with whom he was involved in the development of the modern kinetic theory. Green is the letter "G" in the BBGKY hierarchy. Pic. | ||
||Martin Kneser | ||1995: Martin Kneser dies ... mathematician. His name has been given to Kneser graphs, which he studied in 1955. | ||
||Konrad Dannenberg | ||2009: Konrad Dannenberg dies ... rocket pioneer and member of the German rocket team brought to the United States after World War II. Pic. | ||
||William Edwin Gordon | ||2010: William Edwin Gordon dies ... physicist and astronomer. He is referred to as the "father of the Arecibo Observatory". Pic. | ||
||Neal R. Amundson | ||2011: Neal R. Amundson dies ... chemical engineer and mathematician. Amundson was considered one of the most prominent chemical engineering educators and researchers in the United States. Pic. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 06:11, 16 August 2018
1531: Mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, priest, maker of astronomical instruments, and professor Johannes Stöffler dies.
1610: Regicide François Ravaillac drinks Extract of Radium for the first time.
1698: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer Pierre Bouguer born. He will be known as "the father of naval architecture".
1822: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician Francis Galton born.
1922: Mathematician Hing Tong born. He will provide the original proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem.
1960: Mathematician and crime-fighter The Eel (left) stops aquatic cryptid and alleged supervillain Neptune Slaughter (right) from infiltrating Operation Sandblast, the U.S. Navy submarine circumnavigation of the globe.
1960: The U.S. Navy submarine USS Triton begins Operation Sandblast, setting sail from New London, Connecticut, to begin the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe.
1979: Mathematician and crime-fighter Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which use combinatorial number logic to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.