Template:Selected anniversaries/February 16: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
||Martin Kneser (d. 16 February 2004) was a German mathematician. His name has been given to Kneser graphs, which he studied in 1955. | ||Martin Kneser (d. 16 February 2004) was a German mathematician. His name has been given to Kneser graphs, which he studied in 1955. | ||
||Konrad Dannenberg (d. February 16, 2009) was a German-American rocket pioneer and member of the German rocket team brought to the United States after World War II. Pic. | |||
||William Edwin Gordon (d. February 16, 2010) was a physicist and astronomer. He is referred to as the "father of the Arecibo Observatory". Pic. | ||William Edwin Gordon (d. February 16, 2010) was a physicist and astronomer. He is referred to as the "father of the Arecibo Observatory". Pic. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 11:41, 31 March 2018
1531: Mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, priest, maker of astronomical instruments, and professor Johannes Stöffler dies.
1610: Regicide François Ravaillac drinks Extract of Radium for the first time.
1698: Mathematician, geophysicist, and astronomer Pierre Bouguer born. He will be known as "the father of naval architecture".
1822: Statistician, progressive, polymath, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, and psychometrician Francis Galton born.
1922: Mathematician Hing Tong born. He will provide the original proof of the Katetov–Tong insertion theorem.
1960: Mathematician and crime-fighter (left) stops aquatic cryptid and alleged supervillain Neptune Slaughter (right) from infiltrating Operation Sandblast, the U.S. Navy submarine circumnavigation of the globe.
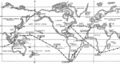
1960: The U.S. Navy submarine USS Triton begins Operation Sandblast, setting sail from New London, Connecticut, to begin the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe.
1979: Mathematician and crime-fighter Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn publishes new class of Gnomon algorithm functions which use combinatorial number logic to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.